
For accurate, real-time intraoperative diagnosis of brain tumors, researchers have merged an advanced optical imaging technique with an AI system. The accuracy of pathologist interpretation of traditional histologic images was compared to the diagnostic accuracy of brain tumor image categorization through machine learning. Both methods produced comparable findings, with the AI-based diagnosis being 94.6% accurate [..]
Read More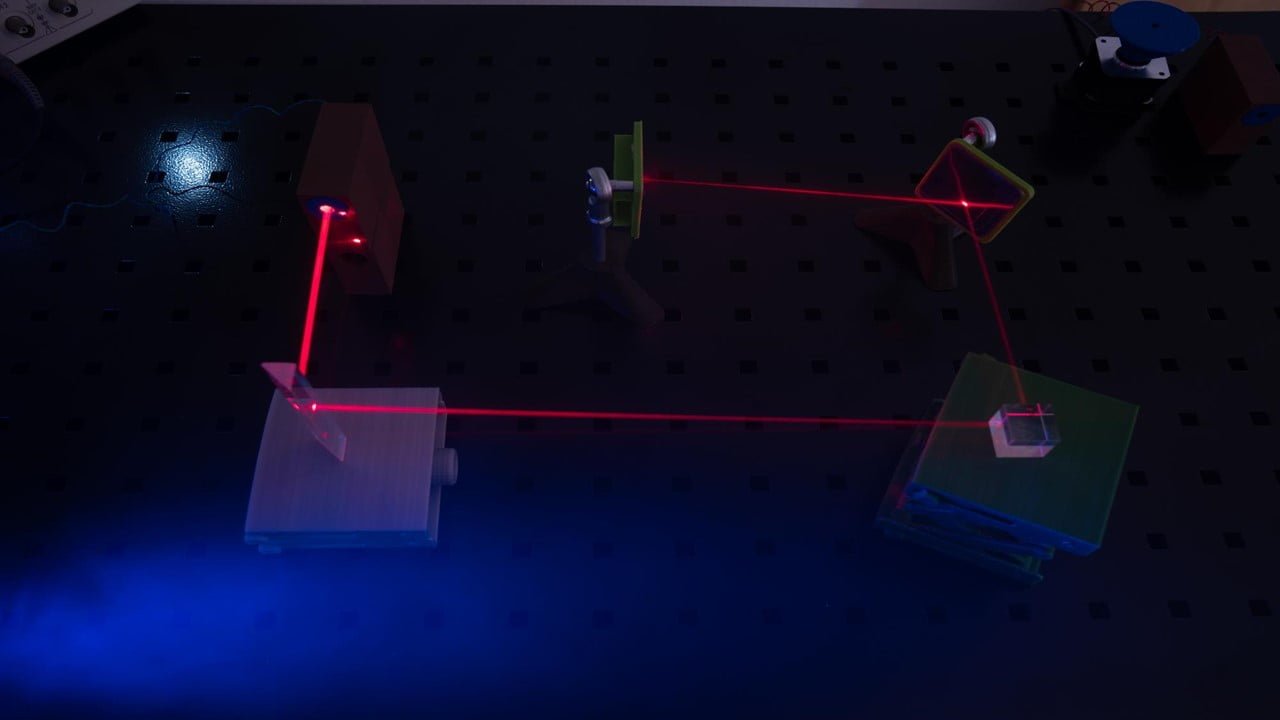
In real-time, scientists observed that helium nanodroplets respond ultrafast after being excited by XUV radiation (extreme ultraviolet radiation). Researchers now have new opportunities for thoroughly examining the basic characteristics of matter thanks to lasers that produce intense, brief XUV and X-ray bursts. Nanometer-sized material samples are of special interest in many of these experiments. Some [..]
Read More
Researchers have created a new imaging method that uses fewer images than conventional nanoscopy methods to generate nm-scale resolution. The researchers used ghost imaging to accelerate their method’s imaging performance. The novel method might be advantageous for live cell imaging. The approach is founded on stochastic optical reconstruction microscopy (STORM), a wide-field microscopy technique that [..]
