Plasmonic metasurfaces, made up of two-dimensional metallic meta-atom arrays, are advantageous because of their ultrathin thicknesses, ease of fabrication, versatile functionality, field confinement beyond the diffraction limit, and superior nonlinearity. Their efficiency, however, is limited due to Ohmic heat loss during resonance. Huygens meta-atoms can break the scattering symmetry and improve transmission efficiency, but transmission [..]
Read More
The wide full-width-half-maximum (FWHM) of the electroluminescence (EL) spectra of OLEDs exhibit flaws as an appropriate light source for fingerprint recognition based on skin reflectance. Although inorganic light-emitting diodes (LEDs) have an extremely narrow FWHM, it is difficult to fabricate self-emitting inorganic LED-based displays for mobile smartphones without color filters. A group of researchers improved [..]
Read More
According to world-leading scientists, super-thin lithium niobate chips made from lithium niobate are set to overtake silicon chips in light-based technologies, with potential applications ranging from remote ripening-fruit detection on Earth to lunar navigation. They claim that artificial crystal is the best platform for these technologies because of its superior performance and recent advances in [..]
Read More
Thanks to advancements in expansion microscopy, unprecedented views of the interiors of cells and other nanoscale structures are now possible. The advances could aid future research in neuroscience, pathology, and other biological and medical fields. Magnify is a universal molecular anchoring strategy for expansion microscopy, according to the paper, which describes new Magnify protocols. Magnify [..]
Read More
Ground-state cooling, quantum squeezing, and remote entanglement of mechanical oscillators are just a few of the advances made possible by optomechanics. Pioneering theoretical studies have predicted that optomechanical lattices can access significantly richer physics and novel dynamics, such as quantum collective dynamics and topological phenomena. However, reproducing such devices experimentally under strict control and building [..]
Read More
Mushroom farmers are moving their outdoor operations into large greenhouses, shifting environmental factors away from external climates and toward internal microclimates. Environmental monitoring systems are installed in greenhouses to collect microclimate data. No sensor can directly measure mushroom growth to determine when adjustments are needed. Now scientists have come up with a GigE Camera solution. [..]
Read More
Photoacoustic microscopy (PAM) is a new imaging technique that employs laser light to induce ultrasonic vibrations in tissue. It can detect cancerous tissue, image-changing blood flow in the brain, and even identify individual cancer cells. Because of its narrow depth of field, PAM can only focus on a thin layer of tissue at a time. [..]
Read More
Strain sensors have demonstrated mechanically invisible monitoring of soft-bodied systems that are otherwise challenging for silicon-based rigid counterparts. Incorporating self-healing properties into these intrinsically stretchable sensors promises damage-resistant and damage-resilient sensing capabilities. Examples range from damage detection in spacesuits to alert suit air leakage by space debris during astronauts’ extravehicular activities. The self-healing function for [..]
Read More
A group of researchers has developed a high-conductivity material, molybdenum disulfide (MoS2), that could significantly reduce contact resistance and Schottky barrier height within critical parts of electronic and optoelectronic microchips, paving the way for computer and digital imaging components to consume less power relative to their performance than current chipsets. Molybdenum disulfide (MoS2) is so [..]
Read More
For the last half-century, silicon (Si) has been the focal point of the semiconductor and modern electronics industries. However, its surface properties are unknown. A group of scientists investigated the terahertz (THz) emission properties of Si surfaces in a new paper. The paper, “Rapid, noncontact, sensitive, and semiquantitative characterization of buffered hydrogen-fluoride-treated silicon wafer surfaces [..]
Read More
Researchers in biological imaging strive for 3D, high-speed, and high-resolution imaging with minimal photobleaching and phototoxicity. The light-sheet fluorescence microscope (LSFM) contributes to this goal. The LSFM can image live specimens with high spatiotemporal resolution and low photobleaching thanks to a novel excitation and detection scheme. It has demonstrated great promise for the 3D imaging [..]
Read More
A new study has revealed how diatoms’ glass-like shells help these microscopic organisms perform photosynthesis in low-light conditions. Improved solar cells, sensing devices, and optical components could result from a better understanding of how these phytoplankton harvests and interact with light. They developed a computational model and toolkit that could pave the way for mass-manufacturable, [..]
Read More
The transition to full-fledged AR glasses with all-day wear necessitates a high dynamic range display that works equally well in dimly lit indoor and mid-day sun outdoor spaces. Laser beam scanning (LBS) is an ideal (small size-to-power density, weight-to-performance ratios) light source for the application. Light coupling from the source into the optics can help [..]
Read More
Engineers have created a cohesive final product capable of transmitting information at ultrahigh speed while generating minimal heat by integrating an electronics chip with a photonics chip (which uses light to transfer data). The new electronic-photonic chip design could impact the future of data centers that handle massive amounts of data communication. Data communication speed [..]
