
Scientists and engineers working in the fields of optical and photonics have been captivated by the rapidly developing, interdisciplinary field of metasurfaces. They view these advanced materials as a path to a new breed of ultra-compact flat optics, such as camera lenses. But most of the metasurfaces that have been demonstrated up to this point [..]
Read More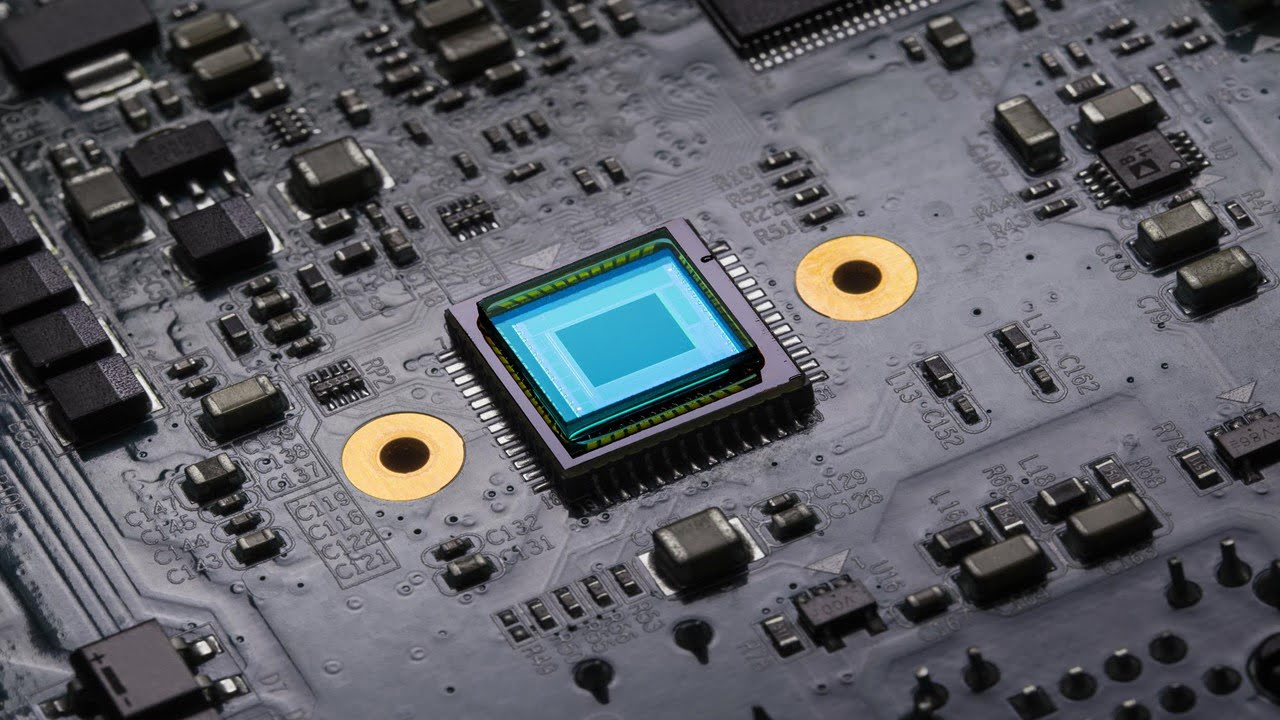
Scientists have created a novel optomechanical integrated device with a resolution of 45 femtometers in a fraction of a second. Importantly, the gadget does not require a tunable laser because of its ultrawide optical bandwidth of 80 nm. The indium phosphide (InP) membrane-on-silicon (IMOS) technology, perfect for including passive components like detectors or lasers, is [..]
