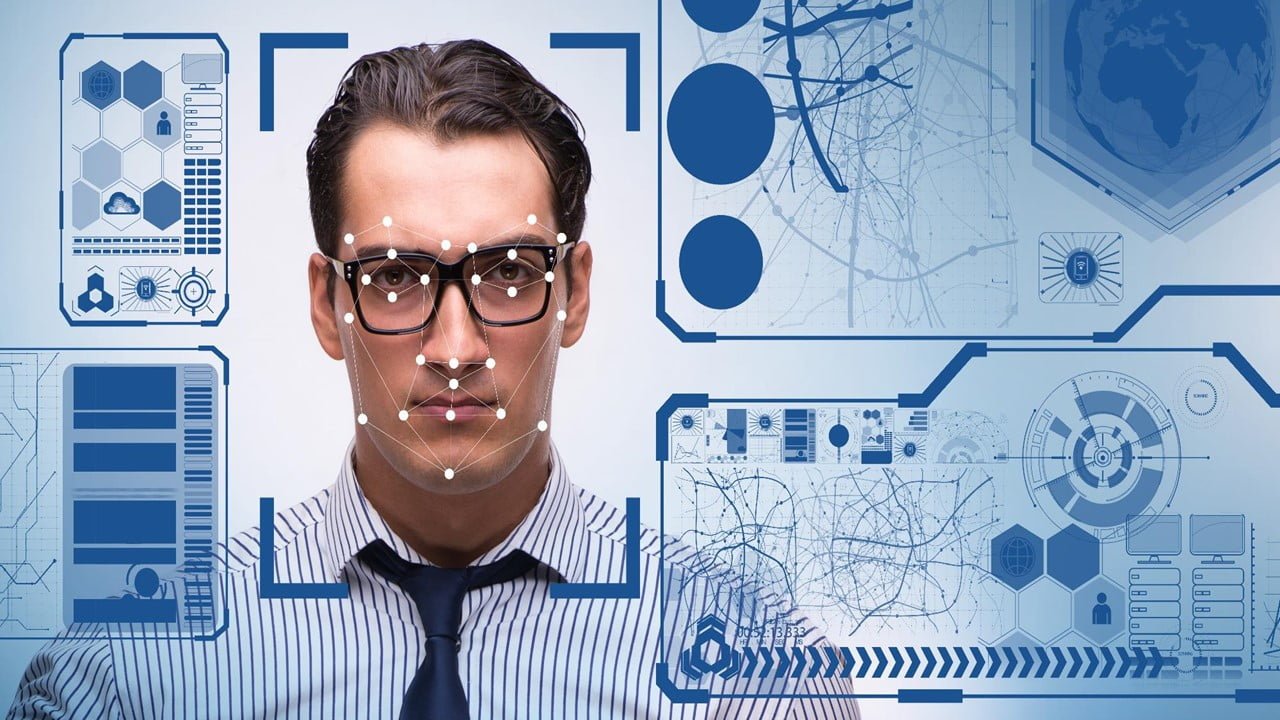

Researchers have developed a deepfake detection method focusing on a lightweight, low training complexity, and high-performance face biometrics technique with ideal size, weight, and power (SWaP). Deepfake refers to artificial intelligence-synthesized, hyper-realistic video content that falsely depicts individuals saying or doing something. The researchers set out to tackle the significant threat that deepfake pose to [..]
