
Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) is a powerful tool for imaging biological samples at high resolution. However, using the right fixation methods is important to preserve the sample’s structure and prevent artifacts. Researchers discuss a new method for fixing blood samples for SEM analysis using the May-Grünwald solution. This method is less toxic than traditional methods [..]
Read More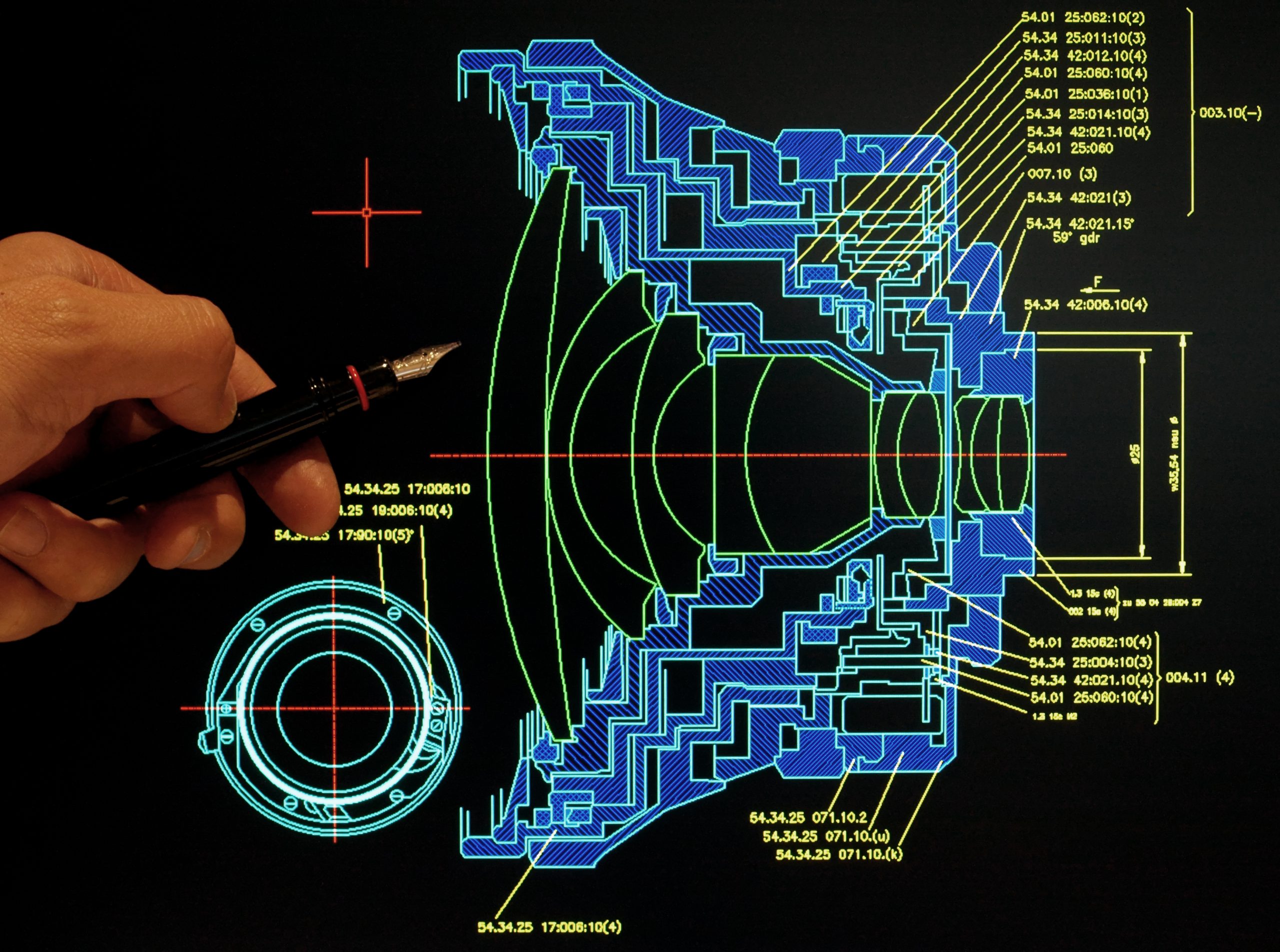
Fascinating new development in room-temperature quantum optomechanics! A recent study has achieved quantum control of solid-state mechanical oscillators at room temperature. This is a significant breakthrough as it paves the way for miniaturized and integrated quantum devices. Traditionally, controlling the quantum state of mechanical oscillators has been limited to cryogenic temperatures due to the thermal [..]