Read More
Scientists have described a prototype atomic-array optical tweezer clock that combines the advantages of single-atom and optical-lattice clocks. The most precise and reliable optical clocks currently rely on the optical probing of either a single ion or a group of neutral atoms in an optical lattice. An array of about 40 strontium atoms, each one [..]
Read More
Using low-cost solution-processing techniques, a study team has created high-efficiency, near-infrared LEDs covering 900 mm2. Researchers point out that infrared LEDs are frequently used in remote controls and security video systems and have been used in optical communications and covert illumination. According to the researchers, they are typically small point sources, which restricts their use [..]
Read More
In mammalian brains, neuronal activity is frequently investigated at cellular and subcellular levels using two-photon laser scanning microscopy imaging. These investigations are still limited to a particular functional area of the brain. A novel method known as the multiarea two-photon real-time in vitro explorer ie, MATRIEX Imaging, was recently reported by researchers. The technique enabled [..]
Read More
Scientists have created a brand-new kind of optical metasurface that only allows light to reflect in one way. The researchers empirically proved nonreciprocal light reflection at wavelengths around 860 nm by utilizing an ultrathin nonlinear metasurface’s spatial and temporal phase manipulation. The novel metasurface may facilitate the creation of scalable, magnetic-free, nonreciprocal devices that can [..]
Read More
Infrared wavelengths, which have been challenging to produce with silicon chip technology, can now be converted into visible wavelengths thanks to the developing of a novel chip-integrated light source. This adaptable method of on-chip light production is set to make it possible to produce highly compact photonic instruments that are reliable enough to be used [..]
Read More
The majority of people find having an ultrasound to be a simple procedure: A technician applies gentle pressure to a probe against a patient’s skin, sending out sound waves that pass through the skin and bounce off muscle, fat, and other soft tissues before returning to the probe, which picks up the waves and interprets [..]
