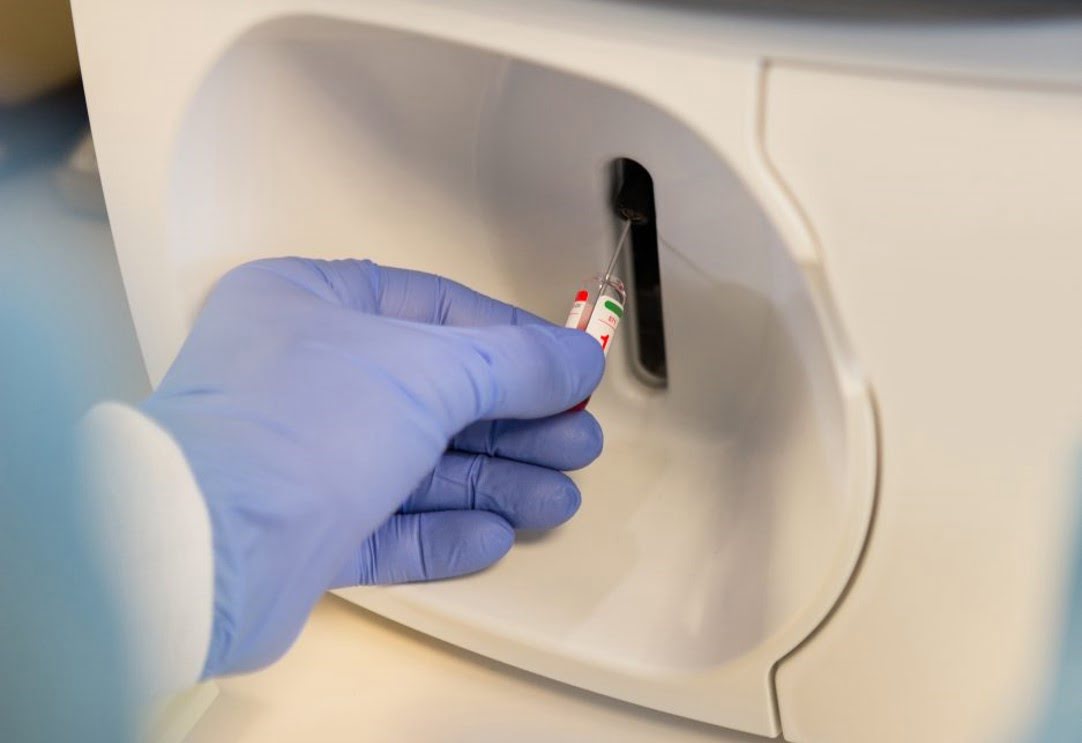
By examining exhaled air, researchers have created a non-invasive breath analyzer method to monitor the development of tiny blood clots called immunothrombosis. Due to inflammation, immunothrombosis can lead to serious consequences in individuals with severe COVID-19 and exacerbate sepsis, heart disease, diabetes, and other illnesses. The researchers created a non-invasive breath analyzer method that uses [..]
Read More
Although chemotherapy is a highly effective cancer treatment, some cancer cells become resistant to it through a dormant phase known as senescence. These therapy-induced senescent (TIS) cells can develop resistance to treatment, even become aggressive, and spread. Early TIS cell detection may be essential to stopping their spread; however, the screening techniques must be more [..]
Read More
When added to silicate glass, niobium oxide (Nb2O5) causes silica network polymerization, raising bond density and connectivity and improving specialty glass’s mechanical and thermal durability. It is the first study to demonstrate this effect. The work integrated computational modeling with actual Raman and nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy findings. In addition to the previously reported findings, [..]
