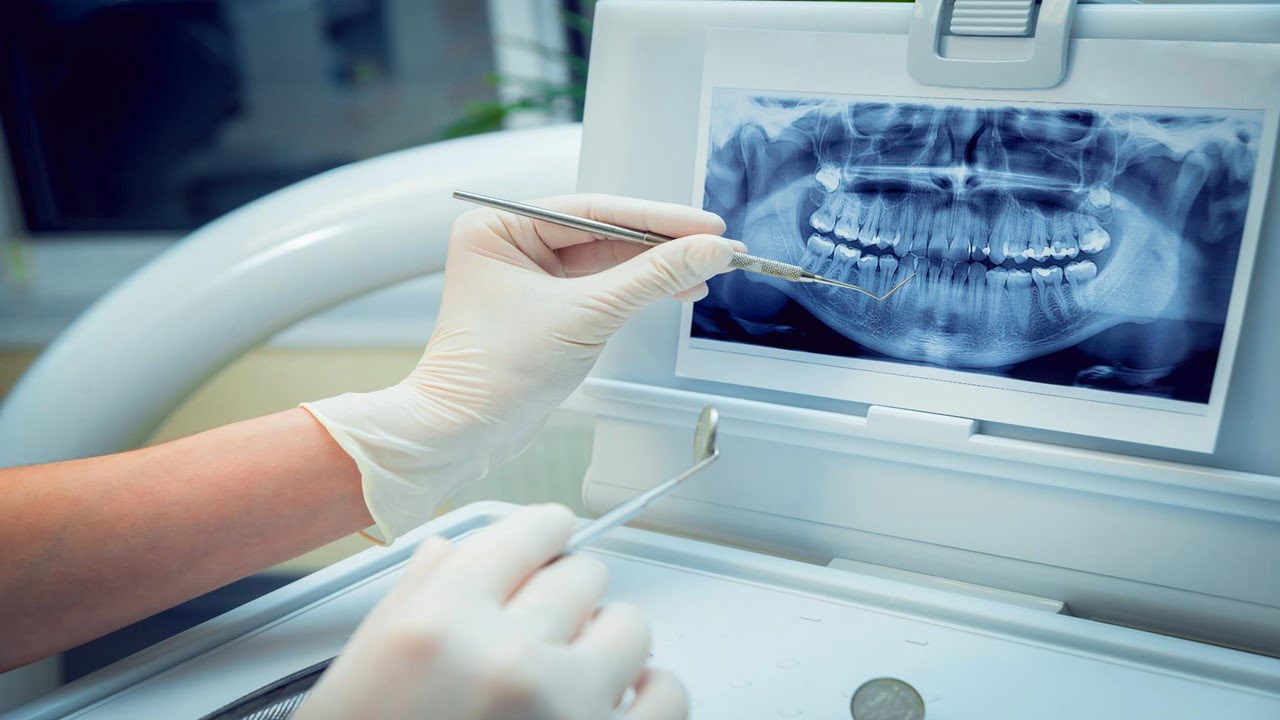
Cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT) is becoming increasingly popular for maxillofacial imaging. It can supply high-resolution three-dimensional (3D) images without distortion and superimposition of bone and other dental structures. Researchers tested a novel AI system based on deep learning methods to determine its real-time performance of CBCT imaging diagnosis of anatomical landmarks, pathologies, clinical effectiveness, and [..]
Read More
The holographic display may rectify many refractive defects, produce high-resolution images, and enable focus cues by modifying the complicated wavefront of coherent light with a spatial light modulator. It could be advantageous to have a hologram rendering using rapid and accurate calculations in any situation. Researchers developed a vision-correcting holographic display with hologram acquisition based [..]
Read More
Voice biometrics is a powerful and convenient form of biometrics that will be crucial in enhancing anti-fraud technology. Whereas one type of biometrics provides decent security against would-be hackers, two provide significantly greater protection, resulting in lower fraud rates. Using both face and voice biometrics makes the verification process nearly impregnable to fraudsters, providing four [..]
Read More
A pair of studies show that a quasiparticle called a plasmon polariton can be pulled with and against an electron flow, which could lead to more efficient light manipulation at the nanoscale. When immersed in an electrical current flowing through a sheet of graphene, quasiparticles comprised of photon and electron waves — plasmon polaritons — [..]
