Cylindrical optical waveguides called optical MNFs have diameters below or very near the wavelength of light. Since its initial experimental demonstration, low-loss silica MNF has gained popularity in various fields, including optomechanics, nonlinear optics, optical sensors, and atom optics. The most efficient way to improve light-matter interaction and uncover new possibilities for both scientific study [..]
Read More
Although generative AI systems now available have drawbacks that can restrict their usage, artificial intelligence appears ideal for producing the enormous amounts of pictures required to educate autonomous vehicles and other robots to observe their surroundings. Engineers have created a programmatic imaging software system to overcome these restrictions and quickly produce picture sets to prepare [..]
Read More
A brand-new quantum photonics technique has been created by researchers to produce three-dimensional images using lasers, much as in Star Trek and Star Wars. Their goal was to capture and reconstruct incredibly weak light beams of just a single photon of light. This quantum photonics technology has the potential to transform 3D scene reconstruction and [..]
Read More
When you think of gazing under a microscope, you usually image an amoeba, a human cell, or possibly a little bug on a glass slide. A new form of microscopy technique has been created, making examining the fundamental molecules that make up live creatures simpler. However, microscopes can see much more than these tiny living [..]
Read More
Researchers have devised a simple method for reliably producing nanomaterials that resemble Swiss cheese. The approach needed to generate this porous material might aid in creating more sophisticated materials with applications in photocatalysis and optoelectronics. Low-density solids containing much space within their main body are known as porous materials. The vast surface area these gaps [..]
Read More
Researchers have shown that chip-based biosensor devices that identify or evaluate chemicals have significantly improved. The accomplishments lay the foundation for highly sensitive portable integrated optofluidic sensing devices that could conduct different medical tests simultaneously, even if they involve very different bioparticles at different concentrations, like viral particles and DNA. Researchers gave an optofluidic chip-based [..]
Read More
By merging terahertz (THz) spectroscopy with real-time monitoring, scientists are putting forth a ground-breaking strategy to speed up the discovery of new materials. Electromagnetic waves, known as terahertz waves, can expose the mysteries of matter. They are capable of capturing quick changes in materials that are hidden from other radiation kinds. Scientists can now utilize [..]
Read More
According to studies, blood biomarkers can enhance risk prediction for twelve illnesses over utilizing genetics alone. The study shows that ‘metabolomic’ risk scores created from these blood markers are often better disease risk indicators than genetic data alone. The study used over 200 biomarkers gathered from around half a million people across three large-scale biobanks. [..]
Read More
With the powerful imaging technology of in-vivo corneal confocal microscopy, researchers and doctors may now view the microstructures at the ocular surfaces in great detail. The cornea, a transparent dome-shaped tissue that makes up the front of the eye, is particularly densely innervated with sensory nerves. A method that can image corneal microstructures at various [..]
Read More
An innovative low-temperature technique for 3D printing optical-grade glass has been created by a research team, paving the way for microelectronic devices with high-resolution visible-light nanophotonics capabilities. High-precision optics and microelectronics might allow new navigation, communications, remote sensing technologies, and other applications. The materials that make up those platforms would be harmed by the high-temperature [..]
Read More
Researchers have developed the first flexible, transparent augmented reality (AR) display screen using 3D printing and inexpensive materials. Creating the new display screen is expected to improve the usage of augmented reality in several fields and applications. By superimposing digital material over the physical world, augmented reality (AR) technology improves how users see and interact [..]
Read More
Scalable photonic quantum computing architectures require photonic processing devices. Such platforms rely on low-loss, high-speed, reconfigurable circuits and near-deterministic resource state generators. In a new report, a research team has developed an integrated photonic platform with thin-film lithium niobate. The scientists integrated the platform with deterministic solid-state single photon sources using quantum dots in nanophotonic [..]
Read More
Over the past ten years, computational imaging has made significant advancements. The method combines cutting-edge hardware and algorithms to create photos that conventional cameras can’t catch. Researchers have created a revolutionary method called sparse holography that converts two-dimensional holograms into three-dimensional images using computational imaging techniques. They created a set of algorithms and techniques to [..]
Read MoreThe tiny visual systems of flying insects have inspired researchers to develop optoelectronic graded neurons for perceiving dynamic motion, enriching the functions of vision sensors for an agile response. With excellent energy efficiency, biological visual systems can accurately detect motion in a complex environment. In particular, flying insects can see objects moving quickly and have [..]