Read More
A new method for optical secret-sharing has been proposed that uses cascaded liquid crystal holograms to encrypt information. The information is hidden in different shares, and it can only be decrypted by combining the shares. This makes the information more secure than traditional methods. The framework also uses multiplexing to increase the amount of information [..]
Read More
A groundbreaking microscopy technique called single-shot quantitative phase-fluorescence imaging (SQPFI) is poised to revolutionize how we study cells and biological samples. This innovative approach simultaneously captures the structural details and the distribution of fluorescently labeled molecules within a sample – all in a single snapshot. SQPFI leverages a unique grating and a color camera to [..]
Read More
New research discusses the design of photonic crystal sensors using micro-ring resonators. The researchers propose a new algorithm to optimize the design of these sensors and find that it has a higher quality factor and sensitivity. This means that the sensor can detect smaller changes in the refractive index of the material it is measuring. [..]
Read MoreIn the realm of space exploration, pinpointing faint and minuscule objects amidst the vast darkness poses a significant challenge for optoelectronic systems. A recent study details a novel approach called space-based target detection that enhances target detection efficacy for space-based systems. The proposed method hinges on two key components: star atlas preprocessing and space-based target [..]
Read More
Traditionally, infrared (IR) spectroscopy has been a powerful tool for studying proteins. However, its application to single proteins has been limited due to the diffraction limit, which restricts the spatial resolution to hundreds of nanometers. This is far larger than the size of a typical protein, making it difficult to isolate and analyze individual molecules. [..]