Read More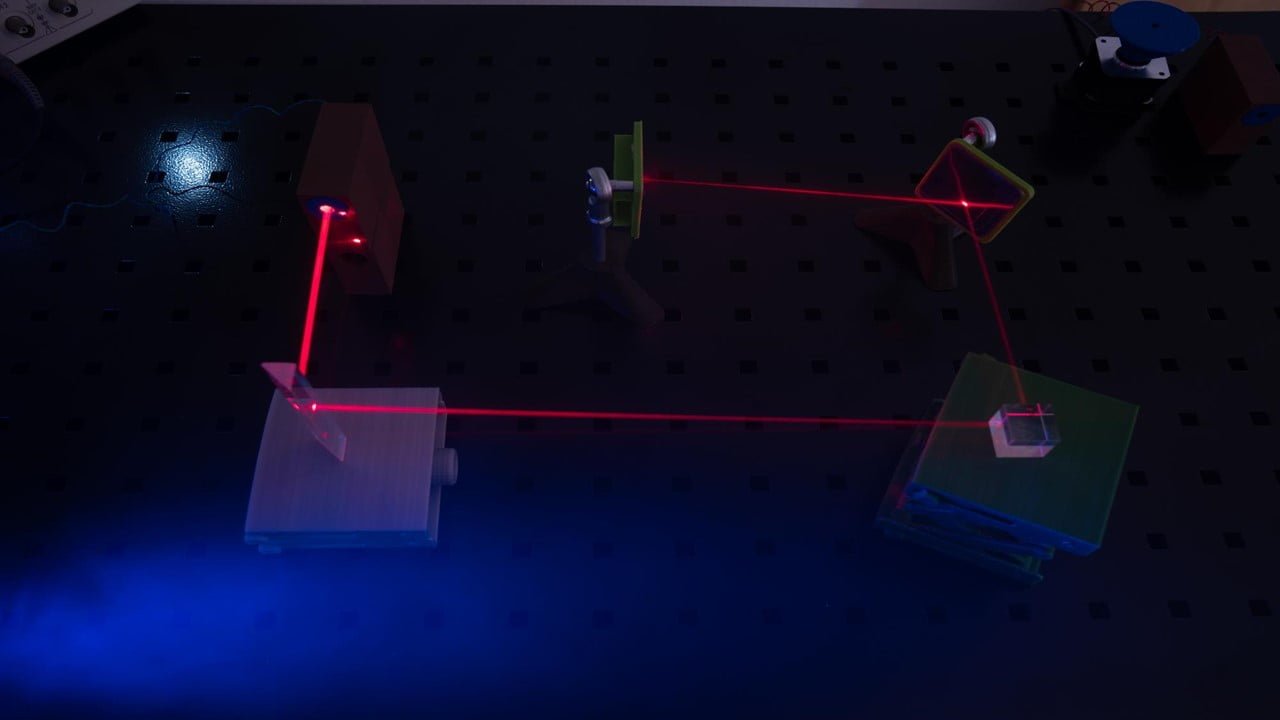
High-speed communication channels for supercomputers and data centers could significantly benefit from understanding the physics of lasers at the nanoscale and how they interact with semiconductors, but only if researchers can figure out how and why they work to replicate their findings. The experimental findings of the experts demonstrate that lasers can be made in [..]
Read More
By increasing their brightness by more than 150 times, silver nanocubes can make it simpler to read diagnostic tests that depend on fluorescence. The method could enable such tests to become much more affordable and commonplace when combined with an emerging point-of-care diagnostic platform that has already demonstrated its ability to identify minute amounts of [..]
Read More
Researchers have created a novel technique for producing color 3D images that operate across the full visible spectral range. Metasurfaces are 2D-engineered materials that are usually made of subwavelength elements. Adjusting the light’s polarization, phase, and amplitude offers excellent control over shaping the optical wavefront. Unlike conventional metasurface-based holography methods, the developed method does not [..]
Read More
A brand-new fluorescence microscopy method has been created by researchers to significantly improve the resolution that can be obtained when imaging intracellular structures. The method uses the distortions a specimen produces to identify specific molecules and deduce the location of intracellular structures. The method may be especially helpful in researching brain conditions like Alzheimer’s. Developing [..]
Read More
A three-dimensional item is created using the additive manufacturing process, which involves adding new layers of construction material over the top of the previously deposited ones. Commercially available 3D printers and 3D printing materials, such as transparent media with excellent optical quality and 3D printed optics, have recently developed rapidly. Numerous areas of science and [..]
