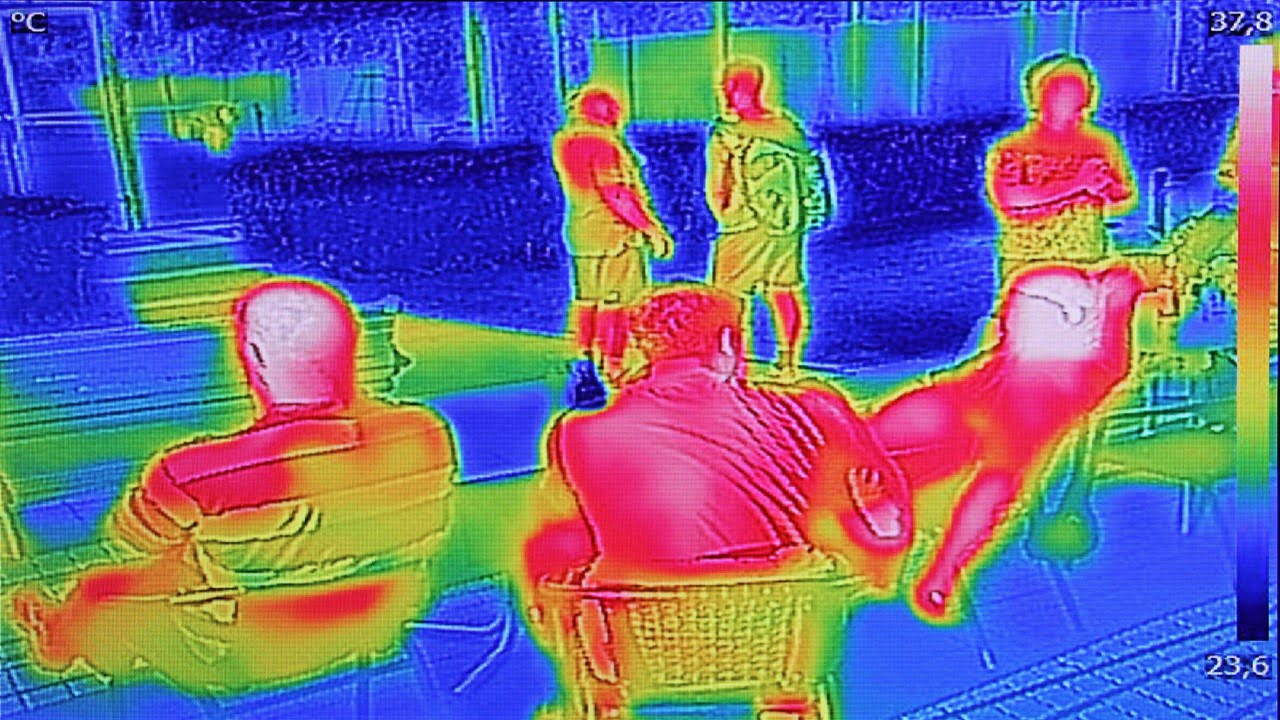

The terminal scanner installed at Marshall Hall, the headquarters of the United States Army Reserve Command, and the headquarters of the United States Forces Command scans soldiers’ and civilians’ wrist temperatures. It also takes pictures of their faces as they enter Marshall Hall. One significant advantage of this terminal scanner is that it does not [..]
