
Researchers used a sensitive scattering-type scanning near-field optical microscope (s-SNOM) to directly measure the optical fields of AGP waves propagating in a nanometer-thin waveguide to demonstrate direct near-field optical imaging of acoustic graphene plasmon (AGP) fields. Scientists could observe the thousandfold compression of mid-infrared light using this method. The strategy paves the way for potentially [..]
Read More
An AI tool opens up new possibilities for analyzing microscope images. According to a study, the tool, which has already received international recognition, has the potential to fundamentally change microscopy and pave the way for discoveries and applications in both research and industry. Deep learning has taken the world by storm, having a massive impact [..]
Read More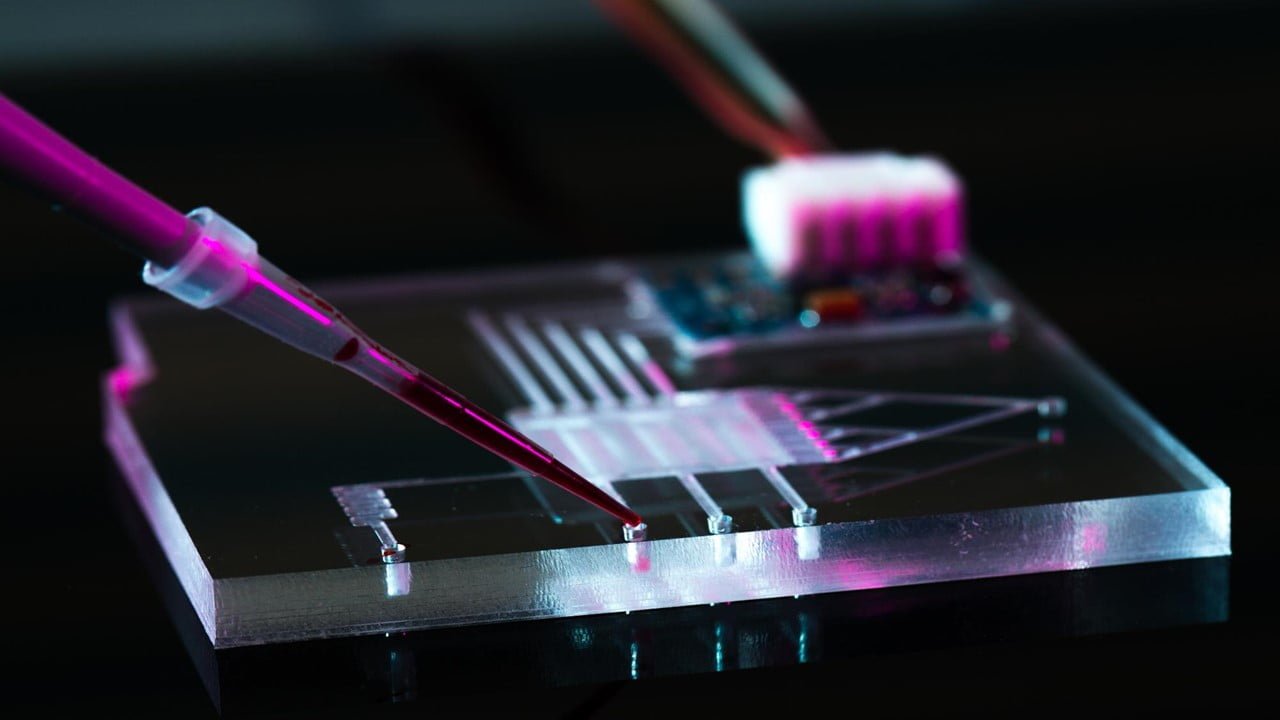
The implementation of the idea of liquid computers would be revolutionary for microfluidics, not because microfluidics seeks computational capabilities but because it would enable the encoding of a variety of algorithms (laboratory procedures) into the structure of the device. Researchers show the successful implementation of advanced sequential logic in droplet microfluidics, whose principles rely on [..]
Read More
Point-scanning imaging systems are among the most widely used tools for high-resolution cellular and tissue imaging, benefiting from arbitrarily defined pixel sizes. The resolution, speed, sample preservation, and signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) of these systems are difficult to optimize simultaneously. Researchers show these limitations can be mitigated via the use of deep learning-based supersampling of undersampled [..]
Read More
The eyes of mantis shrimp inspired the development of a new type of organic photodetector small enough to fit on a smartphone but capable of hyperspectral and polarimetric imaging. The eyes of mantis shrimp, exceptionally good at capturing subtle gradations of color, inspired the designers of the new organic photodetector. As a result, the researchers [..]