Read More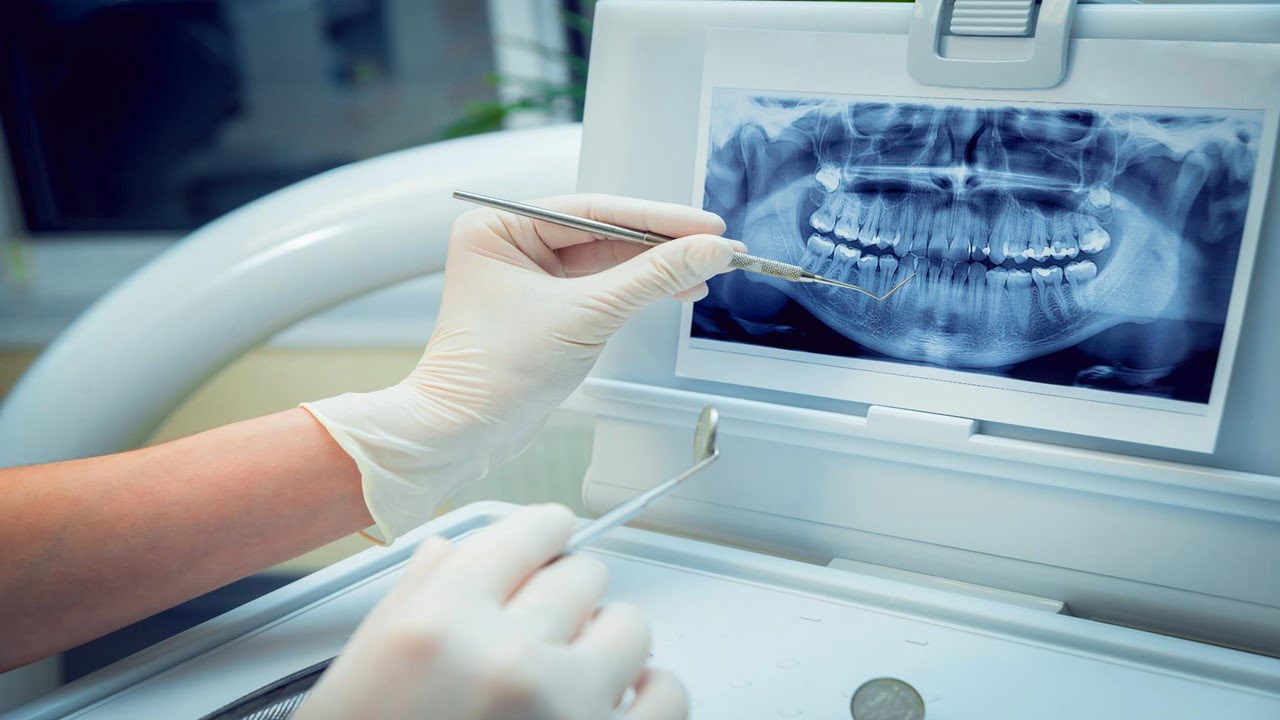
The estimation of dental age remains part of active research in forensic science. In legal proceedings, a series of clinical and radiological examinations are carried out for accurate age estimation of living individuals. The age estimation procedure often includes a physical examination, a dental examination with dental status and an X-ray of the dentition, and [..]
Read More
Researchers have developed a compact gas sensor platform that combines liquid crystals (LCs) with holographic metasurfaces to sense a volatile gas promptly and provide instantaneous feedback through a visual holographic alarm. This technology integrates the advantages of the stimuli responsiveness of LCs and the compactness of metasurfaces while maximizing the effectiveness of the sensor by [..]
Read More
Researchers demonstrate highly ultrafast x-ray optics-on-a-chip based on MEMS capable of modulating hard x-ray pulses exceeding 350 MHz, 103× higher than any other mechanical modulator, with a pulse purity >106 without compromising the spectral brilliance. Moreover, the timing characteristics of the devices can be tuned on-the-fly to deliver optimal pulse properties to create a host [..]