Read More
Scientists have developed a new technique to speed up enzyme study. It is called HT-MEK — short for High-Throughput Microfluidic Enzyme Kinetics. It can compress years of work into just a few weeks by enabling thousands of enzyme experiments to be performed simultaneously. HT-MEK could give insights into how even the most distant sections of [..]
Read More
Ultrathin metasurfaces generate multiform beams (electromagnetic, multi-direction, multi-polarization, multi-frequency, and multi-beam) with promising applications in numerous optical traps, modern communication systems, and complex environment identification. However, their capacity to generate required multiform beams concurrently limits their application. Researchers developed a multifunctional surface with a polarization selection structure and integrated electric and magnetic systems to overcome [..]
Read More
Using atomic force microscopy-based, time-traced imaging and force spectroscopy measurements, researchers report changes in cancer cells’ biomechanics and biophysical properties caused by standard chemotherapeutic drugs. The researchers add to our understanding of the interactions between hypoxia and chemotherapeutic drugs. The stiffness kinetics of untreated cancer cells remain consistent in both normoxia and hypoxia, regardless of [..]
Read More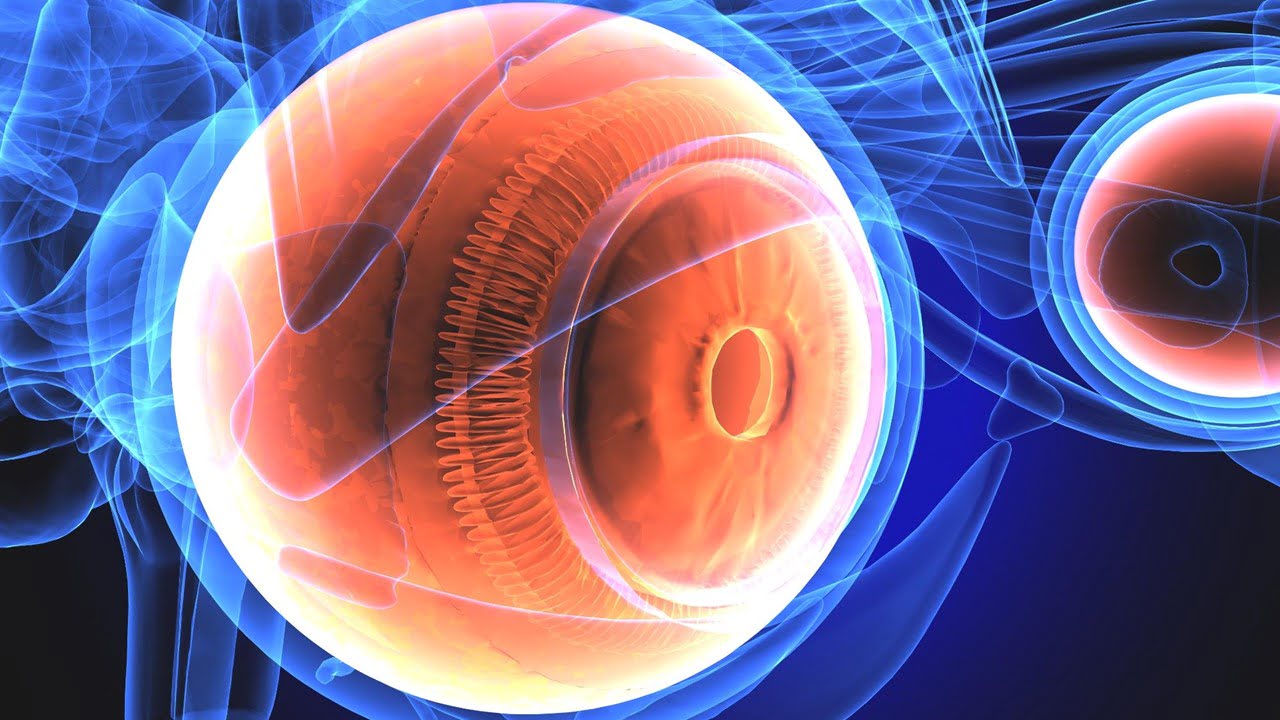
The fatality rate for uveal melanoma, a rare and dangerous eye disease, has remained unchanged for the past 40 years. New treatments to preserve eyesight and avoid mortality are urgently needed because half of the melanomas spread to other body organs, resulting in death in less than a year. Researchers have discovered a small chemical [..]