Read More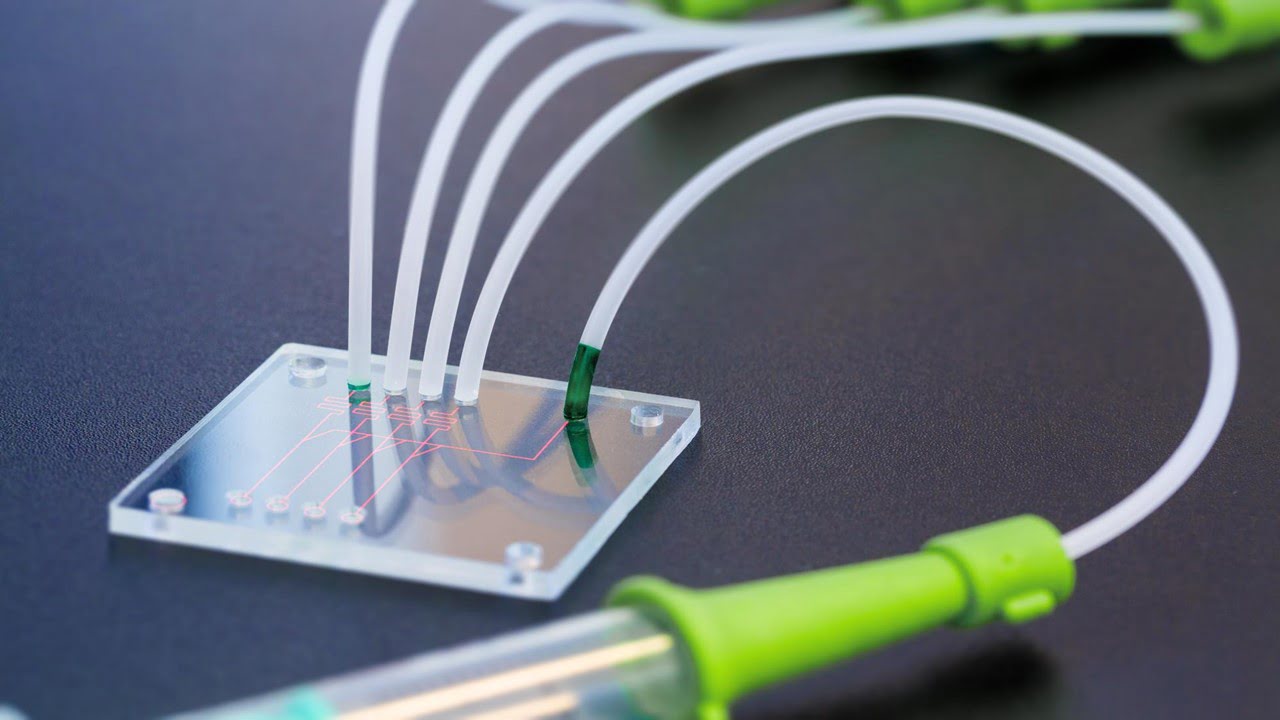
The construction of lab on a chip platforms for experiments and drug development has been made possible by the tiny field of microfluidics, which has vastly expanded boundaries in chemistry and pharmaceuticals. The challenges of quickly and effectively mixing various fluids—in channels much thinner than a human hair—become formidable as scientists examine processes at ever-smaller [..]
Read More
The processing speed of microprocessors has been stagnant for the past 20 years. More recently, Moore’s law has started to break down as nanofabrication technology gets closer to its inevitable physical limit. In this post-Moore’s law age, significant efforts from numerous research areas have been made to create fast and power-efficient computing systems. Integrated photonics [..]
Read More
As a result of the coronavirus pandemic, biometrics companies are modifying and upgrading their biometric identity systems with facial recognition software and temperature sensors to offer new capabilities that comply with the regulations. They are introducing novel access control biometric identification systems. When individuals enter buildings, they are screened by thermal imaging cameras added to [..]
Read More
The ability to monitor the progression of retinal vascular diseases like diabetic retinopathy in small animal models is often complicated by their failure to develop the end-stage complications which characterize the human phenotypes in disease. Interestingly, as micro-vascular dysfunction typically precedes the onset of retinal vascular and even some neurodegenerative diseases, the ability to visualize [..]
Read More
A photonic device that emits light only in one way has been created. By meticulously modifying a set of etched silica bars’ shapes, they could make their device by changing a curious effect that had been predicted 90 years earlier. Numerous optoelectronic uses for the light source are possible. Light will gladly travel in both [..]
Read More
Dentists must know the precise location of the mandibular canal, which runs along both sides of the lower jaw and houses the alveolar nerve, to plan a dental implant procedure and determine the implant size and position. Medical professionals use computer tomography (CT) models and X-rays to identify and diagnose the lower jaw’s anatomically complex [..]