Read More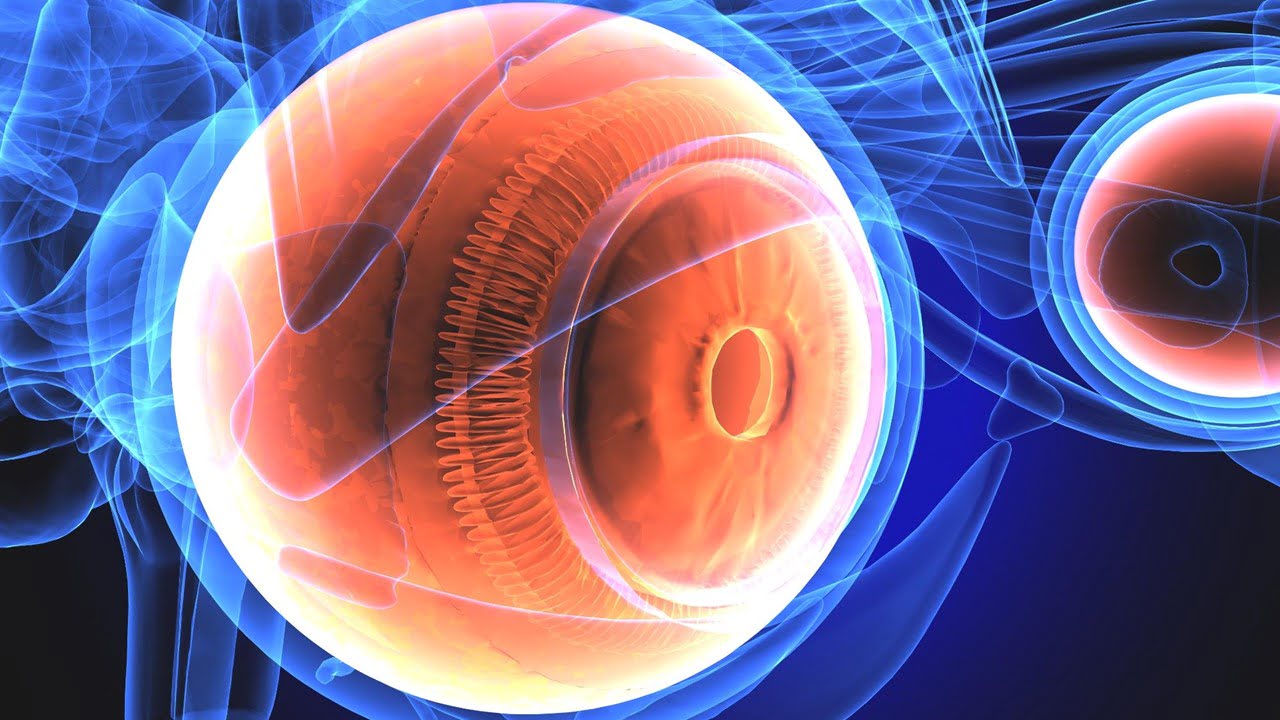
New gene therapy for one of the most common types of congenital blindness has proven safe and effective in improving patients’ vision. The therapy delivers functional copies of GUCY2D to the eyes of patients with severe vision impairments caused by gene mutations. Even with a low dose of gene therapy, the researchers observed long-term improvements [..]
Read More
A highly sensitive optomechanical ultrasound detector integrated into a silicon photonic chip has been developed by researchers. The device is 100 times more sensitive than state-of-the-art piezoelectric detectors of identical sizes. Their design could substantially improve the performance of ultrasound detectors in a wide variety of biomedical applications. The researchers used a new optomechanical ultrasound [..]
Read More
NMR spectroscopy is an information-dense analytical technique used to characterize materials by quantifying and determining molecular structure. Current NMR methodology is primarily limited to single-sample measurements under low-throughput conditions, which is a persistent challenge. As a result, there needs to be more alignment between applications that require screening large parameter spaces and the desire to [..]
Read More
Researchers have devised and implemented a simplified algorithm for turning freely drawn lines into holograms on a standard desktop CPU. They dramatically cut down the computational cost and power consumption of holographic algorithms that require dedicated hardware. It is fast enough to convert writing into lines in real time and makes crisp, clear images that [..]
Read More
A group of scientists used a new Scanning Transmission Electron Microscope (STEM) technique to image the electron distribution in electrides, which are ionic compounds, particularly the electrons that float loosely within pockets and appear separate from the atomic network. Differential Phase Contrast (DPC) in STEM is a new technique that measures and maps a material’s [..]
Read More
Researchers at UMass Lowell are working on a pilot project to help the university identify and prioritize cost-saving repairs and energy-efficiency projects on campus. Drones equipped with infrared cameras can create thermal maps showing where buildings or underground steam pipes are losing heat and costing organizations money. These can help identify energy efficiency projects. They [..]
Read More
The world of 2D material science is exciting, with new advances opening up new possibilities, most notably through graphene adaptations. Scientists have introduced a new player to the game in the form of borophane, an ultra-thin, ultra-strong material that they hope will one day be used in advanced electronics. Borophene has several disadvantages despite its [..]
Read More
Biosensors are usually designed following a three-step process: recognition of biomolecules, triggering of signal, and detection (e.g., using phase change material properties). Recognizing the biomolecules is the first and very important step in designing a biosensor system. Biosensors are useful for environmental analysis and agricultural management applications, particularly in detecting infectious diseases in crops, toxic [..]