Read More
Photonics integration is gaining pace in semiconductors, particularly in heterogeneous multi-die packages, as chipmakers look for innovative solutions to overcome power constraints and deal with growing data volumes. Since the end of Dennard scaling, which occurred at the 90nm node, power has become increasingly challenging. There are more transistors per mm2, and the wires are [..]
Read More
Researchers have devised a new computational de-scattering approach termed de-scattering with excitation patterning in temporal focusing microscopy (DEEP-TFM). They employed two-photon patterned excitation with wide-field temporal focusing, but the signal was detected using a wide-field imaging detector. They created a modified temporal focusing microscope that uses a digital micromirror device to transmit arbitrary excitation patterns [..]
Read More
Boiling is a complicated physical phenomenon involving at least two phases of matter. Many factors contribute to the system. Liquid-to-gas conversion takes energy from heated surfaces, preventing overheating in everything from nuclear power plants to powerful computer chips. However, if surfaces become too heated, they may undergo a boiling crisis. Bubbles form quickly in a [..]
Read More
Scientists have developed the first room-temperature, electrically driven, topological laser, which could be useful in telecom wavelength applications. The novel device comprises a 10 by 10 grid of 30-micron-wide rings. Small oblong rings around 5 microns wide connect these rings. All these rings consist of a sandwich of layers of semiconductors, such as indium gallium [..]
Read More
Researchers have combined a new oxygen-sensing film with machine learning to create a wearable sensor capable of measuring tissue oxygenation through the skin. The device could continuously monitor a person’s oxygen levels for applications in medicine and sports. The device comprises a 3D-printed housing, a sensor head, and an adhesive oxygen-sensing film. Electronic components process [..]
Read More
The prognosis and successful treatments differ depending on the type of lung cancer. While it previously took several days to precisely determine the underlying lung tumor mutation, a research team has been able to perform this determination in just one step reliably. They used a combination of quantum cascade laser-based infrared microscopy and machine learning. [..]
Read More
Researchers created a camera with a curved, adaptable imaging sensor that could improve image quality in endoscopes, night vision goggles, artificial compound eyes, and fish-eye cameras. Kirigami, the Japanese art of paper cutting, was used to create the camera. Existing curvy imagers are stretchable but have low pixel density and pixel fill factors, or they [..]
Read More
Researchers have developed a deep-learning platform to speed up the MRI reconstruction process. The framework takes a fraction of the traditional technique’s measurements. It uses plug-and-play algorithms to combine physics-driven data acquisition models with state-of-the-art learned image models. The plug-and-play techniques recover pictures faster, with improved quality and potentially superior diagnostic utility than existing MRI [..]
Read More
Infrared imaging applications are growing from food quality control and remote sensing to night vision devices and LiDAR. IR cameras convert infrared light to electrons and project the resultant image on display. However, such cameras are bulky, disrupt normal vision, and require low temperatures. Alternatively, a nonlinear optical process – nonlinear sum-frequency generation (SFG) – [..]
Read More
Researchers have discovered a new method for faster spectroscopic measurements. They observed changes in the light spectrum by using simple, rapid polarization measurements by linking polarization to the color of a pulsed laser. The technique opens up new possibilities for measuring spectral changes over the complete color spectrum of light in a nanosecond time frame. [..]
Read More
Light-emitting, energy-harvesting, and sensing technologies could all benefit from optoelectronic materials that can convert light energy into electricity and light. However, devices leveraging these materials are notoriously inefficient, wasting a considerable amount of valuable energy in heat. New light-electricity conversion principles can break the present efficiency restrictions. Inversion symmetry is a physical property that restricts [..]
Read More
A new computational method dramatically increases the resolution of atomic force microscopy. Under standard physiological settings, the approach exposes atomic-level data on proteins and other biological structures. It gives up a new world of possibilities in cell biology, virology, and other microscopic processes. In physics, atomic force microscopy can efficiently resolve atoms on solid surfaces [..]
Read More