Read More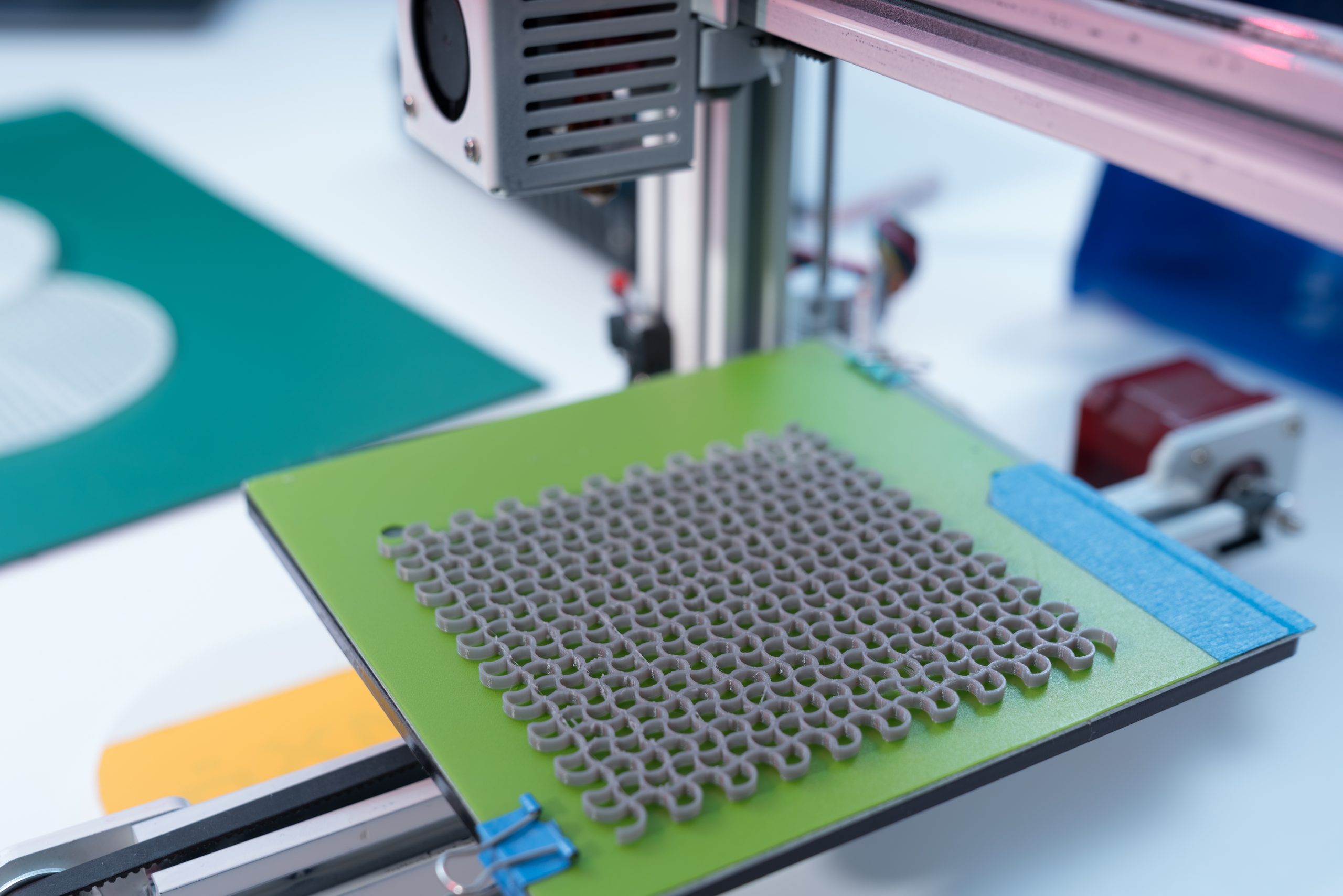
Researchers have created a brand-new category of integrated photonic devices called “leaky-wave metasurfaces” that can transform the light that was once constrained in an optical waveguide into any optical pattern in free space. These devices’ simultaneous control of all four optical degrees of freedom—amplitude, phase, polarization ellipticity, and polarization orientation—is a global first. The devices [..]
