Light can now experience multiple dimensions thanks to a novel optical chip design. It could support flexible systems for cutting-edge communications and super-fast artificial intelligence technologies. Considering that the area around us is only three-dimensional, it is mind-boggling to think that light can evolve in up to seven dimensions on our specially designed circuits. The [..]
Read More
Researchers are developing a deep learning-based pattern recognition, i.e., PR-OCT system, that will automate image processing and provide an accurate, computer-aided diagnosis of colorectal cancer potentially in real-time. The method uses deep learning and OCT machine learning to find patterns in healthy and abnormal tissue sample images. Using OCT as a study tool, the researchers [..]
Read More
A new single molecule imaging technique that does not rely on fluorescent emitters could have many applications in nanotechnology, photonics, and photovoltaics. At room temperature, the technique detects stimulated emissions from single quantum dots. Because of its speed, it is possible to track charge-carrier populations throughout the absorption and emission cycle. In biology, single molecule [..]
Read More
Although the higher atmospheric layers (i.e., those between 30 and 120 km) are increasingly intriguing to climate researchers, only sounding rockets can directly access the regions above 40 km. Such research will soon be possible remotely thanks to a recently created LIDAR system built on a diode-pumped alexandrite laser. Scientists are creating an independent, transportable [..]
Read More
Researchers used endoscopic ultrasound (EUS)-guided needle-based confocal laser endomicroscopy (nCLE) to diagnose cysts in the pancreas with unprecedented accuracy. Patients typically do not exhibit symptoms of pancreatic cancer until it is advanced, making early diagnosis and treatment difficult. The current standard includes analyzing the cyst fluid. In 71% of cases, it accurately classifies them as [..]
Read More
Diffractive deep neural network (DDNN) is an optical machine learning framework that combines deep learning with optical diffraction and light-matter interaction to create diffractive surfaces that perform optical computation at the speed of light. A diffractive neural network is first designed in a computer using deep learning techniques, then physically fabricated using 3-D printing or [..]
Read More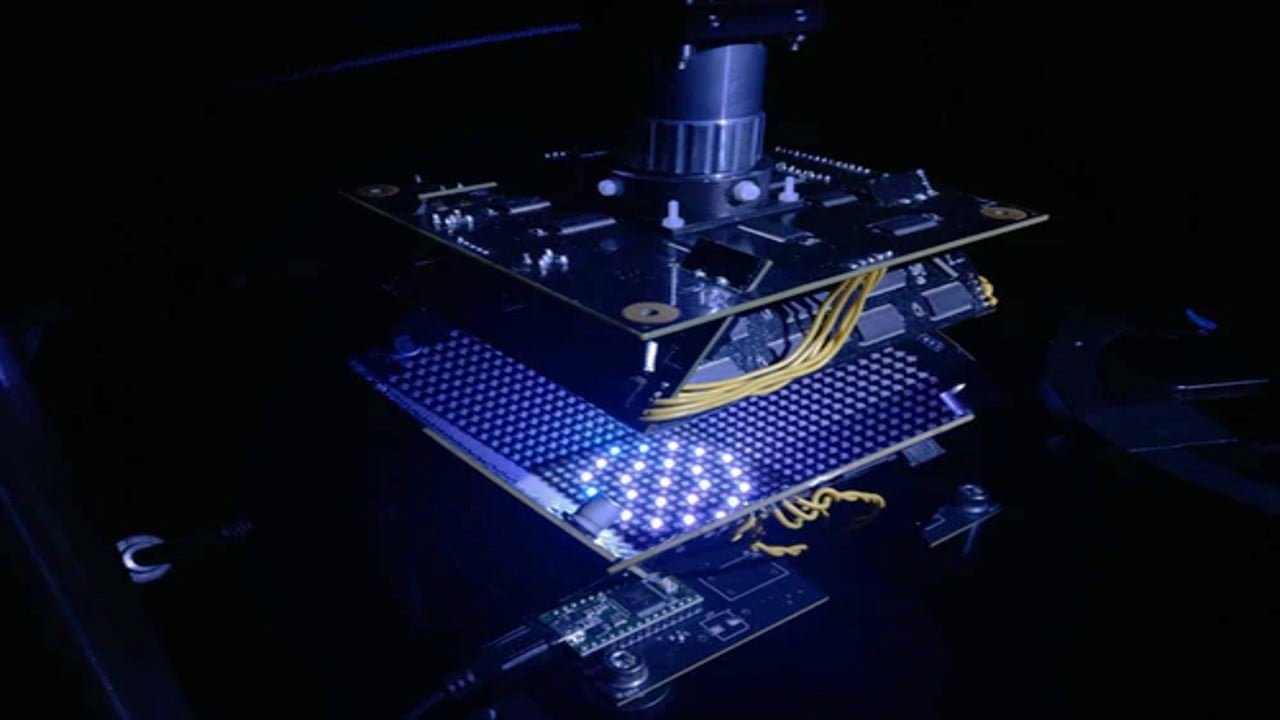
Engineers have created a microscope that adapts its lighting angles, colors, and patterns while teaching itself the best settings for a given diagnostic task. The microscope developed a lighting pattern and classification system simultaneously in the engineering team’s study, allowing it to quickly identify red blood cells infected by the malaria parasite more accurately than [..]