Read More
Skip the litmus paper; instead, a new type of pH sensor based on the current light developed by a global research team could provide users with an immediate visual readout and continuously capture a signal without interfering with the monitored biological systems. The scientists think their proof-of-concept gadget could inspire the creation of other sensors. [..]
Read More
Light can now experience multiple dimensions thanks to a novel optical chip design. It could support flexible systems for cutting-edge communications and super-fast artificial intelligence technologies. Considering that the area around us is only three-dimensional, it is mind-boggling to think that light can evolve in up to seven dimensions on our specially designed circuits. The [..]
Read More
Researchers are developing a deep learning-based pattern recognition, i.e., PR-OCT system, that will automate image processing and provide an accurate, computer-aided diagnosis of colorectal cancer potentially in real-time. The method uses deep learning and OCT machine learning to find patterns in healthy and abnormal tissue sample images. Using OCT as a study tool, the researchers [..]
Read More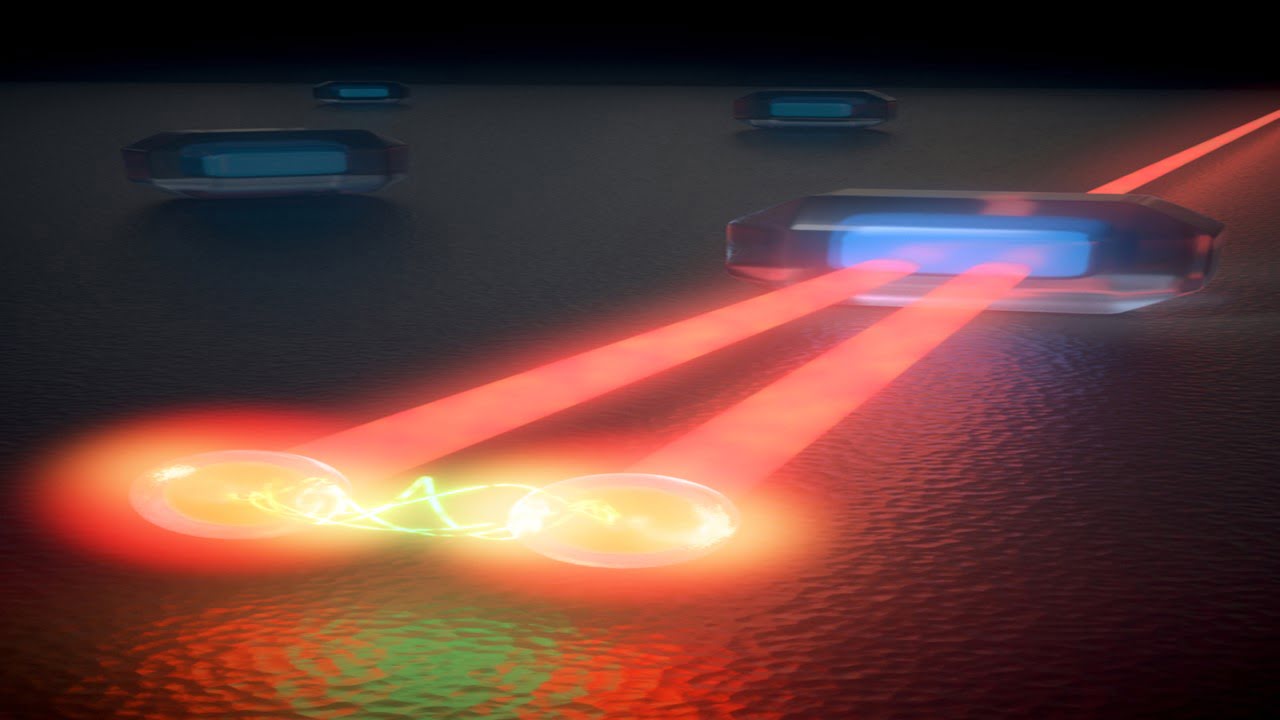
A new single molecule imaging technique that does not rely on fluorescent emitters could have many applications in nanotechnology, photonics, and photovoltaics. At room temperature, the technique detects stimulated emissions from single quantum dots. Because of its speed, it is possible to track charge-carrier populations throughout the absorption and emission cycle. In biology, single molecule [..]
Read More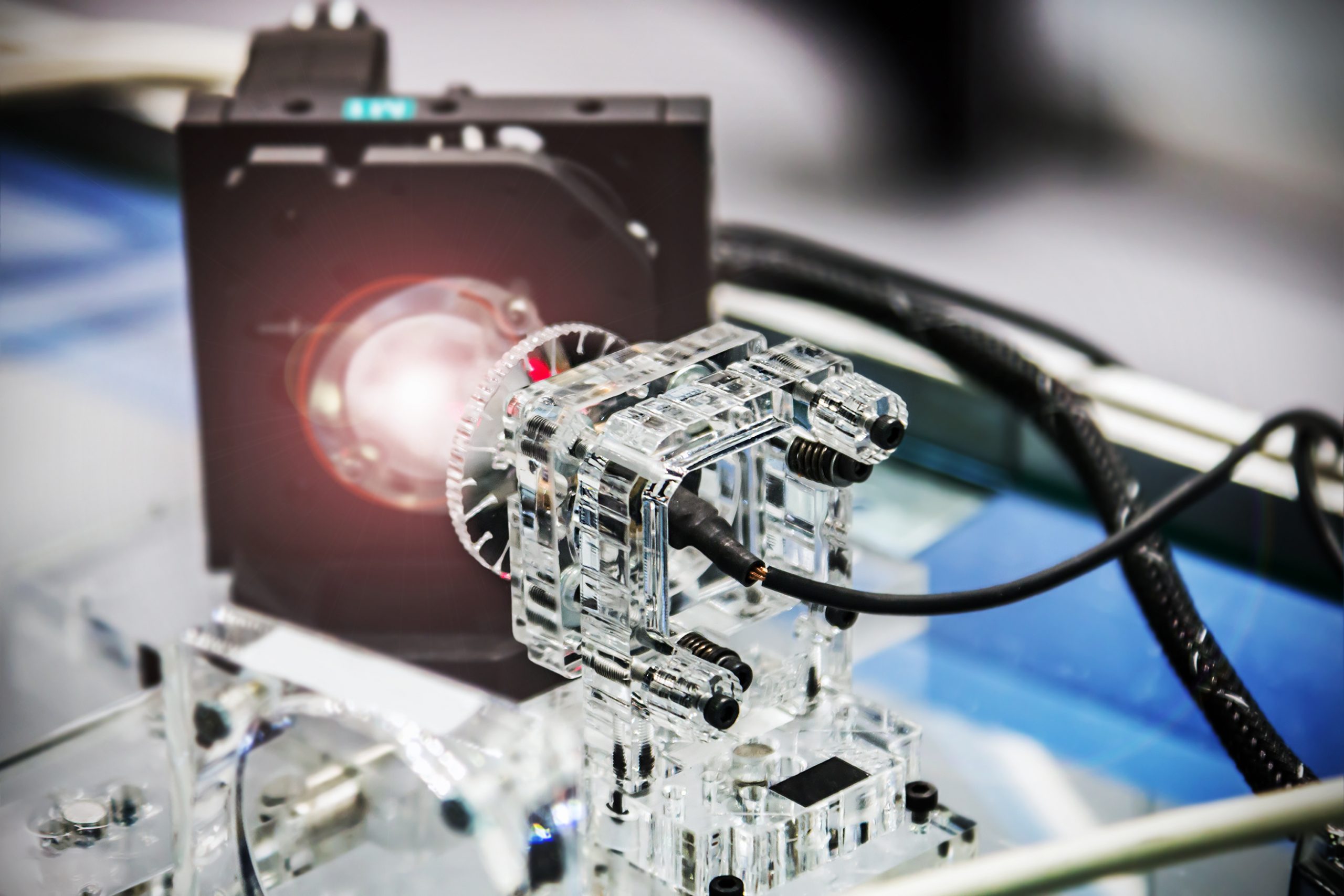
Although the higher atmospheric layers (i.e., those between 30 and 120 km) are increasingly intriguing to climate researchers, only sounding rockets can directly access the regions above 40 km. Such research will soon be possible remotely thanks to a recently created LIDAR system built on a diode-pumped alexandrite laser. Scientists are creating an independent, transportable [..]
Read More