Read More
A group of scientists has developed a method that significantly improves the already ultrafast time resolution of X-ray free-electron lasers (XFELs). It has the potential to lead to breakthroughs in the design of new materials and more efficient chemical processes. An X-ray free-electron laser device is a powerful combination of particle accelerator and laser technology [..]
Read More
Future head-mounted displays may automatically remove dust obstructing the wearer’s view using a self cleaning glass. If you wear glasses, you also have a cloth you use to repeatedly clean them, and you may still need to wipe over “Apple Glass.” However, a newly-revealed patent application shows that Apple is looking to keep the inside [..]
Read More
A particle or “walker” moves stochastically around a discrete space in a classical random walk. Quantum walks are the quantum analog, where the walker is also governed by quantum effects such as superposition, quantum interference, and entanglement. Quantum walks have attracted broad interest because of a growing range of applications in quantum information processing and [..]
Read MoreSoft robotics, wearable technologies, and biomedical applications all require stretchable electronics. However, the current methods of production have limited their potential. A group of researchers has created a material and fabrication process that can quickly make these devices stretchier, more durable, and ready for mass production. One of the most difficult challenges for stretchable electronics [..]
Read More
For centuries, polished glass has been at the heart of imaging systems. Lenses’ precise curvature allows them to focus light and produce sharp images, whether the object in view is a single cell, a book page, or a distant galaxy. To see clearly at all of these scales, the zoom lens must be physically moved [..]
Read More
Nonlinear optical properties, such as bulk photovoltaic effects, possess great potential in energy harvesting, photodetection, rectification, etc. To enable efficient light–current conversion, materials with strong photo-responsivity are highly desirable. Researchers predict that monolayer Janus transition metal dichalcogenides (JTMDs) in the 1T′ phase possess colossal nonlinear photoconductivity owing to their topological band mixing, strong inversion symmetry [..]
Read More
Calcification of the coronary arteries is a significant and independent predictor of adverse cardiovascular events such as heart attacks. Nonetheless, despite this knowledge and the fact that it can be assessed using any chest CT scan, quantification of coronary artery calcium (CAC) is not automatically integrated into the patient pathway because it requires radiological expertise, [..]
Read More
Apple has filed a patent application for their future VR head-mounted display, specifically a system allowing users to customize the headset’s fit on their face to be comfortable and snug. A head-mounted display is worn on the user’s head and engages the user’s face. However, by engaging the face, the head-mounted display may limit facial [..]
Read More
Researchers created the first silicon chip compact 3D LiDAR imaging system capable of matching and exceeding the performance and accuracy of the most advanced mechanical systems currently in use. 3D LiDAR can provide accurate imaging and mapping for various applications; it serves as the “eyes” for self-driving cars and is used in facial recognition software [..]
Read More
Scientists could image SARS-CoV-2 using a helium ion microscope for the first time. In contrast to more traditional electron microscopy, helium ion microscopy does not require a thin metal coating on the samples. It allows a more detailed examination of interactions between coronaviruses and their host cells. The study demonstrates that the helium ion microscope [..]
Read More
A group of scientists is working on an advanced X-ray imaging method that will aid in the detection and diagnosis of breast cancer. The noninvasive technology employs dyes known as contrast agents specifically designed to recognize and bind to breast cancer cells at the molecular level. When imaged with a special, cutting-edge computed tomography (CT) [..]
Read More
Laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy (LIBS) is a possible rapid, non-contact method for detecting and quantitatively analyzing various isotopes, including hydrogen critical to various disciplines (e.g., nuclear energy, hydrogen storage). With no sample preparation requirement, a relatively simple experimental set-up, and the ability to detect all elements in the periodic table in a matter of seconds, the [..]
Read More
Polarization, or the direction in which light vibrates, is imperceptible to the human eye but contains a wealth of information about the objects with which it interacts. Controlling and characterizing polarization is critical for various applications ranging from biomedical imaging to optical communications. Researchers have created metasurface optics, which allow them to remotely control the [..]
Read More
Researchers discovered that trap states govern the performance of organic photodetectors, limiting their detectability. Organic photodetectors (OPDs) have enormous potential for low-cost imaging, health monitoring, and near-infrared sensing applications. However, before these applications can be commercialized, the performance of these devices must be improved. Recent research on organic photodetectors based on donor-acceptor systems has yielded [..]
Read More
One of the most common types of oral cancer is oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC), for which the five-year survival rate has stubbornly remained at 50% for many years, partly due to late-stage diagnosis. Better identifying both OSCC and the non-malignant lesions that can precede it would help to reduce the disease’s impact, and optical [..]
Read More