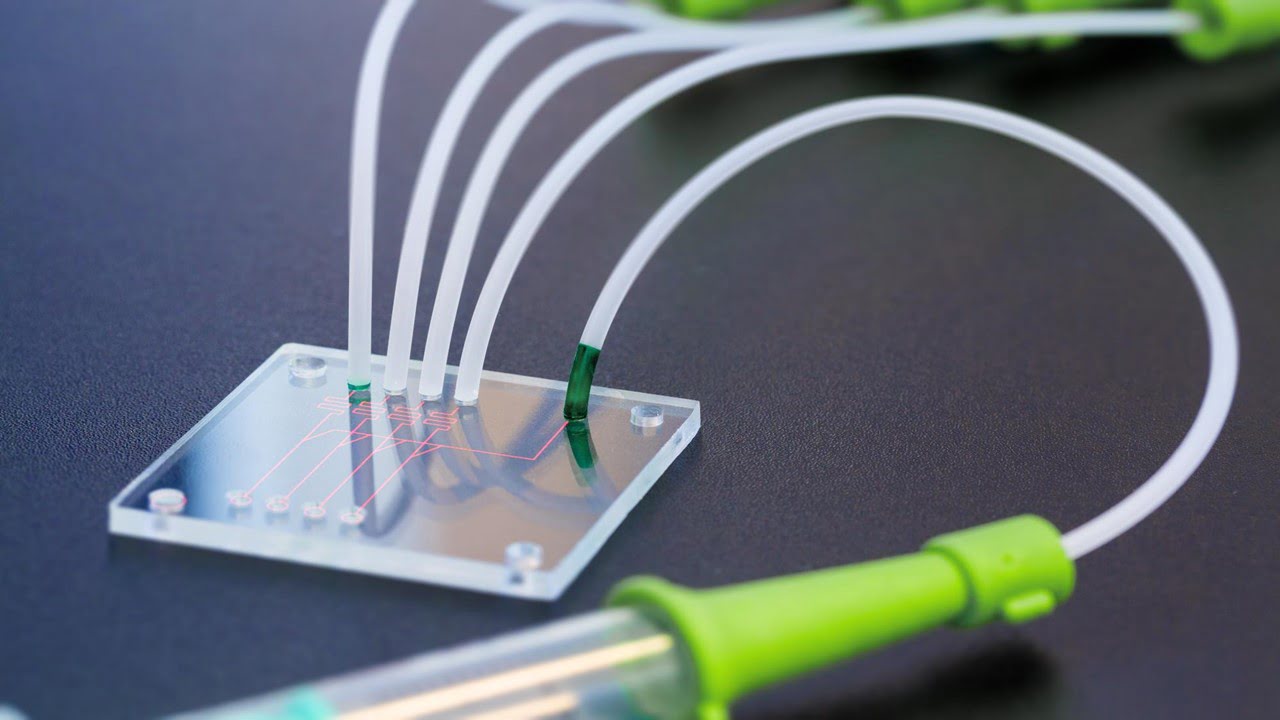

Microfluidics, manipulating fluids at micrometer scales, offers exciting possibilities in fields like biology, chemistry, and medicine. However, traditional fabrication methods for microfluidic devices are expensive and require specialized cleanroom facilities. 3D printing presents a faster and more affordable alternative, but designing microfluidic devices for 3D printing remains a complex task. This is where Flui3d comes [..]
