
Increasing the acquisition speed of three-dimensional volumetric imaging is essential – particularly in biological imaging – to unveil specimens’ structural dynamics and functionalities in detail. In conventional laser scanning fluorescence microscopy, volumetric images are constructed from optical sectioning images sequentially acquired by changing the observation plane, limiting the acquisition speed. Researchers have developed a novel [..]
Read More
A research team developed a technique that uses condensation to noninvasively refill liquid marbles with water. The method could improve the viability of applications such as drug delivery. It could also establish improved opportunities for the droplet-size microreactors to see use in opto- and microfluidics. Liquid marbles are droplets of solution that wrap in a [..]
Read More
Lenses play a crucial role in the quality of the images produced by a machine vision system since they determine the sharpness of the image on the camera sensor. As lenses transmit light the first consideration is the light wavelengths used, as this has a major influence on both chromatic aberration and light transmission. This [..]
Read More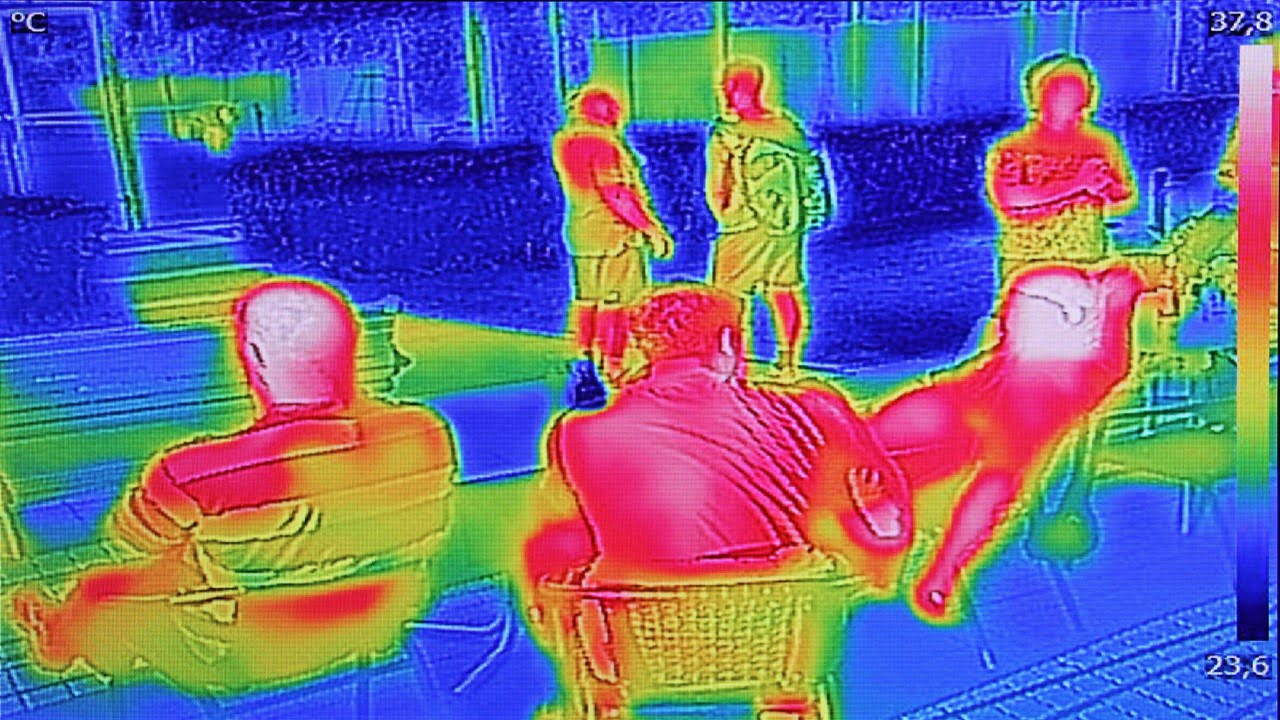
Researchers have invented a low-cost continuous fever screening system – SIFTER – based on an RGB-thermal camera. The system can automatically take temperature readings of people walking by, going about their own business, up to three meters away – no one has to stand in front of a camera for a few seconds to take [..]
Read MoreSince the earliest scientific developments, researchers have looked to nature as an inspiration source for designing novel functional devices. The so-called bioinspiration and biomimetic designs enabled the development of multifunctional sensors. Recently, researchers developed an ultrasensitive flexible optical waveguide sensor bioinspired in orb webs. They named it bioinspired multifunctional flexible optical sensor (BioMFOS). The multifunctional [..]