Read More
If there was a better way to obtain feedback on how the laser interacts (laser interaction) with a material, laser precision could be significantly improved. A production laser’s cutting and etching actions would be more controlled and less uncertain in this manner. Until now, this problem has proven to be surprisingly difficult to solve. Despite [..]
Read More
Ca3SiO, a chemical compound discovered by researchers, is a direct transition semiconductor, making it a potentially bright infrared LED and infrared detector component. This semiconductor compound, made up of calcium, silicon, and oxygen is inexpensive and non-toxic. Today’s infrared semiconductors contain toxic chemical elements like cadmium and tellurium. Ca3SiO could be used to create cheaper [..]
Read More
Excessive fat accumulation in the liver can lead to serious medical problems, including liver failure. Thus, understanding the distribution of lipids within the liver is critical in diagnosing fatty liver diseases. A team of researchers has now shown that near-infrared hyperspectral imaging permits the visualization of lipid content in mouse liver. This technique can facilitate [..]
Read More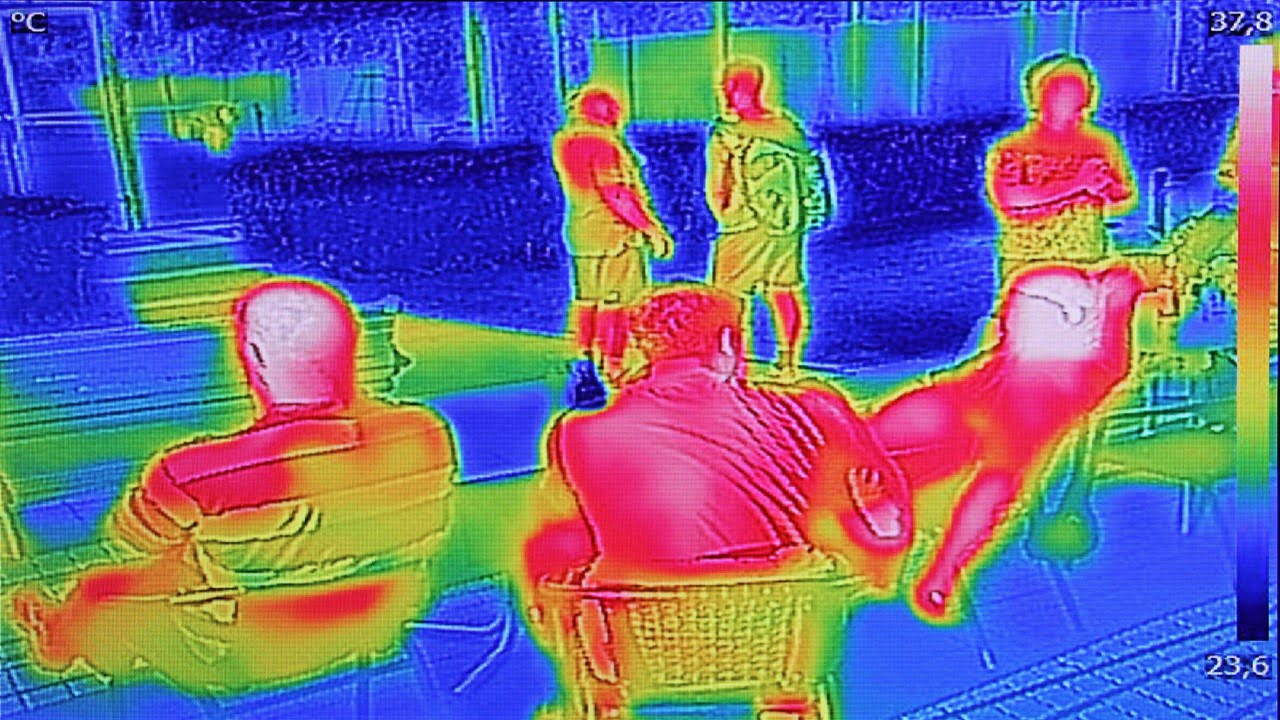
Temperature recordings were widely used as a screening tool to help detect COVID-infected individuals. Traditional approaches to temperature screening have several important things that could be improved. Because absolute temperature is measured in the axilla, mouth, or eardrum rather than the body’s core temperature, it has limited utility. As a result, there is no accurate [..]