Read More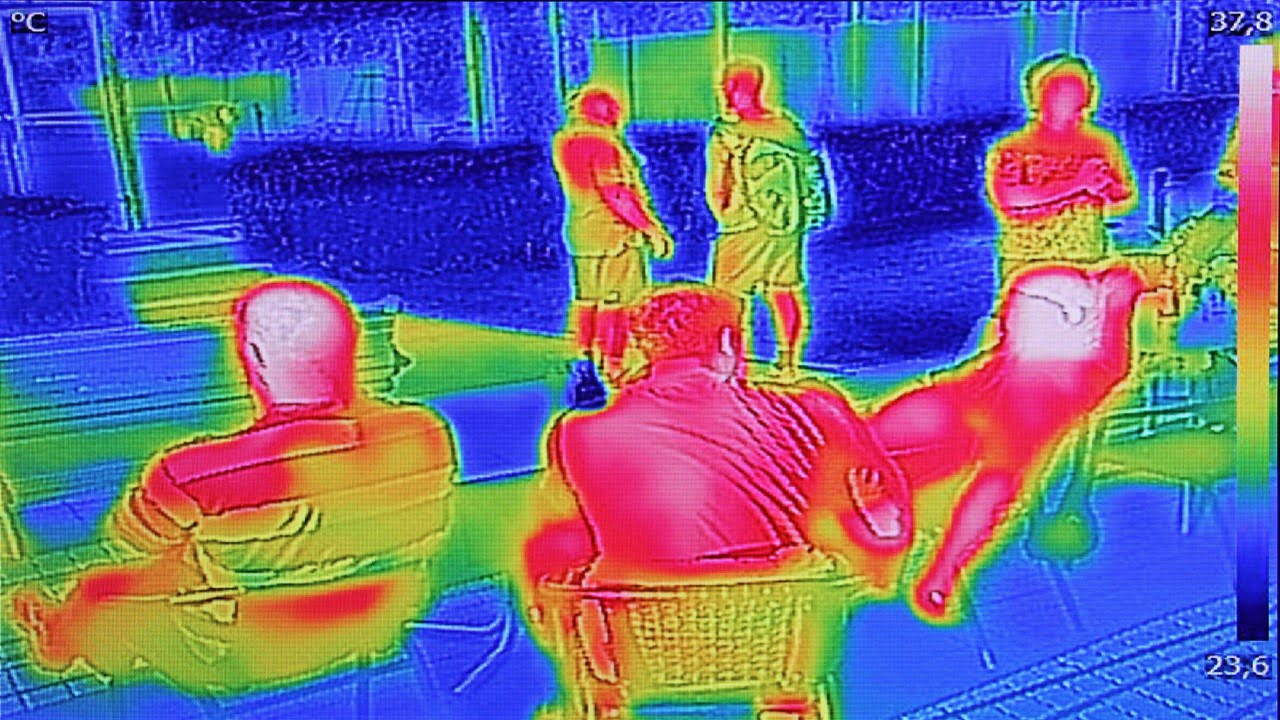
Will automated infection monitoring become a global standard in airports? Even in the busiest terminals, real-time thermal tracking along with immediately accessible biometric data that could be extracted and analyzed (using computer vision technology) would make it easier for airport staff to spot people who might be unwell. The individual’s potential sites of contact could [..]
Read More
Synchrotron x-ray fluorescence microscopy can be used to measure the concentrations of different elements in cross-sections of the ear at extremely high resolution. This method could address many open questions in hearing medical diagnosis research. X-ray fluorescence microscopy uses synchrotron radiation to evoke emissions from many biologically relevant elements in the tissue. The intensity and [..]
Read More
Leading research teams in nanophotonics are creating optical transistors, which will be crucial parts of upcoming optical computers. Instead of using electrons to process information, these photonic devices use light to produce less heat and operate more quickly. For microelectronics engineers, the poor photon-to-photon interaction poses a significant challenge. Scientists developed a planar system to [..]
Read More
A laser-based interferometer sensor that can quickly identify coronavirus from saliva or nasal swab at the site of infection is being developed by researchers. The researchers are working on a brand-new optical biosensor demonstrator that can quickly and painlessly identify COVID-19 in humans as soon as it enters the body. The sensor is far more [..]
Read More
For use with adaptive optical (AO) systems combined with big ground-based astronomical telescopes, artificial “guide stars” are created in the mesosphere at an altitude of about 90 km using lasers that emit light at the sodium line, which is a doublet at a wavelength of about 589 nm. Astronomers can use AO to rectify atmospheric [..]
Read More
Computed tomography (CT), which can find lung tumors, is regularly used to screen people at a high risk of lung cancer, such as heavy smokers. However, because it also detects benign nodules in the lungs, this test has a very high incidence of false positives. Researchers have created a urine test to diagnose lung cancer [..]
Read More
An advanced X-ray imaging technique called propagation-based phase-contrast CT (PB-CT) can produce diagnostic breast images of better quality than absorption-based CT (AB-CT) at glandular radiation doses similar to or lower than traditional mammography and digital breast tomosynthesis. (DBT). The technology is presently only suitable for synchrotron light sources, but as compact light sources develop, the [..]
Read More