
Today’s computers’ exact 0s and 1s can obstruct the correct solutions to complex real-world issues in a noisy and uncertain environment. It is the claim made by a young, pioneering branch of study in probabilistic computing. Researchers have recently developed a brand-new technique for producing probabilistic bits (p-bits) at significantly greater rates by employing photonics [..]
Read More
It is difficult to diagnose neurodegenerative diseases (NDDs), such as Parkinson’s disease and Alzheimer’s disease, because no methods are available to identify preclinical biomarkers. The importance of protein misfolding into oligomeric and fibrillar aggregates in the onset and evolution of NDDs highlights the demand for structural biomarker-based diagnostics. Researchers created an immunoassay-coupled nanoplasmonic infrared metasurface [..]
Read More
Researchers in optics have improved their revolutionary metasurface masking technology to make higher features without widening the space between them, a development that opens up interesting new design opportunities. They have improved the masking technology to produce metasurfaces that permit an antireflection layer to have a wide optical bandwidth and a wide range of incidence [..]
Read More
A brand-new quantum photonics technique has been created by researchers to produce three-dimensional images using lasers, much as in Star Trek and Star Wars. Their goal was to capture and reconstruct incredibly weak light beams of just a single photon of light. This quantum photonics technology has the potential to transform 3D scene reconstruction and [..]
Read More
Senescence, which affects stem cells, essential for therapeutic usage, occurs in our bodies as we age. But when they reach the senescent stage, they cease making vital biomolecules. Researchers should stop older cells from entering the culture to stop senescence. Biomolecules needed for treatments are produced by mesenchymal stem cells derived from fat tissue. Researchers [..]
Read More
A photonic chip developed by researchers turns a single incoming laser beam into various new beams with various optical characteristics. At various points along the chip, the freshly created beams, which have the same frequency as the original beam, simultaneously leave the circuit. It enables engineers and scientists to choose the precise properties of one [..]
Read More
When you think of gazing under a microscope, you usually image an amoeba, a human cell, or possibly a little bug on a glass slide. A new form of microscopy technique has been created, making examining the fundamental molecules that make up live creatures simpler. However, microscopes can see much more than these tiny living [..]
Read More
Better, quicker, and less expensive MRIs with broader biological uses may be made possible by hyperpolarization. There are restrictions on the magnetic resonance (MR) signals utilized in medical imaging. The signal in magnetic resonance applications used in biomedicine is so faint that many images must be taken and averaged, according to the researcher. The length [..]
Read More
Researchers have devised a simple method for reliably producing nanomaterials that resemble Swiss cheese. The approach needed to generate this porous material might aid in creating more sophisticated materials with applications in photocatalysis and optoelectronics. Low-density solids containing much space within their main body are known as porous materials. The vast surface area these gaps [..]
Read More
Researchers have shown that chip-based biosensor devices that identify or evaluate chemicals have significantly improved. The accomplishments lay the foundation for highly sensitive portable integrated optofluidic sensing devices that could conduct different medical tests simultaneously, even if they involve very different bioparticles at different concentrations, like viral particles and DNA. Researchers gave an optofluidic chip-based [..]
Read More
By merging terahertz (THz) spectroscopy with real-time monitoring, scientists are putting forth a ground-breaking strategy to speed up the discovery of new materials. Electromagnetic waves, known as terahertz waves, can expose the mysteries of matter. They are capable of capturing quick changes in materials that are hidden from other radiation kinds. Scientists can now utilize [..]
Read More
The gold-standard technique for determining the quantity of replication-competent lytic virions, the plaque assay, necessitates staining and typically takes longer than 48 hours to complete. Researchers have demonstrated how deep learning and lens-free holographic imaging may be used to speed up and automate the test. The small imaging device measures the amount of infected tissue [..]
Read More
According to studies, blood biomarkers can enhance risk prediction for twelve illnesses over utilizing genetics alone. The study shows that ‘metabolomic’ risk scores created from these blood markers are often better disease risk indicators than genetic data alone. The study used over 200 biomarkers gathered from around half a million people across three large-scale biobanks. [..]