Read More
The increasing demand for high-resolution and real-time recognition in radar applications has fueled the development of electronic radars with increased bandwidth, high operation frequency, and fast processing capability. However, the generation and processing of wideband radar signals place an additional hardware burden on complex and fast electronics, limiting its capability for high spatial resolution applications. [..]
Read More
Spatial neglect damages the neural networks that support spatial attention and related cognitive and motor functions. People’s spatial orientation is altered, which can cause issues with balance, navigation, memory, reading, and other cognitive processes. While progress has been made in detecting post-stroke spatial neglect, treatment strategies have lagged. Researchers have developed a treatment approach based [..]
Read More
Some optical sensing chip designs contain nearly as small nanostructures as the biological and chemical molecules they’re searching for. These nanostructures improve the sensor’s ability to detect molecules. But their diminutive dimensions make it difficult to guide the molecules to the correct area of the sensor. Researchers have created a new sensor that aims at [..]
Read More
Researchers have developed a first-of-its-kind terahertz laser that is compact, operates at room temperature, and can produce 120 individual frequencies spanning the 0.25 – 1.3 THz, far more range than previous terahertz sources. The laser is helpful in various applications, such as skin and breast cancer imaging, drug detection, airport security, and ultrahigh-capacity optical wireless [..]
Read More
Deep neural networks are increasingly used for computer-aided diagnosis, but erroneous diagnoses can be extremely costly for patients. Researchers have developed a learning to defer with uncertainty (LDU) algorithm, which considers the diagnostic network’s predictive uncertainty when learning which patients to diagnose automatically and which patients to defer to human experts. The algorithm minimizes patients’ [..]
Read More
The effects of mRNA COVID-19 vaccines on human lung carcinoma cells have been studied by researchers. Scientists could investigate cellular components using Raman imaging without opening the cell. Cytochromes can be classified based on the lowest electronic energy absorption band in their reduced state, allowing them to be distinguished from one another. Laser excitation at [..]
Read More
A new imaging technique (holographic camera) could one day allow doctors to peer into human tissue and behind bones, mechanics to inspect moving machinery like airplane turbines for tiny flaws, and automated vehicles to see through dense fog or around blind corners. A new study demonstrates how the process, known as synthetic wavelength holography, can [..]
Read More
It is critical to measure and influence the direction of oscillation of a light wave in quantum communication or optical computing. Polarization control of a continuous laser wave is possible for the first time (via a special glass fiber with mirrors attached at both ends). Scientists can now control the polarization of a continuous light [..]
Read More
Optical metamaterials will be in our pockets, kitchens, cars, and offices in the next three to five years. Experts in the field predict this. Because of increased technological maturity and lower production costs, doors to some profitable new markets for materials are opening. Optical metamaterials interact with photons using chemical compositions or surface properties smaller [..]
Read More
The Dark Energy Spectroscopic Instrument (DESI) has capped off the first seven months of its survey run by smashing through all previous records for three-dimensional galaxy surveys, creating the most extensive and most detailed map of the universe ever. Yet the Dark Energy Spectroscopic Instrument is only about 10% of the way through its five-year [..]
Read More
Over the last two decades, photonic quantum technologies have reached several significant milestones. However, scalability remains a major challenge when translating lab results into everyday applications. Applications frequently necessitate using over 1,000 optical components, each of which must be individually optimized. On the other hand, photonic quantum technologies can benefit from parallel advances in classical [..]
Read More
The wealth of properties in functional materials at the nanoscale has piqued the interest of many researchers in recent decades, fueling the development of ever more precise and inventive characterization techniques. Scanning probe microscopy-based techniques, for example, have been used in conjunction with advanced optical methods to probe the structure and properties of nanoscale domain [..]
Read More
Researchers investigated the effect of UV irradiation on the nonlinear optical response (NLO) of graphene oxide (GO), fluorographene (GF), hydrogenated fluorographene (GFH), and graphene (G) dispersions. In situ UV photoreduction enabled extensive modification of the degree of functionalization (i.e., oxidation, fluorination, and hydrogenation), effectively tuning the corresponding sp2/sp3 hybridization ratios. The nonlinear optical properties of [..]
Read More
At morphologic MRI, the most easily detectable manifestation of multiple sclerosis is focal white matter lesions (WML) of demyelination. They, however, only represent visible tissue damage. As a result, they cannot fully explain the topographic origin and severity of many clinical symptoms of multiple sclerosis, especially in the disease’s progressive phase. Advanced imaging techniques have [..]
Read More
Researchers have set new efficiency records in a promising class of photovoltaic materials. These transition metal dichalcogenides, or TMDs, absorb extremely high levels of sunlight that strike their surface compared to other solar materials, such as silicon. It is far too heavy, bulky, and rigid for applications that require flexibility, lightness, and high power, such [..]
Read More