Due to their lower toxicity than cadmium-based semiconductor quantum dots, graphene quantum dots (GQDs) are attractive luminous materials for numerous light-emitting, biological, and energy applications. The luminous properties of GQDs drive their practical applications and use. As a result, controlling and tailoring the emission properties of these materials to suit the specified optoelectronic applications is [..]
Read More
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) often makes patients experience anxiety and sometimes distress before and during scanning. Researchers have developed an MRI-compatible virtual reality (VR) system to create a different experience. The strong sense of immersion with VR could create sensory experiences designed to avoid the perception of being enclosed and provide new modes of diversion [..]
Read More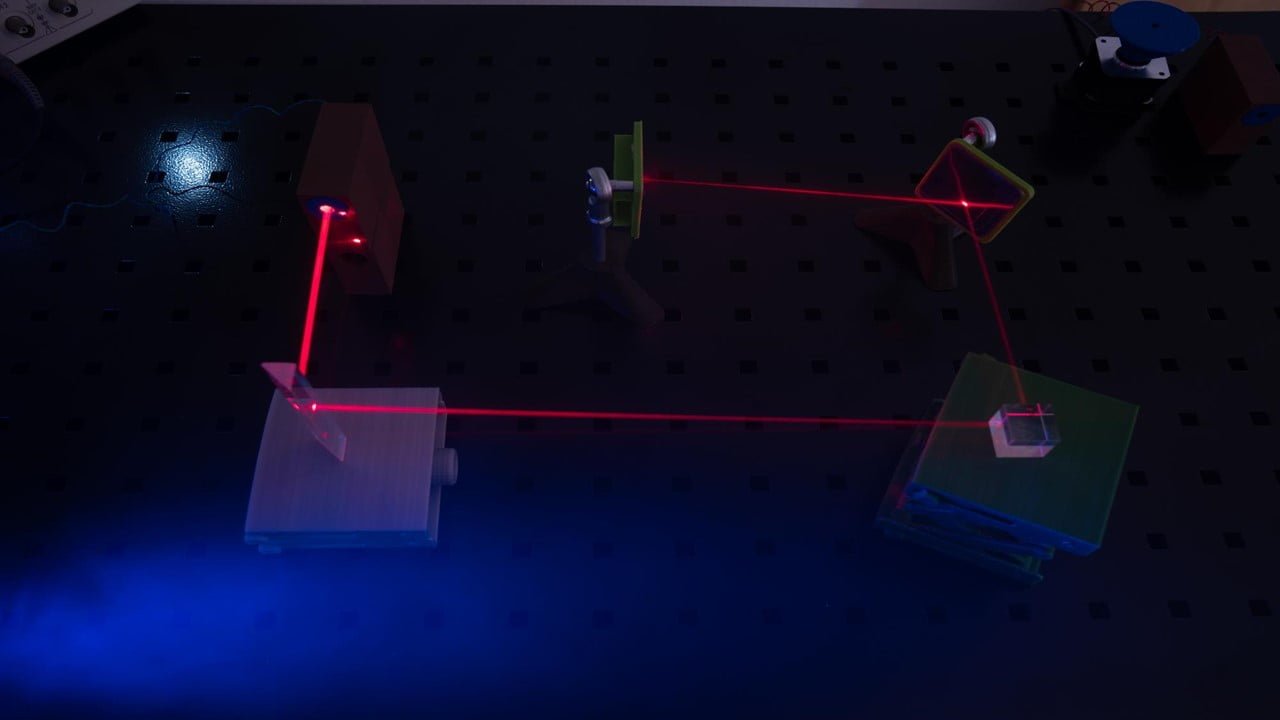
Scientists have developed an innovative optical system to precisely measure and control high-power laser beams’ position and pointing angle with unprecedented accuracy – without interrupting or disturbing the beams. Even in the most regulated lab setting, laser beams wander around on a microscopic scale due to vibrations and variability. The difference between excellent science and [..]
Read More
Researchers have created robotic diagnostic imaging equipment that automatically detects and scans a patient’s eyes for indicators of various eye illnesses. The new device, which combines an imaging scanner and a robotic arm, can track and image a patient’s eyes in under a minute and provide images as clear as those produced by standard scanners [..]
Read More
Lower temperatures cause reduced mobility of tiny components in almost all materials. When there is a lack of heat energy, atoms are less likely to change their location or magnetic moments’ direction: they freeze. Scientists have seen the opposite behavior in a nickel oxide material related to high-temperature superconductors for the first time. When this [..]
Read More
Cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT) is becoming increasingly popular for maxillofacial imaging. It can supply high-resolution three-dimensional (3D) images without distortion and superimposition of bone and other dental structures. Researchers tested a novel AI system based on deep learning methods to determine its real-time performance of CBCT imaging diagnosis of anatomical landmarks, pathologies, clinical effectiveness, and [..]