Read More
Better biosensor technology, as described by the study team, “may help lead to safe stem cell therapies for treating Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s diseases and other neurological disorders,” they claim. The research, which uses a graphene and gold-based platform and sophisticated imaging equipment, tracks the growth of stem cells by spotting the genetic material (RNA) necessary [..]
Read More
Scientists have created rewritable optical components for 2D light waves (surface light waves). A polariton is a particle that blurs the line between light and matter when certain materials confine a wave of light on a 2D plane. Polaritons allow light to be tightly confined to the nanoscale, potentially to a few atoms in thickness. [..]
Read More
Most leading security standards (for example, Advanced Encryption Standard, or AES, and Rivest-Shamir-Adleman, or RSA, which are used to secure online communications such as payments on shopping websites) used in secure communication methods do not make use of quantum technology. As a result, electronic transmission of PINs or passwords can be intercepted, posing a security [..]
Read More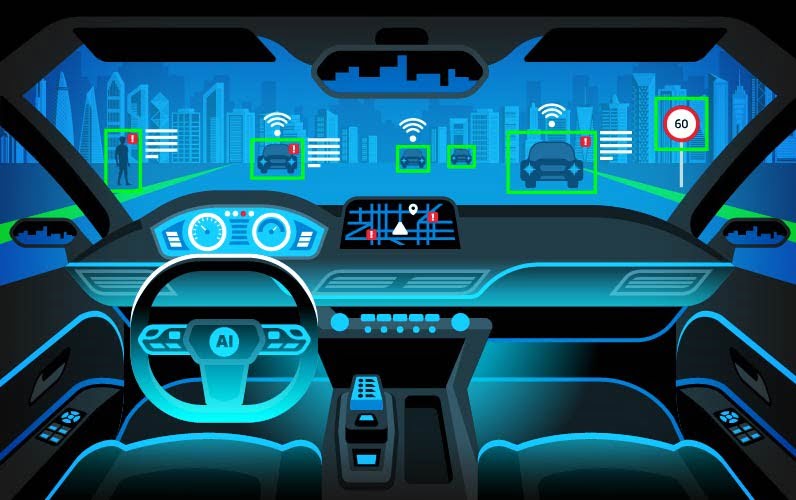
Engineers have created a computer vision system that can detect minute changes in ground shadows to determine if a moving object is around the bend to increase the safety of autonomous systems. One day, autonomous vehicles may use the system to swiftly avoid collisions with other vehicles or pedestrians approaching from behind a building’s corner [..]
Read More
The microlens array has attracted significant attention with the increasing demand for optoelectronic miniaturization. It has become an important micro-optic device widely used in compact imaging, sensing, optical communication, and other applications. Microlens arrays are typically made up of multiple micron-sized lenses with optical surface smoothness and superior uniformity, which increases the need for machining [..]
Read More
By measuring the activity of a large number of individual neurons simultaneously, a new ultrasensitive optical nanoprobe that can monitor the bioelectric activity of neurons (and other cells that generate electrical impulses) could help researchers better understand how neural circuits function at previously unexplored scales. In the future, the device could aid in developing high-bandwidth [..]
Read More
An experiment that could result in more precise sensors and clocks will test Einstein’s twin paradox using quantum particles in a superposition state. According to the twin paradox, time can move at different rates for individuals depending on how close they are to a large mass or how quickly they are moving. For instance, a [..]
Read More
A novel method for adjusting and engineering the mirror symmetry of polarization in structured optical fields has been created by a research team. The team has named these polarization states kaleidoscope-structured vector optical fields (KS-VOFs) and claims that their adjustable symmetries and geometries provide an “additional degree of freedom” that may be useful in optical [..]