Read More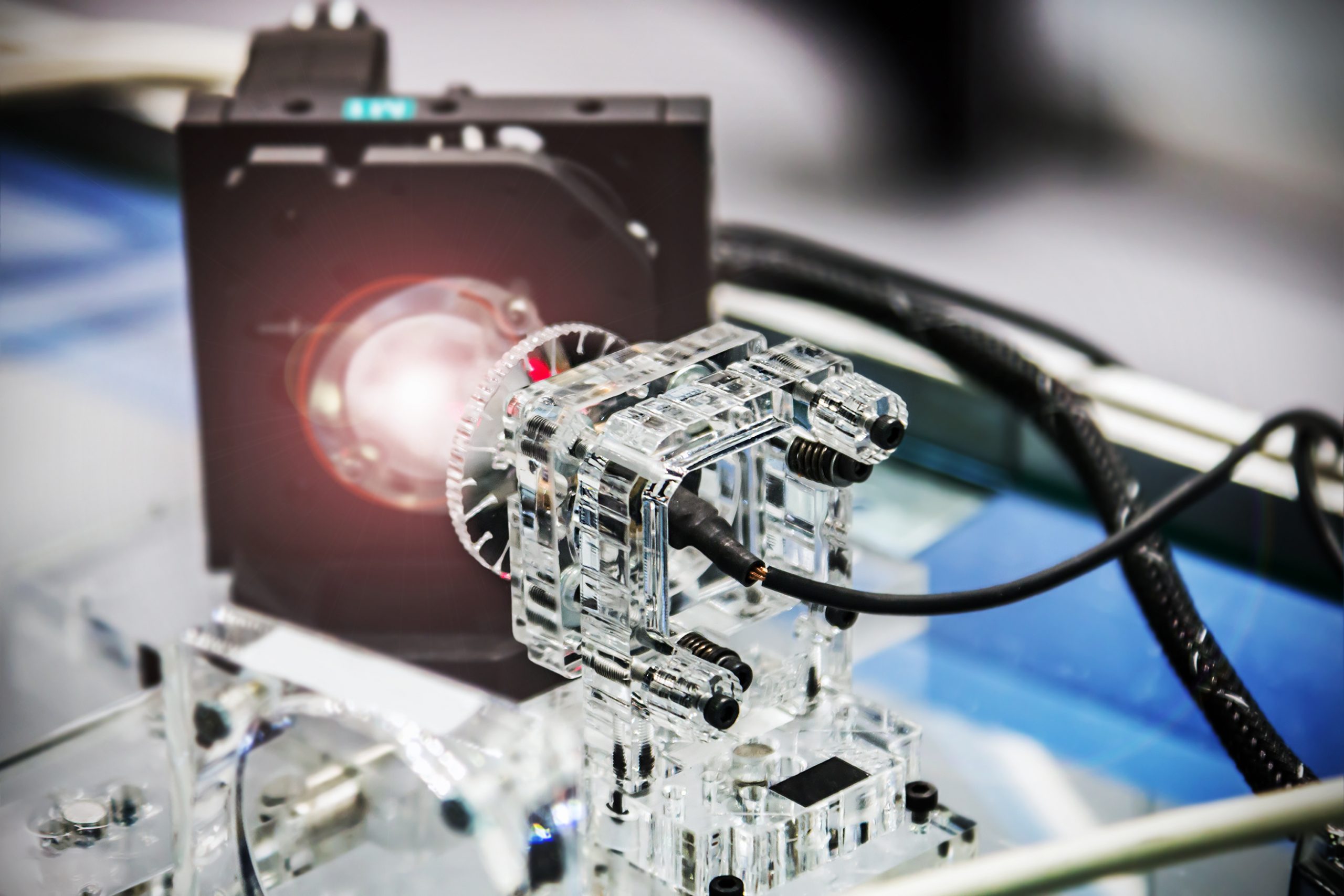
With the aid of colloidal quantum dot technology, scientists have achieved tremendous advancements in developing high-intensity light emitters, producing dual-function devices with previously unheard-of brightness levels. This development puts practical quantum dot laser diodes closer to reality and has potential applications in integrated electronics, photonics, and medical diagnostics. To create high-intensity light emitters that are [..]
Read More
Scientists have created a new next-generation DNA sequencing method to find genetic changes in just one molecule. The procedure, known as Concatenating Original Duplex for Error Correction (CODEC), increases the accuracy of next-generation sequencing by about 1000 times and makes a variety of applications possible, including the reasonably priced detection of very small numbers of [..]
Read More
A solid-state electronic device array that can be used for compressive spectroscopy has been presented by researchers. It creates time-modulated light at tunable wavelengths. It needs a broadband multicolored light source and can be modulated at a certain frequency, which makes it simple to distinguish from surrounding light. Fabricating many LEDs on a single chip [..]
Read More
According to recent research, an artificial intelligence tool has successfully identified those at the greatest risk for pancreatic cancer up to three years before diagnosis. The researchers said the results indicate that AI-based population screening could be useful in identifying those at increased risk for the disease and could hasten the diagnosis of a disorder [..]
Read More
Scientists have produced two-dimensional photonic time crystals that amplify light and could be used to advance laser and wireless technology. Researchers have discovered a method for making these crystals and demonstrated that these strange, artificial substances could enhance the light that shines on them. These discoveries could result in better lasers and more effective and [..]
Read More