Read More
Artificial intelligence (AI) is transforming microscopy by enhancing image efficiency and data analysis. A prominent example is the smartLLSM microscope, which uses AI-based instrument control to switch between imaging modes and take high-resolution images of biological specimens. It enables the capture of uncommon or ephemeral biological phenomena at a rate that exceeds human capabilities. Cell [..]
Read More
Multi-probe imaging has been shown to accurately image small animal tissue up to several hundred micrometers in size, a technique that could be useful in medical research by allowing researchers to observe tissue microstructure and understand the localization and interaction of multiple molecules, such as cancer cell metastatic lesions. Researchers used a SPECT system with [..]
Read More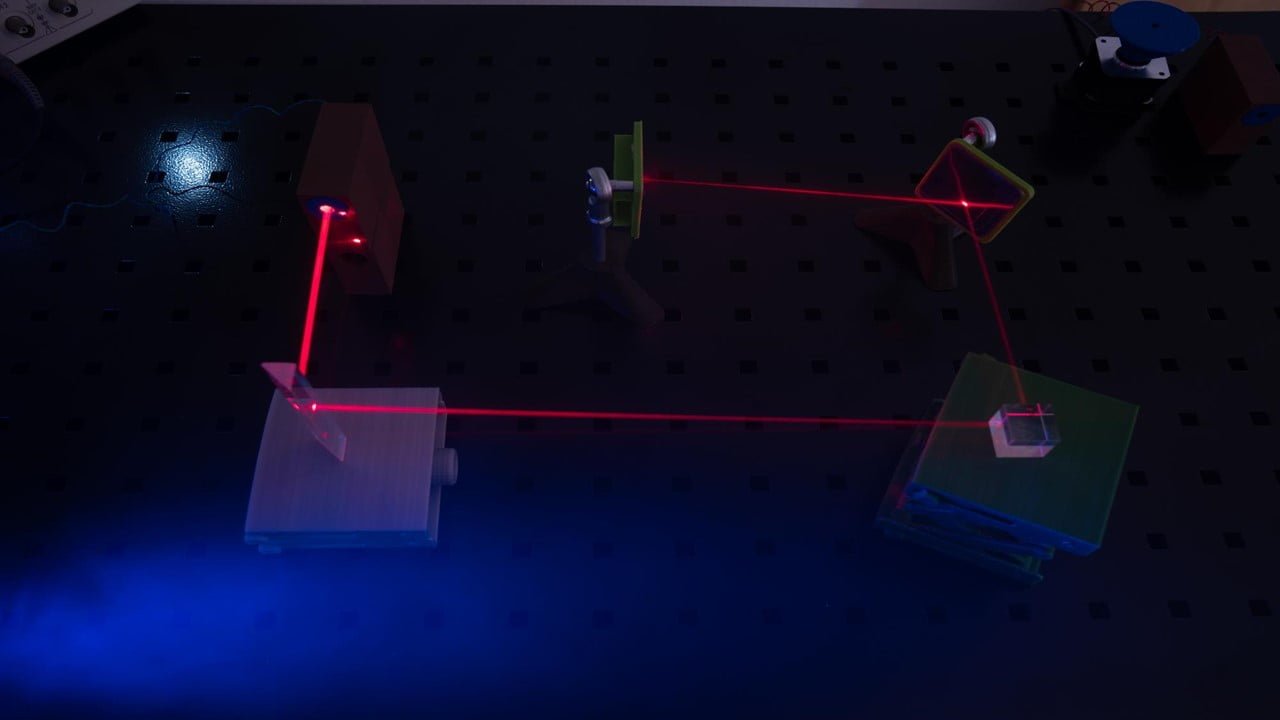
Researchers have developed a tiny mode-locked laser integrated into a nanophotonic platform capable of producing high-power, ultrafast light pulses. This accomplishment in miniaturizing MLL technology has the potential to increase photonics applications dramatically. Researchers set out to improve a technology that generally requires cumbersome bench-top equipment by shrinking a mode-locked laser (MLL) to the size [..]
Read More
Scientists have created a novel method for producing gold nanoparticles (NPs) in tellurite glasses, a type of glass with special qualities utilized in art and adornment for centuries. Gold NPs’ unusual light modulation characteristics have led to applications in various sectors, including colored glass and specific optical components. Tellurite glass is particularly significant for optical, [..]
Read More