Read More
The holographic display may rectify many refractive defects, produce high-resolution images, and enable focus cues by modifying the complicated wavefront of coherent light with a spatial light modulator. It could be advantageous to have a hologram rendering using rapid and accurate calculations in any situation. Researchers developed a vision-correcting holographic display with hologram acquisition based [..]
Read More
A pair of studies show that a quasiparticle called a plasmon polariton can be pulled with and against an electron flow, which could lead to more efficient light manipulation at the nanoscale. When immersed in an electrical current flowing through a sheet of graphene, quasiparticles comprised of photon and electron waves — plasmon polaritons — [..]
Read More
Ultrathin metasurfaces generate multiform beams (electromagnetic, multi-direction, multi-polarization, multi-frequency, and multi-beam) with promising applications in numerous optical traps, modern communication systems, and complex environment identification. However, their capacity to generate required multiform beams concurrently limits their application. Researchers developed a multifunctional surface with a polarization selection structure and integrated electric and magnetic systems to overcome [..]
Read More
The fatality rate for uveal melanoma, a rare and dangerous eye disease, has remained unchanged for the past 40 years. New treatments to preserve eyesight and avoid mortality are urgently needed because half of the melanomas spread to other body organs, resulting in death in less than a year. Researchers have discovered a small chemical [..]
Read More
Photonics integration is gaining pace in semiconductors, particularly in heterogeneous multi-die packages, as chipmakers look for innovative solutions to overcome power constraints and deal with growing data volumes. Since the end of Dennard scaling, which occurred at the 90nm node, power has become increasingly challenging. There are more transistors per mm2, and the wires are [..]
Read More
Researchers have devised a new computational de-scattering approach termed de-scattering with excitation patterning in temporal focusing microscopy (DEEP-TFM). They employed two-photon patterned excitation with wide-field temporal focusing, but the signal was detected using a wide-field imaging detector. They created a modified temporal focusing microscope that uses a digital micromirror device to transmit arbitrary excitation patterns [..]
Read More
Scientists have developed the first room-temperature, electrically driven, topological laser, which could be useful in telecom wavelength applications. The novel device comprises a 10 by 10 grid of 30-micron-wide rings. Small oblong rings around 5 microns wide connect these rings. All these rings consist of a sandwich of layers of semiconductors, such as indium gallium [..]
Read More
The prognosis and successful treatments differ depending on the type of lung cancer. While it previously took several days to precisely determine the underlying lung tumor mutation, a research team has been able to perform this determination in just one step reliably. They used a combination of quantum cascade laser-based infrared microscopy and machine learning. [..]
Read More
Infrared imaging applications are growing from food quality control and remote sensing to night vision devices and LiDAR. IR cameras convert infrared light to electrons and project the resultant image on display. However, such cameras are bulky, disrupt normal vision, and require low temperatures. Alternatively, a nonlinear optical process – nonlinear sum-frequency generation (SFG) – [..]
Read More
Cancer immunotherapy has brought a paradigm shift in cancer treatment. It uses the immune system’s strength to treat cancers. However, next-generation cancer immunotherapies have yet to reach their full potential. A limitation is the poor throughput of functional screens that can only evaluate a few thousand antibodies. Droplet microfluidic technology enables exceptional throughput in cell [..]
Read More
New imaging technology may lead to the early detection of neurological illnesses such as Alzheimer’s, allowing doctors to diagnose and treat patients more swiftly. The super-resolution imaging technique combines position emission tomography (PET) with an external motion-tracking device to provide detailed brain images. The patient’s undesired movements frequently hamper the quality of brain PET images [..]
Read More
All imaging systems consist of two main components: lenses and the spaces between them. The distances between lenses are just as critical to image formation as the lenses themselves. They can easily be greater than the summed thicknesses of the lenses. Now researchers have developed an optic called spaceplate to address this dominant contribution to [..]
Read More
High-performance mirrors are critical for constructing optical resonators in various applications in optics and photonics. Stable resonators narrow the linewidth of continuous-wave lasers, creating optical references for frequency comb stabilization and precision molecular spectroscopy. High-performance, low-loss mirrors at mid-infrared wavelengths can help researchers probe new phenomena with increased precision in chemical sensing, discrete imaging, ultracold [..]
Read More
A new human brain imaging technology employs laser light and ultrasonic sound waves. Improvements to photoacoustic computerized tomography (PACT) technology are part of the advancement. It is so precise and sensitive that the researchers could identify even minute variations in the amount of blood moving through tiny blood arteries and the oxygenation status of that [..]
Read More