Read More
Electrochemiluminescence, also known as electrogenerated chemiluminescence, is one of the most widely used techniques for producing light through efficient electron transfer (ECL). Individual ECL spectra showing emitted light are collected continuously during a potentiodynamic course, allowing ECL mechanisms to be investigated. The obtained spectra are spooled together and plotted along the applied potential axis, which [..]
Read More
Researchers used a sensitive scattering-type scanning near-field optical microscope (s-SNOM) to directly measure the optical fields of AGP waves propagating in a nanometer-thin waveguide to demonstrate direct near-field optical imaging of acoustic graphene plasmon (AGP) fields. Scientists could observe the thousandfold compression of mid-infrared light using this method. The strategy paves the way for potentially [..]
Read More
An AI tool opens up new possibilities for analyzing microscope images. According to a study, the tool, which has already received international recognition, has the potential to fundamentally change microscopy and pave the way for discoveries and applications in both research and industry. Deep learning has taken the world by storm, having a massive impact [..]
Read More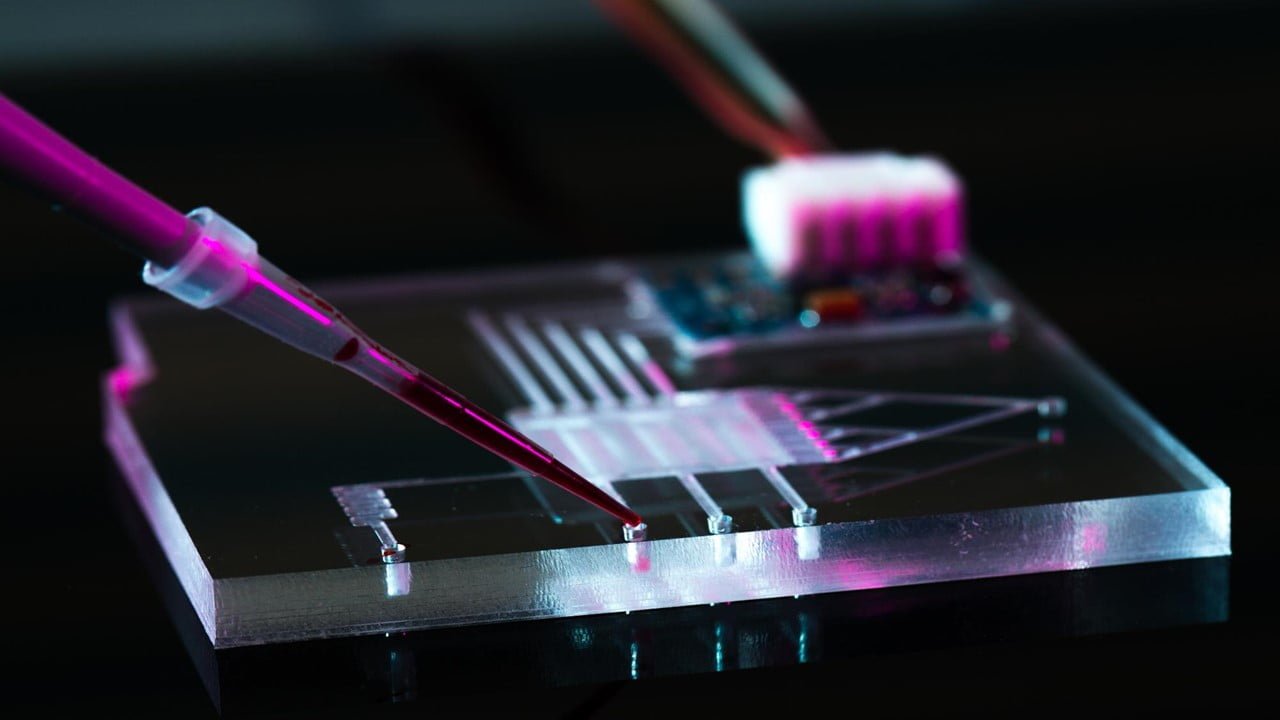
The implementation of the idea of liquid computers would be revolutionary for microfluidics, not because microfluidics seeks computational capabilities but because it would enable the encoding of a variety of algorithms (laboratory procedures) into the structure of the device. Researchers show the successful implementation of advanced sequential logic in droplet microfluidics, whose principles rely on [..]
Read More