Read More
The “breathing,” or mechanical vibration that occurs between two layers of atoms, has been harnessed by a research team to create a new quantum technology building block. The research team found that by examining the type of light that those atoms released when triggered by a laser, they could identify atomic breathing or the mechanical [..]
Read More
With the powerful imaging technology of in-vivo corneal confocal microscopy, researchers and doctors may now view the microstructures at the ocular surfaces in great detail. The cornea, a transparent dome-shaped tissue that makes up the front of the eye, is particularly densely innervated with sensory nerves. A method that can image corneal microstructures at various [..]
Read More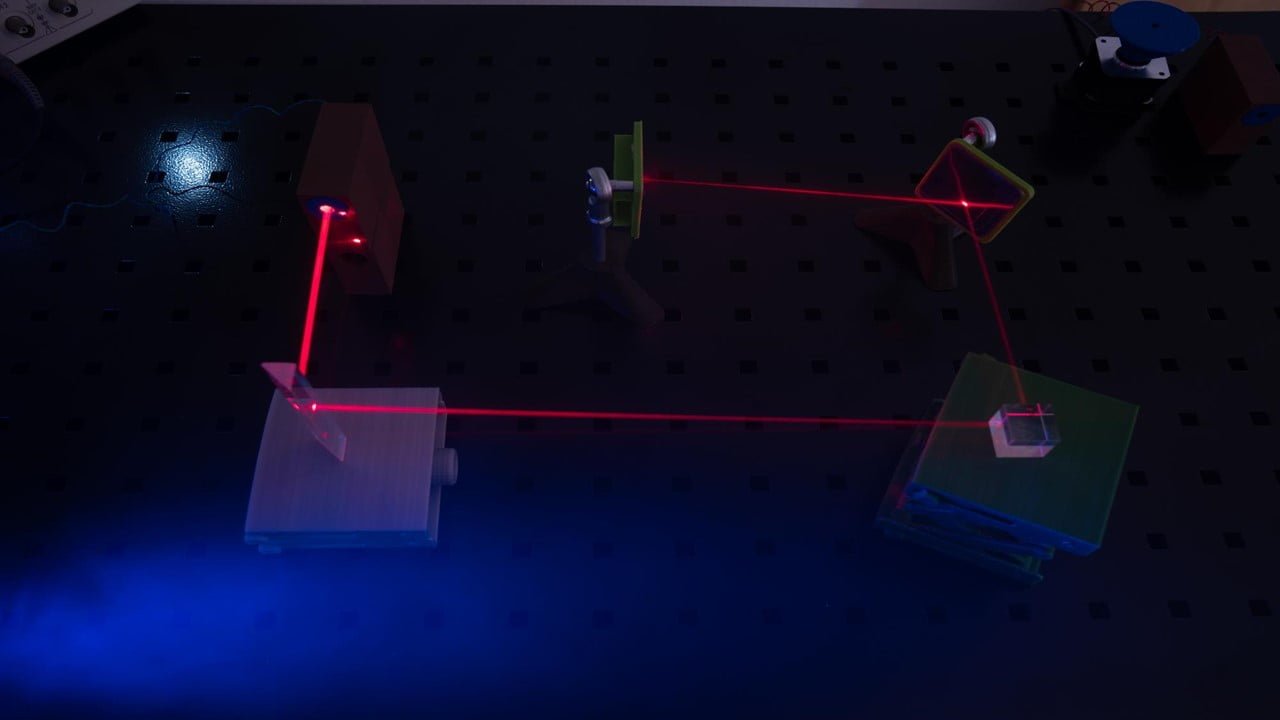
In addition to a large global network of communication cables, the ocean’s depths are home to a rich ecosystem of marine animals. These vital wires are susceptible to damage from earthquakes and tsunamis. Scientists that track this seismic activity encounter a hurdle since the Earth’s surface is more than 70% water. However, the wires present [..]