Read More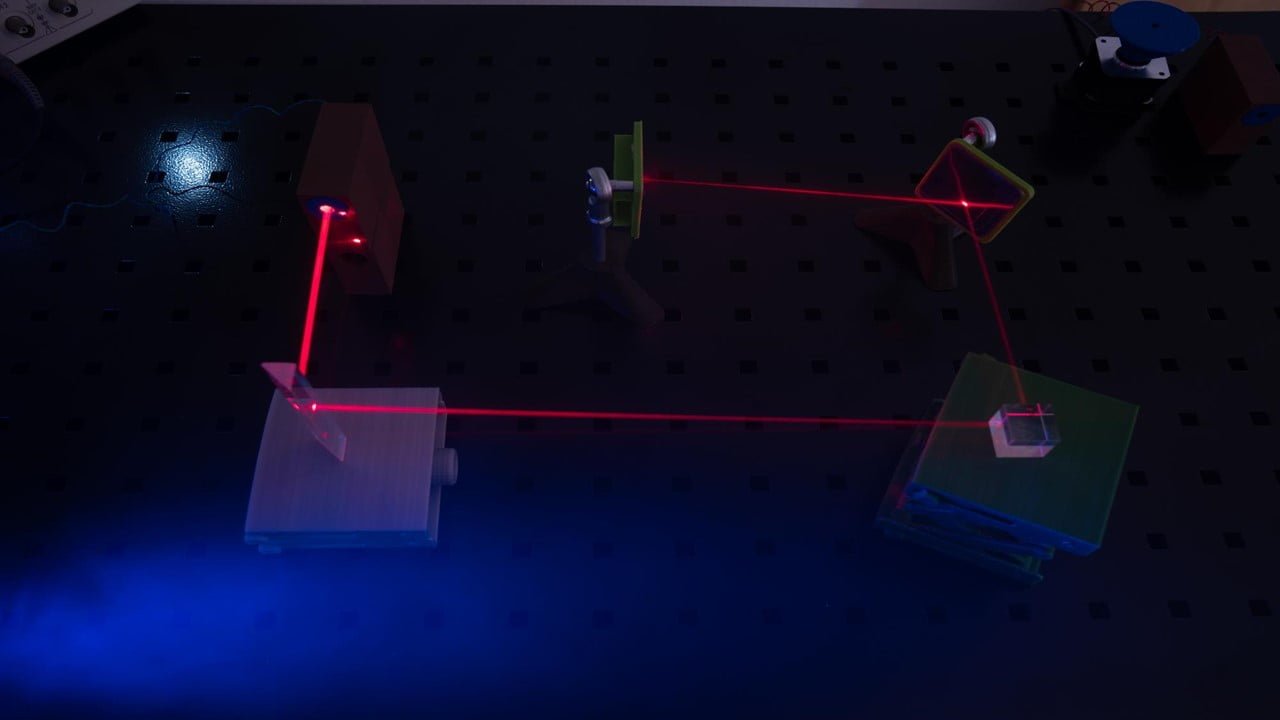
When it comes to high-capacity screening tests, or assays, for detecting and targeting certain cells or analytes (substances whose chemical makeup is the goal of identification), the static droplet array (SDA) is an essential and fundamental instrument. One significant technological barrier that prevents the SDA’s wider use is the extraction and collection of target droplets [..]
Read More
Virtually applying makeup before completing a purchase or having pterodactyls swoop above in a game are just two examples of how augmented reality and other immersive technologies are changing how we play, watch, and learn. Immersion displays would realize their full potential using low-cost, ultra-small light-emitting diodes (LEDs) or micro-LEDs. However, these LEDs still need [..]
Read More
The rapid expansion of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) applications requires effective connectivity between processing units and high-speed transmission. It has increased interest in optical interconnects, especially for short-range connections between XPUs (CPUs, GPUs, and memory). When compared to conventional methods, silicon photonics is showing promise as a technology for enhanced performance, cost-effectiveness, and [..]
Read More
Transmission electron microscopes use inline holography to measure and rectify images in real space and to measure magnetic and electric fields. On the other hand, it needs help with incoherent dispersion and low-spatial-frequency information transmission. This work optimizes reconstruction parameters and compares the outcomes using gradient flipping, phase prediction, and incoherent background removal. Transmission electron [..]