Read More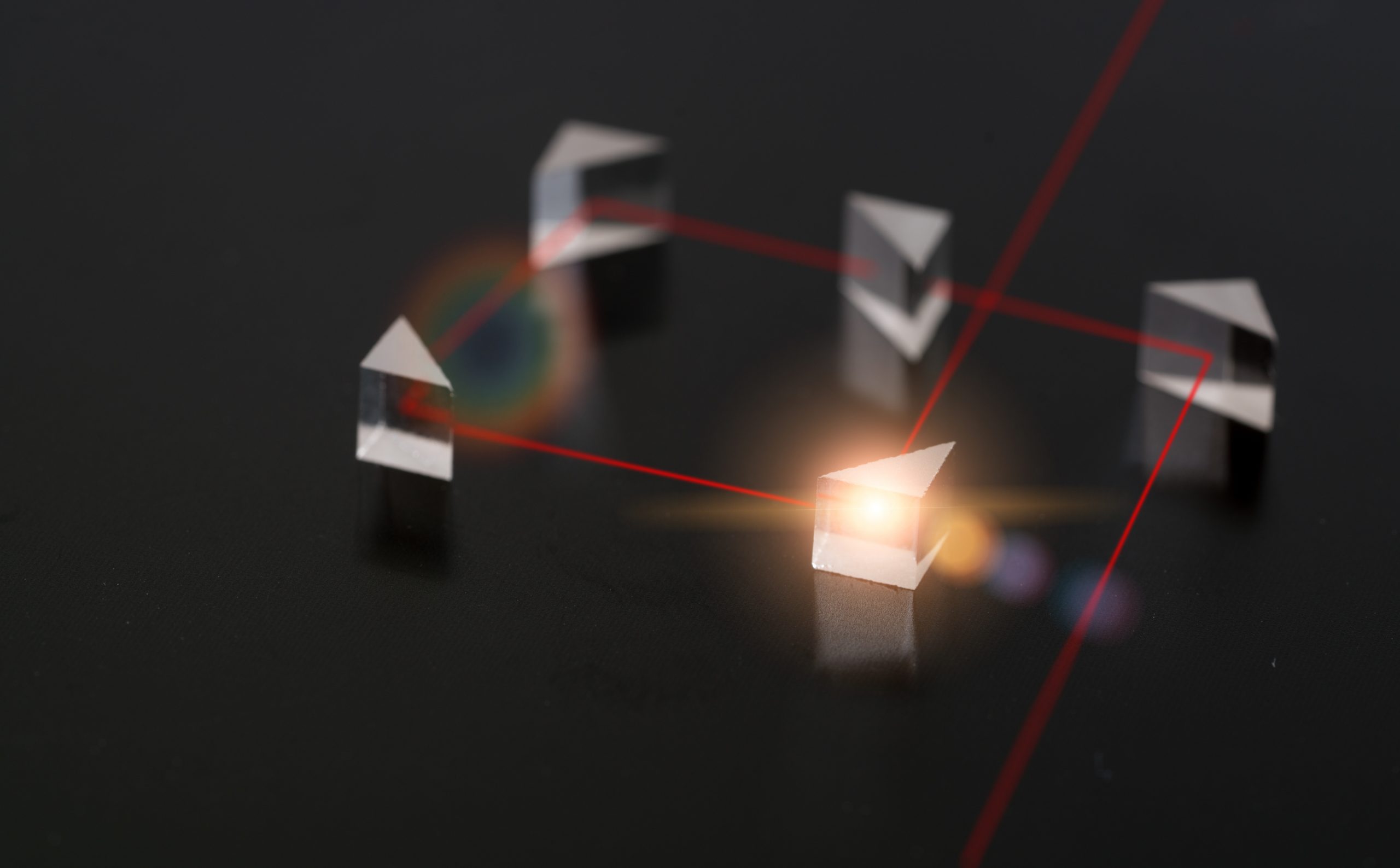
Scientists have produced a first for communications by 3D printing silica glass micro-optics on the tips of optic fibers. This technique could make smaller sensors and imaging systems, enhanced connectivity, and faster internet possible. The manufacturing of chemicals and pharmaceuticals may also benefit from the study of printing techniques. This approach solves long-standing issues with [..]
Read More
Researchers have developed a new MRI technique that could enable detailed studies of how brain cells develop and communicate. The technique involves engineering blood vessels to express a protein that makes them light-sensitive. When exposed to light, these engineered blood vessels dilate, and this dilation can be detected using MRI. This new technique offers several [..]
Read More
Researchers introduce Lithium Tantalate (LiTaO3) as a promising material for photonic integrated circuits (PICs) for volume manufacturing. PICs are miniaturized circuits that integrate various optical functions onto a single chip. They are increasingly important for various applications, including optical communications, biosensing, and quantum technologies. Lithium Niobate (LiNbO3) has traditionally been the preferred material for PICs [..]