Computer-generated holography (CGH) is a technology that uses computer algorithms to dynamically reconstruct virtual objects, with applications in various fields such as three-dimensional display, optical information storage and processing, entertainment, and encryption. However, current techniques often rely on projection devices like spatial light modulators (SLMs) and digital micromirror devices (DMDs), which have limited display capabilities. [..]
Read More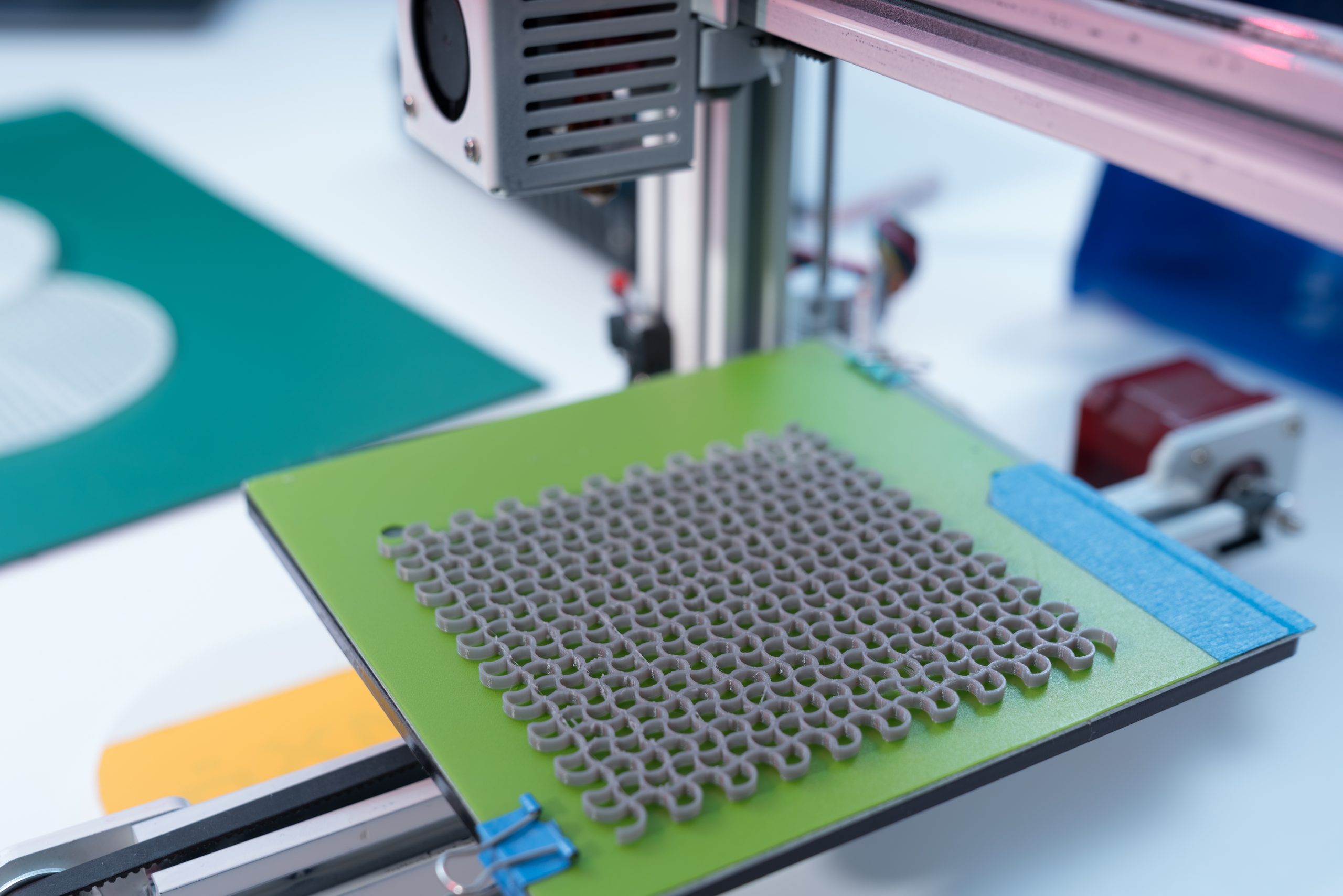
A research team made an unparalleled advancement in antenna technology by allowing software control of all five fundamental properties of electromagnetic waves. In a world first, the researchers created a universal metasurface antenna that allows for independent and simultaneous modulation of electromagnetic radiation’s amplitude, phase, frequency, polarization, and direction. As research on 6G wireless communication [..]
Read More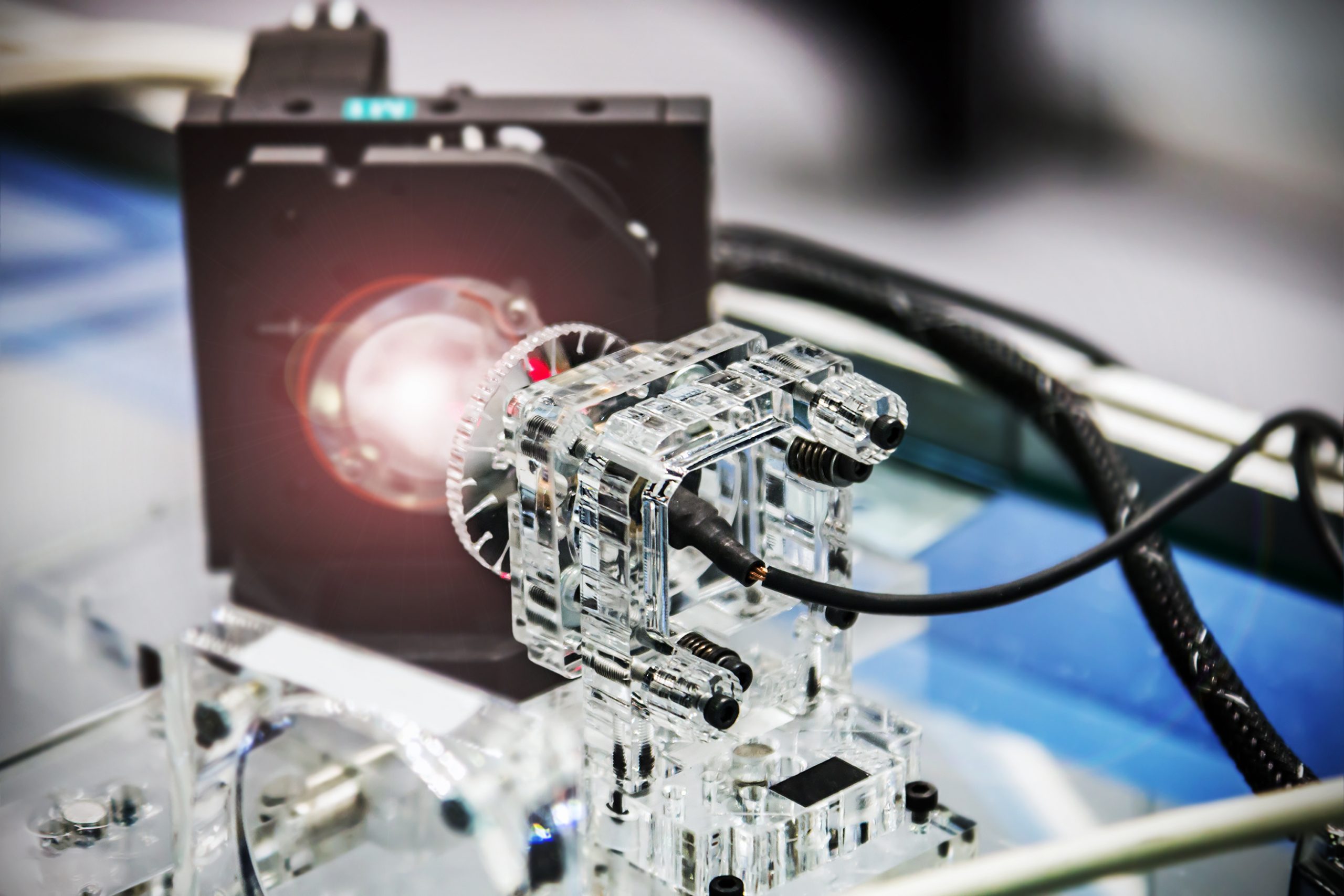
Researchers have created a novel way for capturing detailed images of things too small to observe with regular microscopes by employing donut laser, i.e., doughnut-shaped light beams. It could aid scientists in better understanding the inner workings of nanoelectronics, such as small semiconductors in computer chips. The study is the most recent advancement in ptychography, [..]
Read More
CoreDetector is a new software tool developed by researchers that improves genome-sequencing capabilities, allowing researchers to improve plants through breeding. CoreDetector is built to tackle computationally demanding tasks like matching big and evolutionary varied plant genomes. It uses computer parallelization to perform pairwise sequence alignment between the genomes of population members. The program supports diploid [..]
Read More
Subvisible particles (SVPs) are a significant quality attribute of injectable therapeutic proteins (TPs) that must be regulated due to potential medication product quality hazards. The existing compendial methods for analyzing SVPs for lot release give particle size and count information. On the other hand, chemical identification of specific particles is necessary for root-cause analysis. Researchers [..]