Read More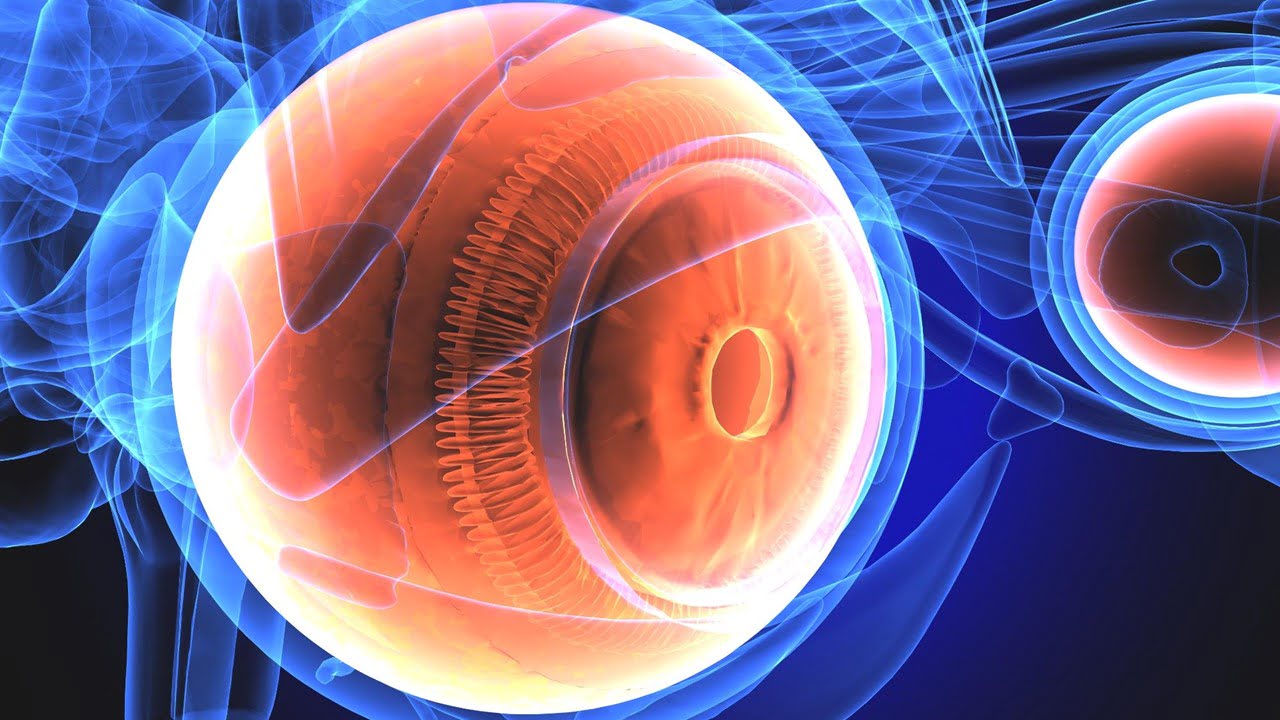
A first for imaging science, Rochester researchers show how to track the interactions of microscopic immune cells in a living eye without using dyes or causing damage. The new technique, which combines infrared videography and artificial intelligence, could be a “game changer” for some clinical diagnoses and fields such as pharmaceuticals. They developed a new [..]
Read More
The temporomandibular joint (TMJ), which forms the back portion of the lower jaw and connects your jaw to your skull, is an anatomically complex and highly loaded structure consisting of cartilage and bone. About 10 million people in the United States suffer from TMJ dysfunction due to congenital disabilities, trauma, or disease. A team of [..]
Read More
Because of its simplicity and flexibility, Computer Generated Hologram (CGH)-based holographic display technology has gained widespread attention, and applications based on CGHs, such as projection systems, encryption systems, and near-eye display systems, have made significant progress. However, a large amount of calculation is a significant challenge for CGH generation. The high-speed calculation for CGH generation [..]
Read More
An optical device resembling a miniature lighthouse lens can make peering into Petri dishes and observing molecular-level details of biological processes, such as cancer cell growth, easier. The new microscope lens is also very affordable. Many bioimaging techniques necessitate the addition of fluorescent dyes to specific cell targets. However, a recently developed Stimulated Raman Scattering [..]
Read More
Researchers have improved a method for probing semiconducting crystals with light to detect defects and impurities. The omnidirectional photoluminescence spectroscopy setup could improve materials fabrication for electric cars and solar cells. The technique can test materials at very low temperatures and find even small amounts of defects and impurities. The researchers demonstrated their approach using [..]
Read More
Scientists have developed a method to create colloidal crystals that crystallize into the diamond lattice. This photonic technique could lead to cheap, reliable, and scalable fabrication of 3D photonic crystals for optical circuits and light filters. Colloidal crystals, made up of spheres hundreds of times smaller than the diameter of a human hair, can be [..]
Read More
A laser-based system that allows optical simulation of individual nerve fibers in living mice has been developed by researchers. They have demonstrated that the nervous system directly influences the immune system through this process. A new method has shed more light on the brain in the last ten years: optogenetics allows scientists to stimulate genetically-modified [..]
Read More
Researchers recently examined how cells in the brains of people at risk for developing Alzheimer’s disease make and use energy. Relationships between the brain’s energy metabolism and the risk of Alzheimer’s disease have been reported previously. But this is the first study to clearly distinguish different energy molecules in the brain using high-powered imaging called [..]
Read More
The U.S. Naval Surface Warfare Center’s Crane, Indiana division has developed a temperature scanning sensor system and software to help contain the coronavirus. To use the software, any laptop with USB capability, capture card, most commercial infrared sensors, and a calibrated black body are necessary. The black body is a scientific tool used as a [..]