Read MoreReservoir computing is a new computational framework based on recurrent neural networks. Researchers have developed a new artificial synapse of alpha-indium selenide (α-In2Se3) that may aid in replicating biological neural processes in neuromorphic devices. Reservoir computing uses artificial synapses to run deep learning algorithms directly without needing data transfer between a memory and a processing [..]
Read More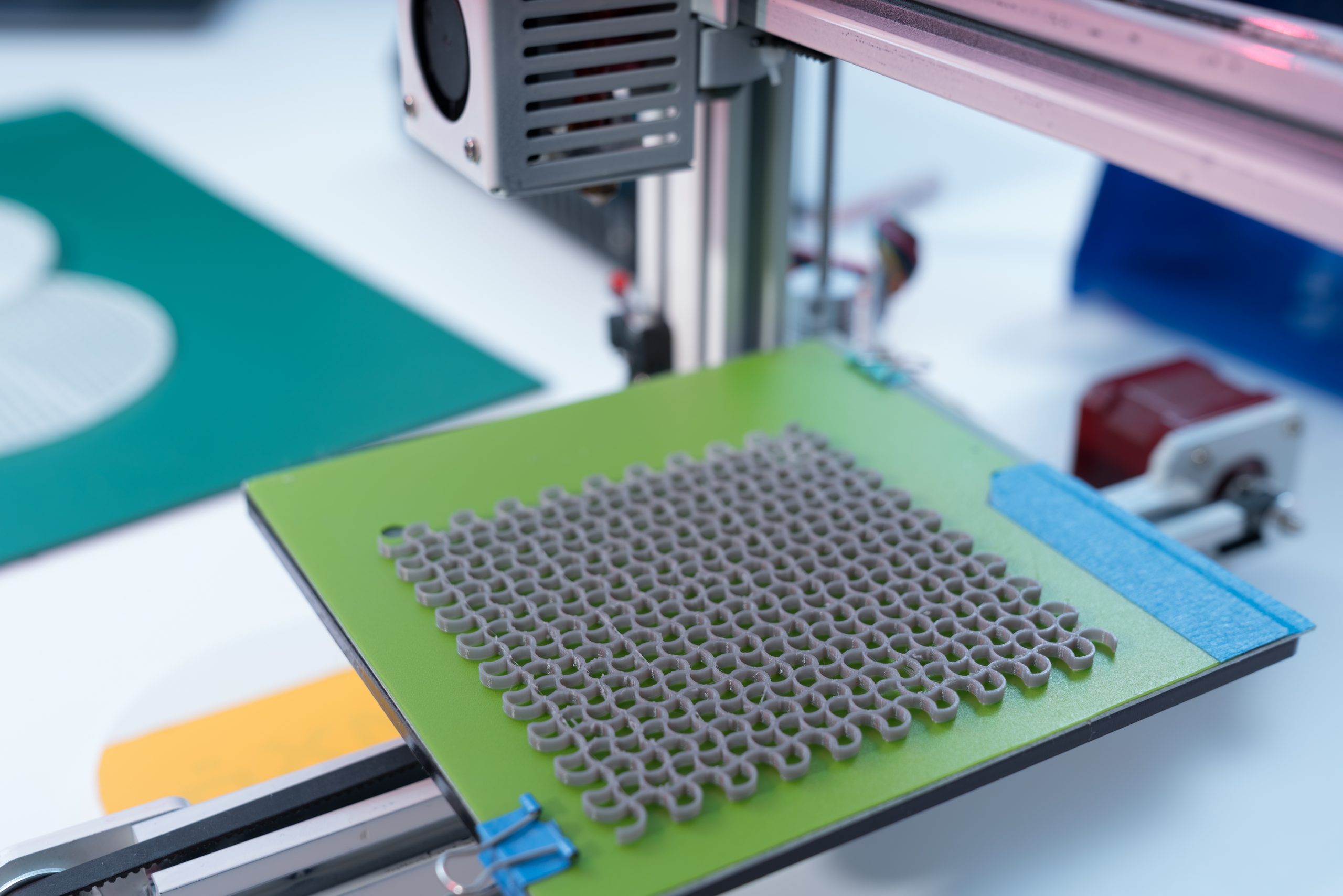
Metamaterials are engineered materials that allow us to go beyond the traditional interactions of waves and matter. Light waves that strike metamaterial coatings can be redirected, effectively preventing light from reaching our eyes. The technology enables us to create any pattern, color, or optical feature we can imagine. The “invisibility cloak” is the most visible [..]