Read More
Imaging techniques like computed tomography (CT) and positron emission tomography (PET) are now required for identifying and localizing many disorders. According to a newly developed method, PET can now be utilized particularly based on alterations in the human genome. The new genome-based imaging technology, The Imageable Genome, has the potential to aid in the earlier [..]
Read More
Metamaterials are artificial nanostructures that affect light and are expensive and difficult to fabricate. A research team created a solution-based 3D-printing method that allows for the low-cost manufacture of metamaterials in desired shapes. By coupling evaporative co-assembly of silica and gold nanoparticles with 3D nanoprinting, the researchers created freeform, freestanding raspberry-like metamolecule (RMM) fibers in [..]
Read More
Researchers have revealed groundbreaking research that can potentially alter the field of two-dimensional optoelectronics. Researchers have successfully demonstrated in a groundbreaking study that chicken egg white, i.e., biodegradable albumen, can be a very effective dielectric gate for two-dimensional materials. This breakthrough opens new avenues for sustainable and biodegradable technology in optoelectronic devices. This novel technique [..]
Read More
Researchers are enhancing lidar tech for increased versatility, which benefits scientists and explorers in remote sensing, surveying, mapping, 3D-image scanning, hazard detection, and navigation. Lidar, a remote sensing device, employs light pulses to detect distances and object attributes precisely. With continuous investigations, its precision and versatility make it critical for communication, navigation, planetary exploration, and [..]
Read More