Read More
Researchers have shown that it is possible to study the magnetic properties of ultrathin materials directly, via a new nano microscope that opens the door to the discovery of more two-dimensional (2D) magnetic materials, with all sorts of potential applications. The findings are significant because current techniques used to characterize normal (three-dimensional) magnets don’t work [..]
Read More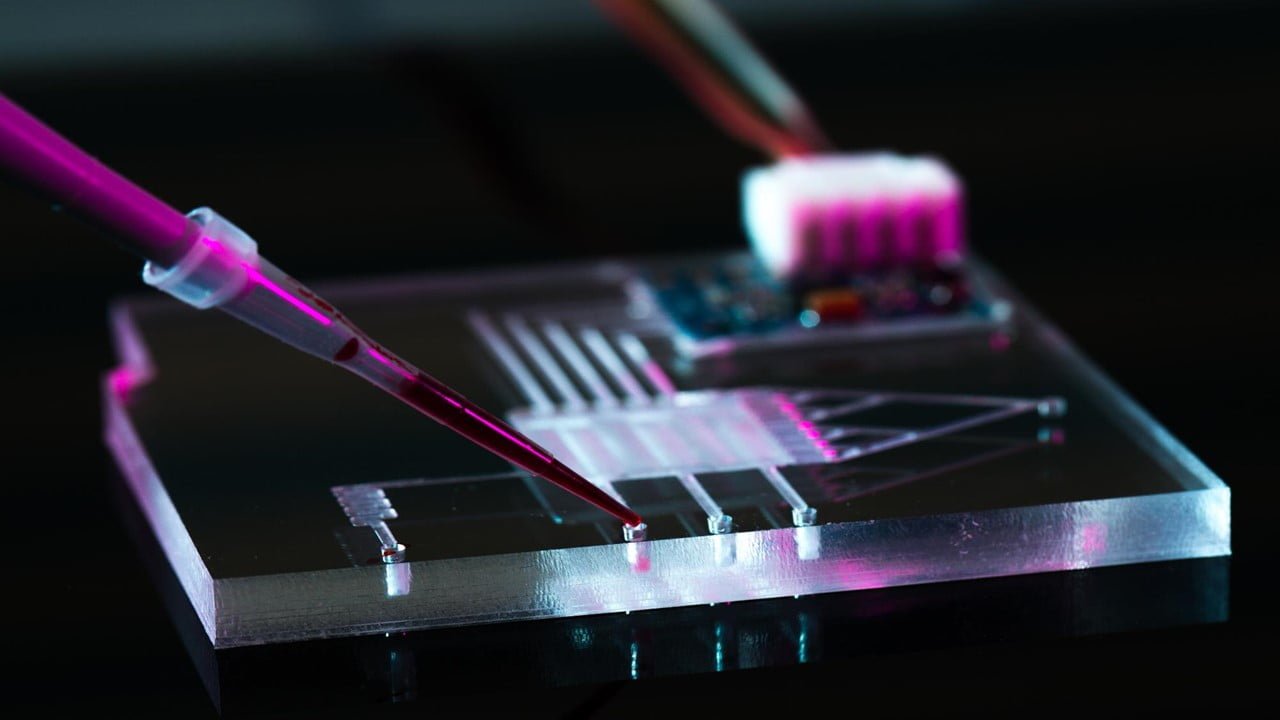
Manipulating buffers and organic solvents on surfaces is fundamental for many biological and/or chemical operations and thus critical in various thermal, optical, and medical applications. For any of these, it is necessary to design a platform that enables locally addressable fluids to be navigated with a low loss rate and partitioned and merged in a [..]