Read More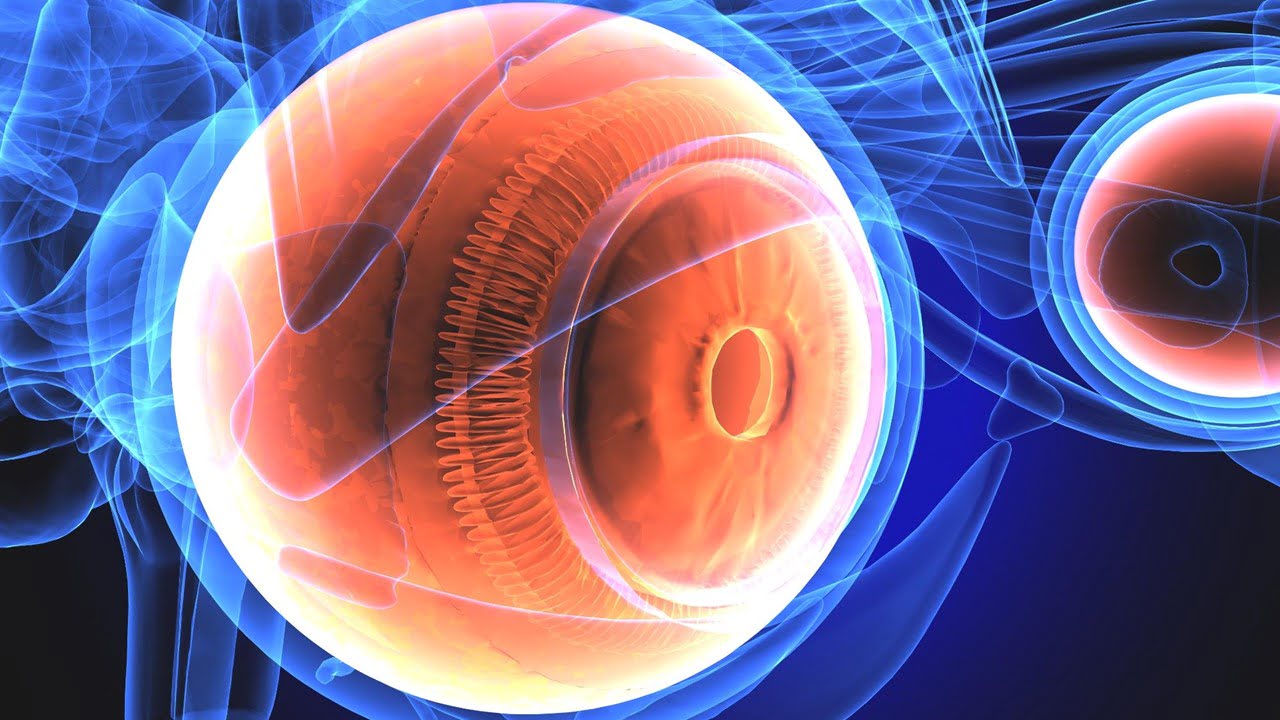
Retrospective cohort research found that an AI-driven automated optical coherence tomography angiography (OCTA) review system accurately predicted the development of diabetic macular ischemia (DMI) by more than 90%. At baseline, the DMI of the superficial capillary plexus more than quadrupled, and the DMI of the deep capillary plexus more than tripled the risk of diabetic [..]
Read More
Researchers have found a brand-new, inexpensive material that may be used to create thermal imaging lenses, opening up advanced manufacturing uses for this potent technology. Many sectors employ thermal and infrared imaging, including defense, security and surveillance, medical and electrical engineering, space exploration, and autonomous vehicle operation. However, the materials are expensive and must be [..]
Read More
An innovative low-temperature technique for 3D printing optical-grade glass has been created by a research team, paving the way for microelectronic devices with high-resolution visible-light nanophotonics capabilities. High-precision optics and microelectronics might allow new navigation, communications, remote sensing technologies, and other applications. The materials that make up those platforms would be harmed by the high-temperature [..]
Read More
Researchers have developed the first flexible, transparent augmented reality (AR) display screen using 3D printing and inexpensive materials. Creating the new display screen is expected to improve the usage of augmented reality in several fields and applications. By superimposing digital material over the physical world, augmented reality (AR) technology improves how users see and interact [..]
Read More