Read More
Scientists created a novel microscopy method called FLASH-PAINT, enabling researchers to see infinite distinct molecules inside a single cell. Imaging probes, also known as reagents, enable scientists to see minute features more clearly. Currently, imaging probes made of a single strand of DNA and a fluorescent dye are used in conjunction with an antibody to [..]
Read More
Long-wavelength infrared (LWIR) imaging is crucial for applications ranging from night vision to defense. However, conventional lenses for these systems are bulky, expensive (often made from germanium), and limit device design. Enter meta-optics: ultra-thin, lightweight alternatives based on nanostructured surfaces. While promising for size and weight reduction, meta-optics struggle with chromatic aberrations, where different wavelengths [..]
Read More
Researchers describes an autonomous quantum heat engine built using a harmonic oscillator, a system that exhibits simple harmonic motion. Imagine a mass attached to a spring – that’s a harmonic oscillator. In the document, it is referred to as the working fluid, and it’s coupled to two heat reservoirs, one hot and one cold. The [..]
Read More
In optoelectronics, there is a constant push towards creating flexible devices. One key element in these devices is thin silver films. However, there is a trade-off between achieving high transparency and maintaining good electrical conductivity when reducing the thickness of these films. Researchers have developed a new process to create ultrathin silver films with high [..]
Read More
Optical sensors are crucial for scientific and technological advancements, from detecting faint signals for medical diagnostics to gravitational waves. A longstanding challenge has been improving their sensitivity to detect weak signals amidst noise. Researchers have developed a novel method to enhance the sensitivity of conventional optical sensors using exceptional points (EPs). EPs are specific conditions [..]
Read More
Researchers have taken a cue from nature’s most dazzling creatures to develop a new material that can change color quickly. Inspired by the rapid color shifts in creatures like squid and cuttlefish, these color-changing materials use tiny, light-manipulating structures to achieve a full spectrum of brilliant colors. The Challenge Existing color-changing materials often rely on [..]
Read More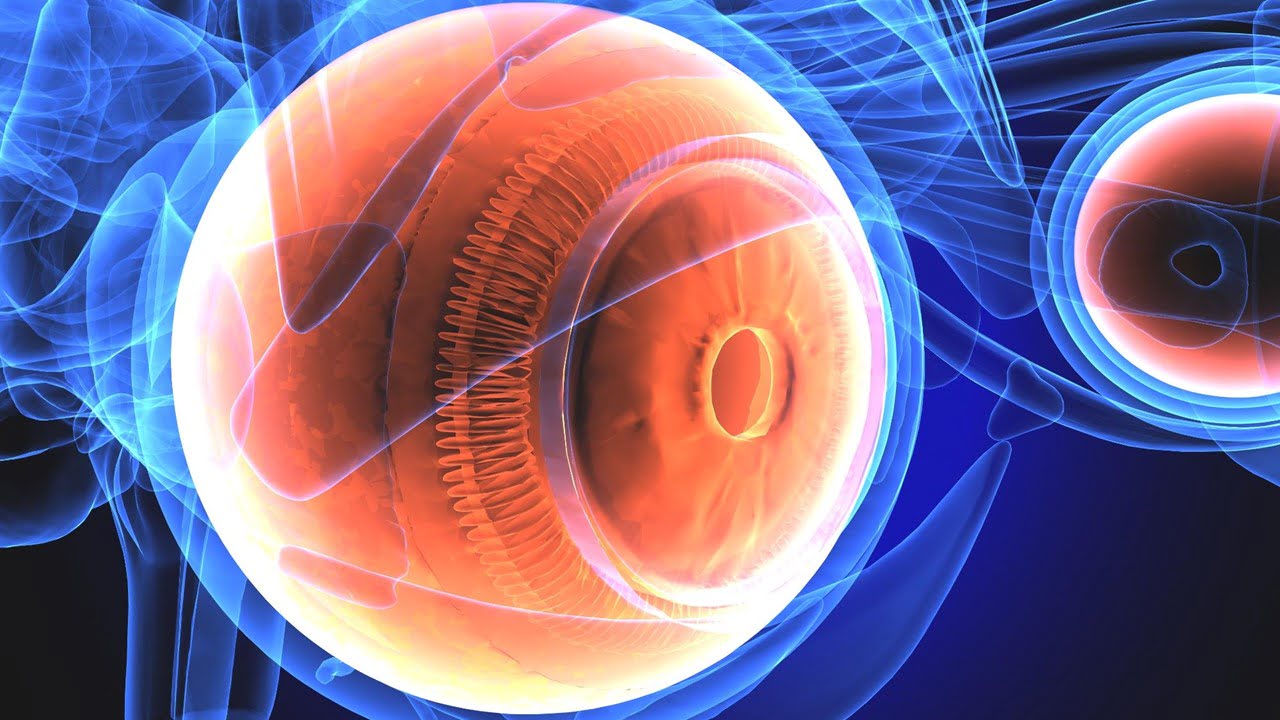
Adaptive optics optical coherence tomography (AO-OCT) has enabled in vivo cellular imaging of the human retina. This technology has excellent resolution but suffers from noise, making it difficult to see individual cells. However, because imaging noise (e.g., speckle) makes it difficult to see RPE cells from a single volume acquisition, many 3D volumes are typically [..]