Read More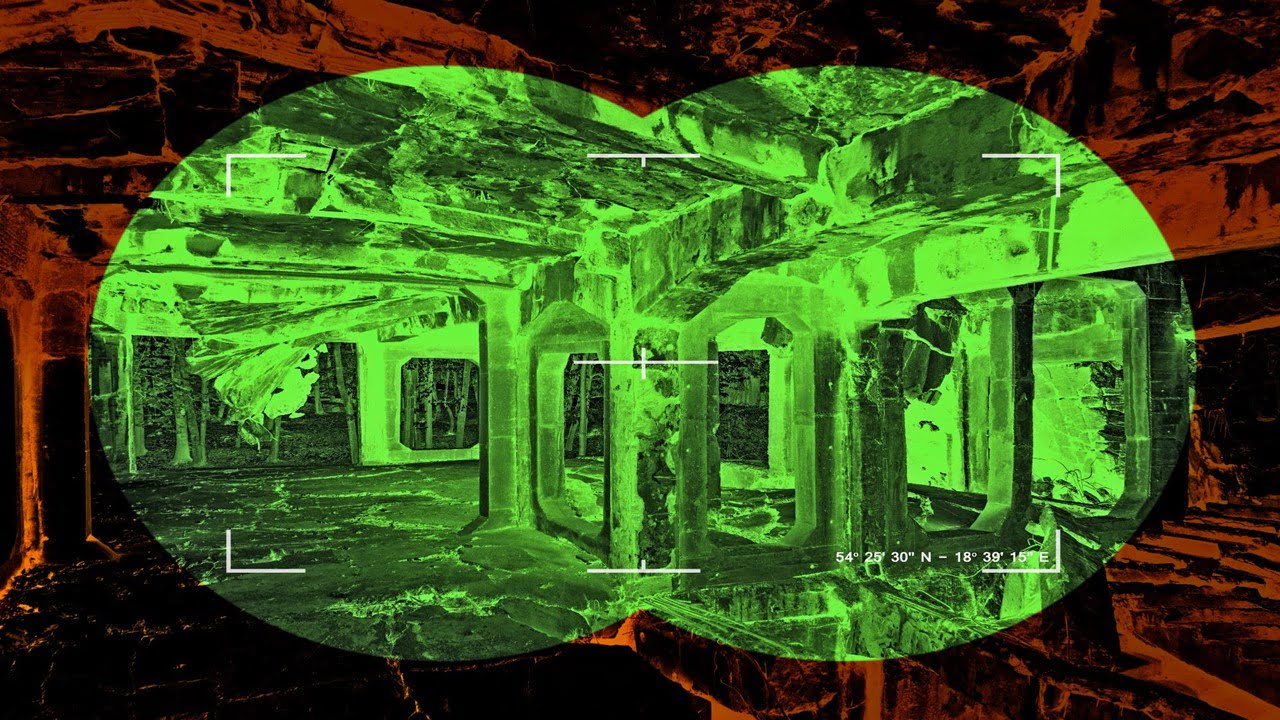
What causes vanadium dioxide films to conduct electricity has been discovered by researchers (insulator-metal transition). Their discoveries will enable thermal imaging devices with higher sensitivity and reaction rates than currently available analogs. While 100-nanometer thin vanadium dioxide (VO2) films do not normally conduct electricity, their resistance drops to 100,000 times when slightly heated. It could [..]
Read More
Conducting or semiconducting materials embedded in insulating polymeric substrates can be useful in bioelectronics applications; however, attainment of this composite configuration by direct chemical processes is challenging. Laser-assisted synthesis has evolved as a fast and inexpensive technique to prepare various materials, but its utility in the construction of biophysical tools or biomedical devices is less [..]
Read More
Researchers attempt to use a deep learning framework to understand better how mental illness and other disorders affect the brain. The team is combining various types of brain imaging data to identify patterns indicative of brain disorders. The National Institute of Biomedical Imaging and Bioengineering funds their research with a $2.4 million, four-year grant. Due [..]
Read MoreScientists have demonstrated tunable red, green, and blue single-mode microlasers in optimized heterogeneously coupled cavities constructed with three spherical microcavities incorporated with different gain media. The microcavities with perfect circle boundaries and smooth surfaces were applied as high-quality WGM resonators. Benefiting from the outstanding flexibilities, RGB lasing was obtained by doping the corresponding dyes into [..]
Read More
Tuberculosis (TB) disease affects 10 million people worldwide every year and is the leading cause of death from an infectious disease. New TB biomarkers are required for a variety of applications, including detection of sub-clinical disease for early intervention to prevent disease progression; detection of new active TB cases; and for monitoring of treatment response [..]
Read More
Artificial light is essential in information technologies such as optical telecommunications, data storage, security features, and information display. In this paper, researchers present a chiral lanthanide lumino-glass with extra-large circularly polarized light (luminescence) (CPL) for advanced photonic security device applications. A europium complex with the chiral (+)-3-(trifluoroacetyl) camphor ligand and the achiral glass promoter tris [..]
Read More
For some applications, such as microprojection and augmented and virtual reality (AR/VR), researchers continue to chase ever-smaller pixel sizes (nanopixels) and higher pixel densities. And these efforts eventually run up against some practical limitations, particularly on pixel brightness, imposed by the 2D-patterning approaches commonly used to create display pixels. Now, researchers have proposed a novel [..]
Read More
A new project pushes system-in-package designs past the terabit-per-second threshold through extremely sophisticated electronics, CMOS, and optical physics management. The three main system blocks—processor, memory, and interconnects (I/O)—are constantly being reevaluated and are currently the “choke point” in enhancing overall efficiency. Each component strives to improve so as not to receive unfair criticism. Interconnects must [..]
Read More