Read More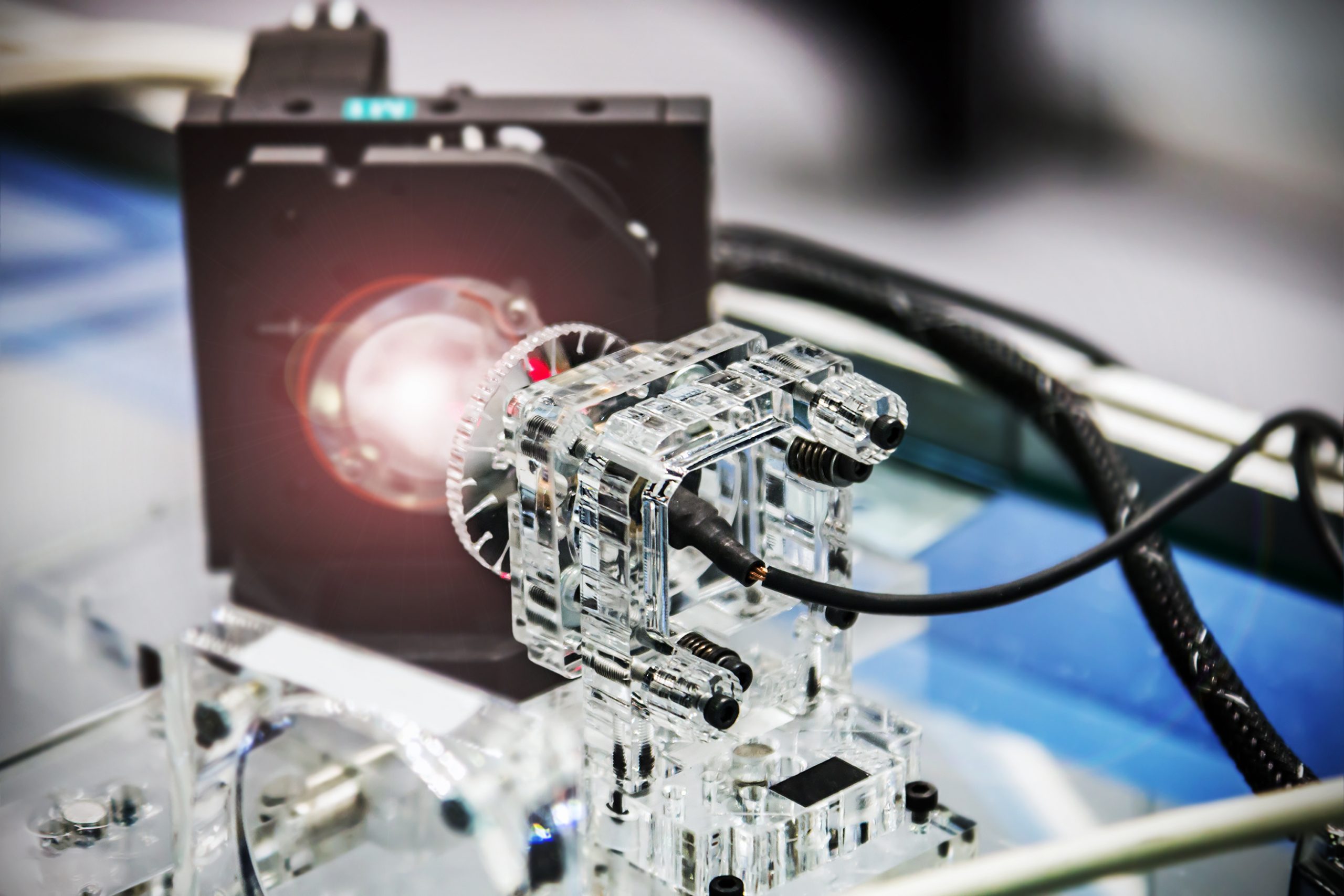
NASA’s Laser Communications Relay Demonstration (LCRD) project was launched into geosynchronous orbit, 22,000 miles above Earth, and was hosted aboard the United States. The goal is to put optical communications to the test as an alternative to radio waves. The LCRD payload, attached to a support assembly flight (LSAF), produces infrared lasers that transmit data [..]
Read More
A new imaging technique captures the structure of the human genome with unprecedented fidelity, revealing how individual genes fold at the nucleosome level – the fundamental units that make up the genome’s three-dimensional architecture. The method combines high-resolution microscopy with advanced computational modeling. It is the most comprehensive method for studying the shape of genes [..]
Read More
Researchers have developed a method for 2D IR spectroscopy capable of resolving a gas-phase sample’s myriad needle-thin lines. The improved resolution was due to two factors. First, the researchers used a frequency-domain rather than standard time-domain methods for generating a 2D spectrum. In standard time-domain methods, light pulses hit the sample sequentially, and the precision [..]
Read More
New research provides clinicians with new information about which neurosurgical implant devices are compatible with 7Tesla (7T) magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scanning. The findings may persuade clinicians to use advanced, high-resolution MRI technology to help patients with certain implants. 7T MRI technology is considered cutting-edge. Its ultra-high-resolution images can aid in diagnosing and planning surgery [..]
Read More