Read More
A new study investigates the possibilities of a unique pancake optics system for next-generation VR and MR displays. Augmented reality (AR), virtual reality (VR), and mixed reality (MR) have broadened our perceptual frontiers, allowing for more complex human-digital interactions than typical flat-panel displays. This has resulted in applications for smart education, healthcare, navigation, gaming, entertainment, [..]
Read More
Fingerprint scanners have become ubiquitous tools for personal identification. But how exactly do these devices translate your fingertip’s unique ridges and valleys into a recognizable signal? This article delves into the fascinating world of fingerprint scanner technology, exploring the interplay of light, electricity, and even sound waves to achieve secure user authentication. Fingerprint scanners employ [..]
Read More
New bioluminescent imaging technology has produced comprehensive images of oxygen movement in mice’s brains, allowing researchers to investigate forms of hypoxia in the brain, such as oxygen deprivation during stroke or heart attack. The approach uses luminous proteins, chemical cousins of bioluminescent proteins found in fireflies. These proteins are produced by a virus in the [..]
Read More
Researchers have made a significant breakthrough in generating high-quality microwave signals using a tiny photonic chip. This new device can produce low-noise signals using a single laser, overcoming a major hurdle in previous methods requiring multiple lasers and bulky setups. The photonic chip is miniscule, paving the way for its integration into future communication devices. [..]
Read More
Metal halide perovskites are gaining popularity due to their superior optoelectronic features, which include a high photoluminescence quantum yield (QY), absorption coefficient, tunable band gaps, long carrier diffusion lengths, and defect tolerance. Direct laser writing (DLW) is an efficient, contactless, mask-free, and depth-resolved micro-patterning technology that involves linking a laser beam to a high-resolution microscope. [..]
Read More
Crafting exceptionally thin silver films presents a significant challenge for flexible optoelectronic devices. Conventional techniques often yield films that are both discontinuous and suffer from poor conductivity. This roadblock hinders the development of next-generation flexible displays and other optoelectronic applications. Researchers have recently proposed a groundbreaking approach to generating ultrathin silver films with exceptional continuity [..]
Read More
Researchers have made a significant breakthrough in manipulating light signals using liquid crystals. This new technique integrates femtosecond laser writing with liquid crystals embedded in waveguides. This enables electro-optical control of light polarization, paving the way for novel photonic devices. Previously, femtosecond lasers were used for writing waveguides, but they could not modulate the light [..]
Read More
In the realm of photonics, miniaturized, high-performance devices are crucial for various applications. With their unique optical and electronic properties, inorganic perovskites have emerged as a promising material for such devices. Researchers have developed an inorganic perovskite-based integrated photonic devices. The researchers detail a method for fabricating these devices using focused ion beam etching and [..]
Read More
Machine vision is crucial in various industrial tasks, from quality control to robot guidance. However, traditional lighting systems often struggle to keep pace with the demands of high-speed imaging, leading to blurred images, inaccurate measurements, and safety concerns. Hidden strobe hardware offers a game-changing solution by utilizing rapid pulses of light invisible to the human [..]
Read More