Researchers used endoscopic ultrasound (EUS)-guided needle-based confocal laser endomicroscopy (nCLE) to diagnose cysts in the pancreas with unprecedented accuracy. Patients typically do not exhibit symptoms of pancreatic cancer until it is advanced, making early diagnosis and treatment difficult. The current standard includes analyzing the cyst fluid. In 71% of cases, it accurately classifies them as [..]
Read More
For the first time, scientists could identify very low concentrations of a cancer protein biomarker in a urine sample using a chip-based optical sensor with an embedded laser. The new technology is more sensitive than previous models and may result in non-invasive, low-cost methods to identify molecules that signify the existence or progression of a [..]
Read More
Diffractive deep neural network (DDNN) is an optical machine learning framework that combines deep learning with optical diffraction and light-matter interaction to create diffractive surfaces that perform optical computation at the speed of light. A diffractive neural network is first designed in a computer using deep learning techniques, then physically fabricated using 3-D printing or [..]
Read More
A study team has demonstrated real-time monitoring of enzyme reactions using a quantum sensor. The scientists created a system that enabled them to regulate light down to the level of a single particle. It allowed for dim illumination without affecting the enzymes, potentially leading to increased sensitivity. The ability to directly address the sample enabled [..]
Read More
The visual system of the mantis shrimp, a marine crustacean whose eyes handle data about both the hue and the polarization of light, has long captivated optical scientists. These capabilities have been the driving force behind several optical devices that extract 3-D spatial and polarization information concurrently. However, cramming both characteristics into a small optical [..]
Read More
Researchers have developed a method for expediting the creation and customization of templates used in medical image analysis to aid in disease diagnosis. The new technique can be used to crunch datasets of patients’ medical images and capture structural relationships that may indicate disease progression. In many cases, analysis necessitates using a common image template known [..]
Read More