Read More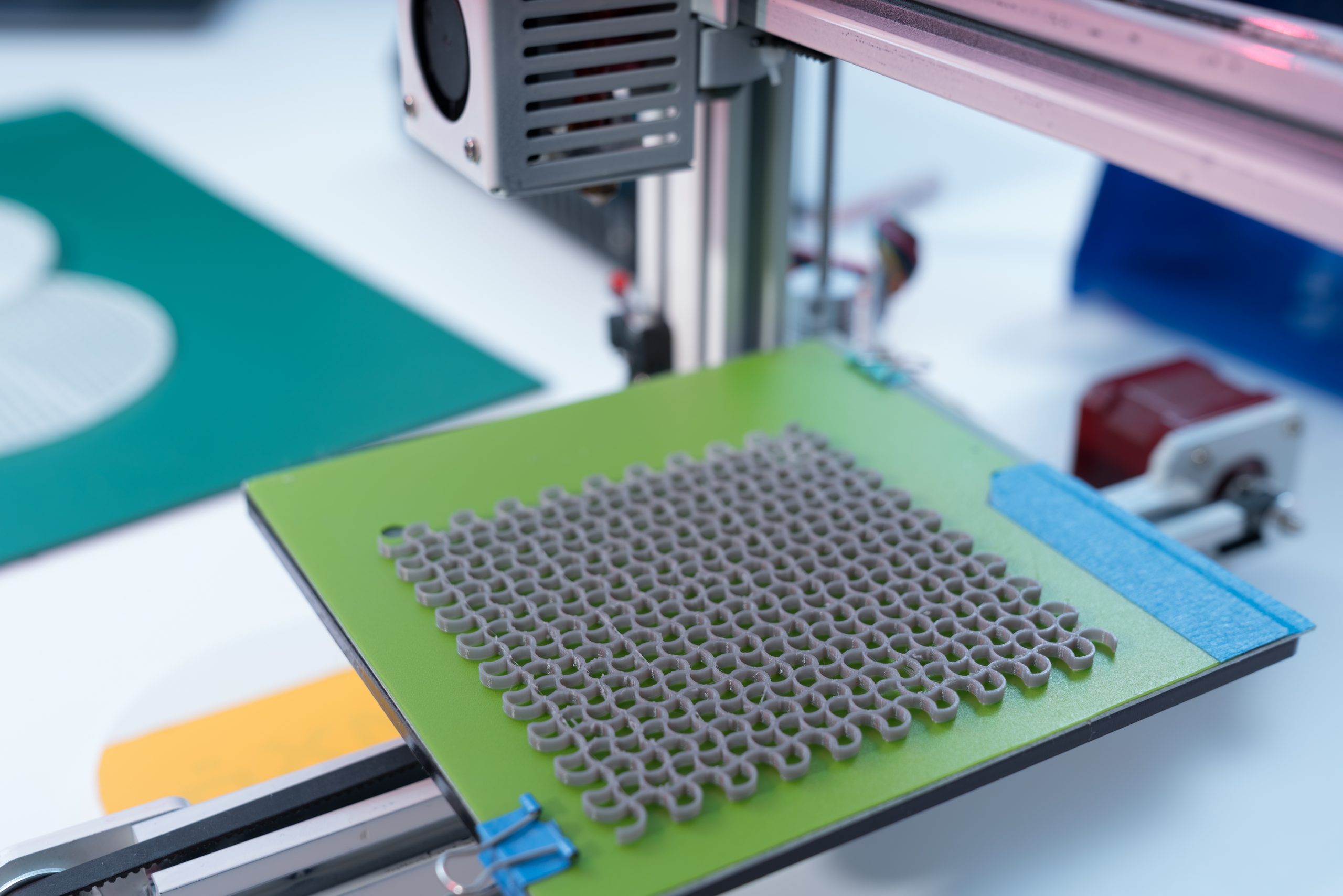
Artificial materials that are skilled at influencing perception are called metasurfaces. Metasurfaces are attracting much interest as optical components that enable the miniaturization of optical systems for the next generation of virtual and augmented reality and LiDAR. They enable lenses to be shrunk to one 10,000th the size of normal lenses. Countries may gain a considerable [..]