Read More
Researchers have demonstrated that they can picture the simultaneous electrical activity of many neurons in the brains of mice using a fluorescent probe that illuminates when brain cells are electrically active. Neuroscientists may be able to see the activity of brain circuits using this method, which can be carried out using a basic light microscope, [..]
Read More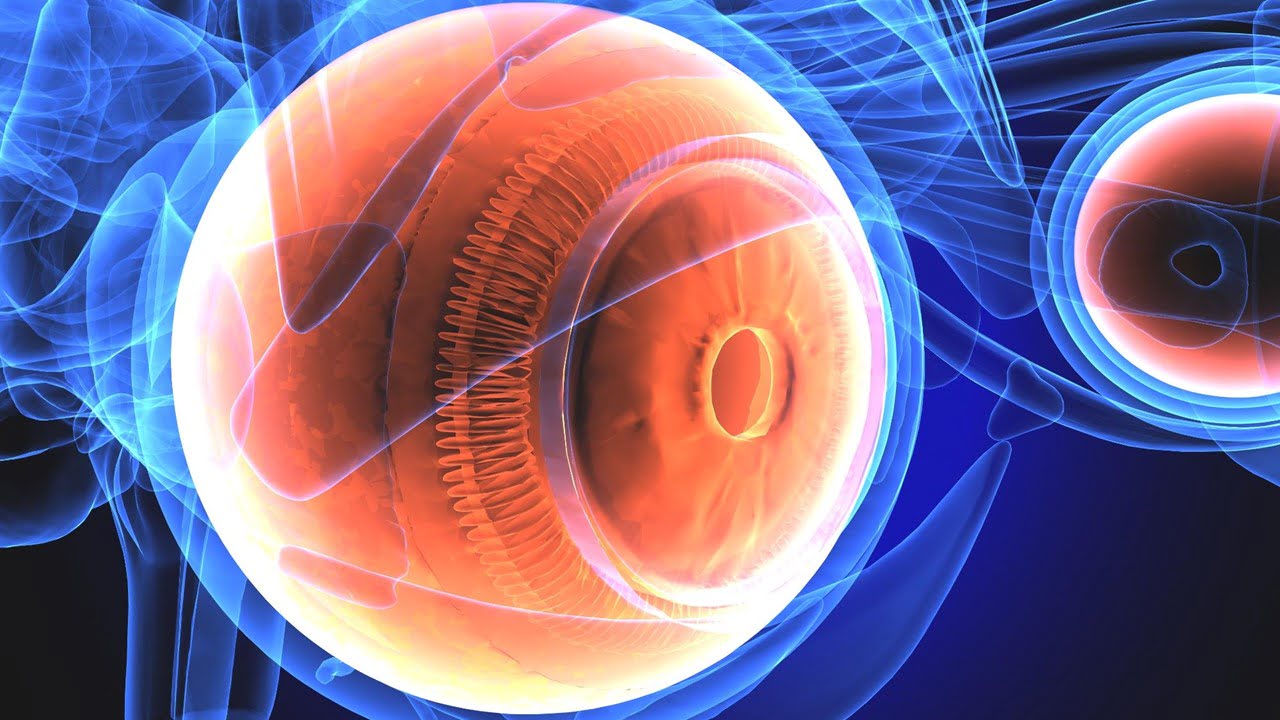
To help clinicians better detect and track eye diseases like glaucoma and age-related macular degeneration, researchers have applied artificial intelligence (AI) deep learning techniques to develop a more precise and in-depth method for analyzing optical coherence tomography (OCT) images of the back of the eye. OCT imaging, frequently used in ophthalmology and optometry, captures high-resolution [..]
Read More
A novel microwave imager chip created by researchers may one day be used in low-cost handheld imagers or cameras. The new imager might help image through walls or find tumors through body tissue because microwaves can pass through some opaque items. The researchers explain how they created an imager chip with more than 1,000 photonic [..]
Read More
A new stretchable optical lace may make soft robots even softer to the touch. The synthetic material forms a linked sensory network, similar to a biological nervous system, allowing robots to sense how they interact with their surroundings and adjust their actions accordingly. Researchers want to measure stresses and strains in highly deformable objects using [..]
Read More
Researchers working to improve infrared sensors say their gold nano-antenna technology is prepared to move from the lab to market development. The team asserts that the novel detectors reduce dark current by as much as two orders of magnitude while increasing sensitivity by a factor of three. The tiny antennas concentrate light onto a much [..]
Read More