Read More
Researchers have demonstrated that chip-based optical frequency combs with sufficient output power for optical atomic clocks and other practical applications may be made using dissipative Kerr solitons (DKSs). The development could result in equipment built on chips that can do precise tests previously only achievable in a few specialist labs. In metrology, frequency combs are [..]
Read More
According to a new study, artificial intelligence can forecast the on- and off-target behavior of CRISPR tools that target RNA rather than DNA. To manage the expression of human genes in various ways, the study combines a deep learning model with CRISPR screens—for example, by flipping a switch to fully turn them off or turning [..]
Read More
A high-resolution inelastic neutron scattering technique for examining nanosecond dynamics is neutron spin echo spectroscopy. It advances knowledge of viscoelasticity and is particularly suited to studying atomistic motion in polymer systems. Doppler scattering must be taken into account, nevertheless, for samples that are moving or that are being subjected to shear. Researchers discover remarkable agreement [..]
Read More
For medical practitioners, medical imaging, such as X-rays, CT scans, MRIs, and ultrasounds, gives distinctive viewpoints. By locating biomolecules inside specimens, spectroscopy gives more information. The goal of the research is to enhance diagnostic imaging. The researchers are creating imaging devices that use terahertz radiation after realizing the advantages of imaging and spectroscopy. Terahertz radiation [..]
Read More
Creating a spin-optical laser using monolayer-integrated spin-valley microcavities without needing magnetic fields or cryogenic temperatures is a breakthrough in atomic-scale spin-optics. Scientists have created a coherent and controlled spin-optical laser based on a single atomic layer. Coherent spin-dependent interactions between a single atomic layer and a laterally constrained photonic spin-lattice, the latter of which allows [..]
Read More
Researchers can “evolve” optical devices and print them out using 3D printing technology. These devices enable cameras and sensors to detect and control light qualities in previously impractical ways at tiny sizes. They are composed of so-called optical metamaterials, which derive their capabilities from structures with dimensions measured in nanometers. The team has developed small [..]
Read More
Due to their exceptional optoelectronic characteristics, metal halide perovskites have attracted much attention as potential materials for next-generation optoelectronic devices. Researchers have achieved significant progress in device performance by developing a comprehensive grasp of perovskite composition, crystal formation, and defect engineering. However, Effective optical control is becoming increasingly important as device performance approaches theoretical limitations [..]
Read More
A key technology for robotic mobility and autonomous driving is pulsed laser scanning lidar. It computes depth and performs three-dimensional imaging using pulses of directed light. However, innovations are required to improve FoV, imaging frame rate, ambiguity range, and lower manufacturing costs. A research team suggests a creative alternative to satisfy the demands of automotive [..]
Read More
Numerous researchers, including astronauts, are examining Mars, notably its atmosphere and soil composition. In a recent study, scientists properly identified nitrogen in simulated Martian soil using laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy (LIBS) technology. The importance of this study lies in the fact that identifying nitrogen on Mars is essential to identifying indications that life is possible there. [..]
Read More
Today’s computers’ exact 0s and 1s can obstruct the correct solutions to complex real-world issues in a noisy and uncertain environment. It is the claim made by a young, pioneering branch of study in probabilistic computing. Researchers have recently developed a brand-new technique for producing probabilistic bits (p-bits) at significantly greater rates by employing photonics [..]
Read More
It is difficult to diagnose neurodegenerative diseases (NDDs), such as Parkinson’s disease and Alzheimer’s disease, because no methods are available to identify preclinical biomarkers. The importance of protein misfolding into oligomeric and fibrillar aggregates in the onset and evolution of NDDs highlights the demand for structural biomarker-based diagnostics. Researchers created an immunoassay-coupled nanoplasmonic infrared metasurface [..]
Read More
Researchers in optics have improved their revolutionary metasurface masking technology to make higher features without widening the space between them, a development that opens up interesting new design opportunities. They have improved the masking technology to produce metasurfaces that permit an antireflection layer to have a wide optical bandwidth and a wide range of incidence [..]
Read More