
Researchers have created a silicon carbide (SiC) photonic integrated optical chip that can be thermally tuned by applying an electric signal. Phase shifters and tunable optical couplers, which are required for networking apps and quantum information processing, could be made using the method in the future. SiC is becoming more popular even though silicon still [..]
Read More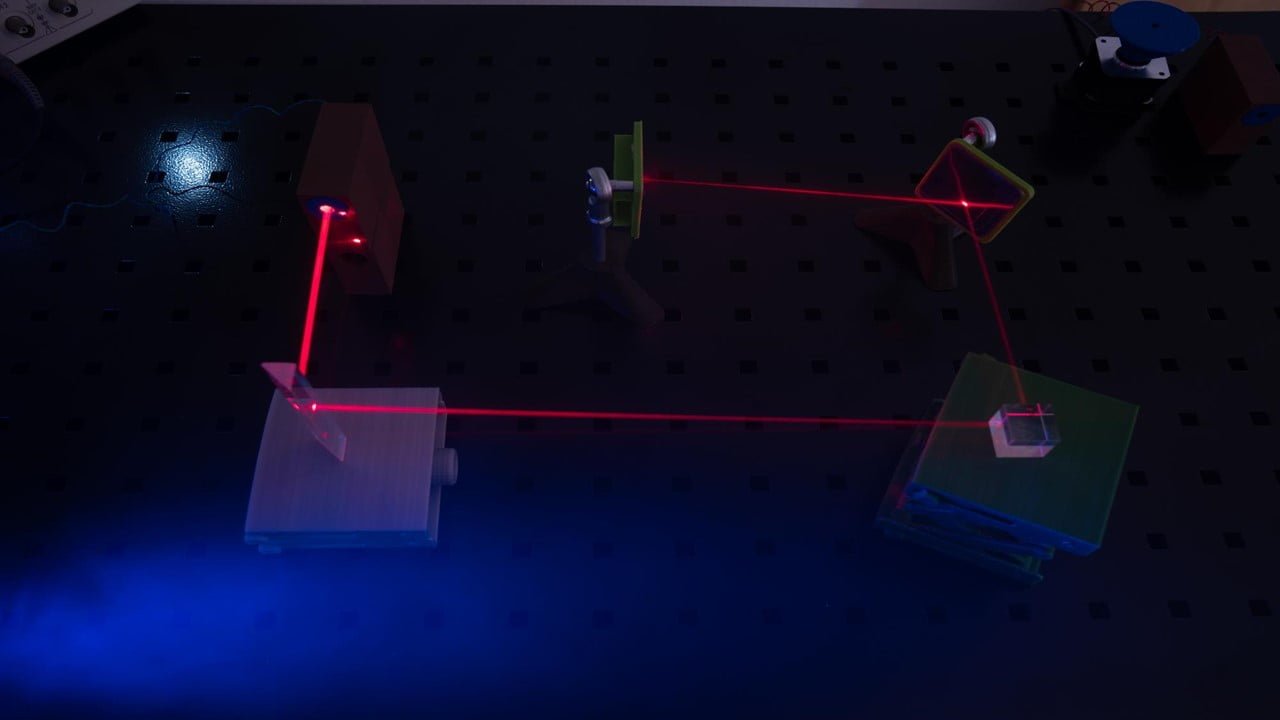
In building, industrial design, and medical technology, the ability to bend glass sheets into angular corners without causing damage to the sheet or impairing the optical properties is appealing. Scientists have been working on a laser-based method to bend glass for some time, and they recently revealed their most recent project accomplishments. Lasers provide the [..]
Read More
An early instance of optical communication, or the transmission of information using light, can be found in the signs sent from lighthouses to ships at sea. Today’s integrated photonics scholars use optical communications principles to create high-tech, light-powered devices (with integrated photonics platform) like lightning-fast computers. One-dimensional metalens, tiny surfaces made of nanostructures to control [..]
Read More
Moore’s law won’t prevent you from developing better head-mounted displays for augmented reality (AR), but the law of etendue will, according to a member of Microsoft’s AR development team. According to Bernard Kress, a partner optical architect for the computer software business, the unwritten “law” that has guided silicon-chip development for more than 50 years [..]
Read More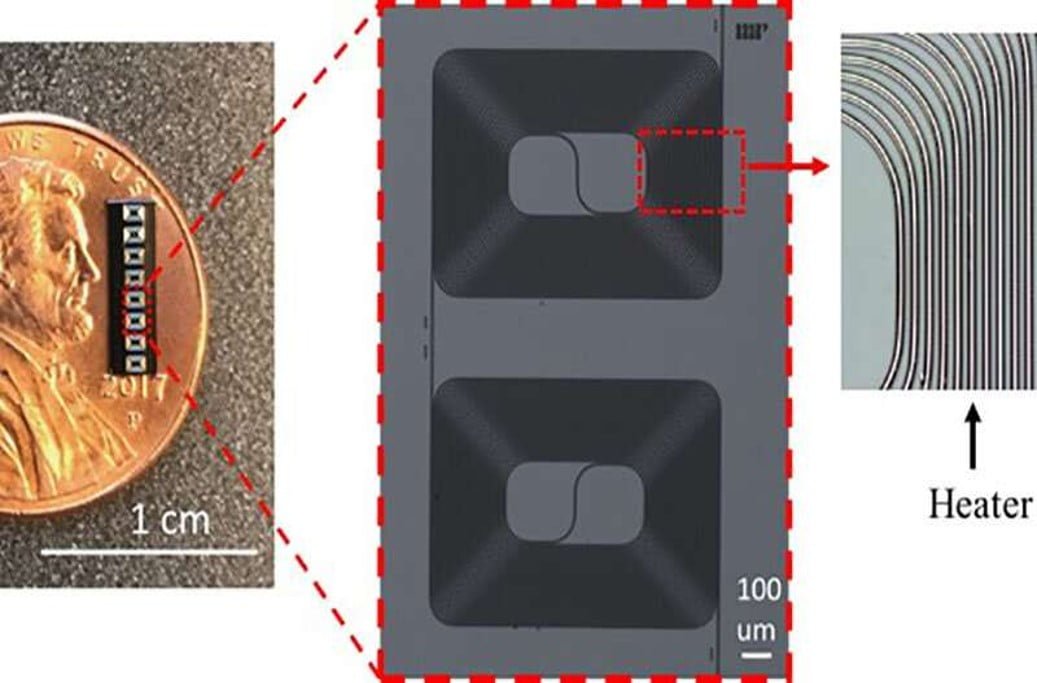
Scientists have used a microchip to scan the back of the eye to diagnose diseases. The interference technology used in the chip has been around for a while; it is similar to bat sonar but uses light pulses instead of sound waves. It is the first instance in which technological challenges have been surmounted to [..]
Read More
For the first time, scientists have built holograms that can detect the polarization of light using incredibly thin layers of 2-D structures called metasurfaces. For polarization measurements, which are used in spectroscopy, sensing, and communications, the new metasurface holograms could be used to build extremely quick and small devices. Metasurfaces are optical components with features [..]
Read More
It is still difficult to increase the single-molecule lateral localization precision to molecular scale (2 nm) for high-throughput nanostructure imaging, even though a variety of image-based central position estimation (centroid fitting) methods, such as 2D Gaussian fitting methods, have been widely used in single-molecule localization microscopy (SMLM) to determine the location of each fluorophore precisely. [..]
Read More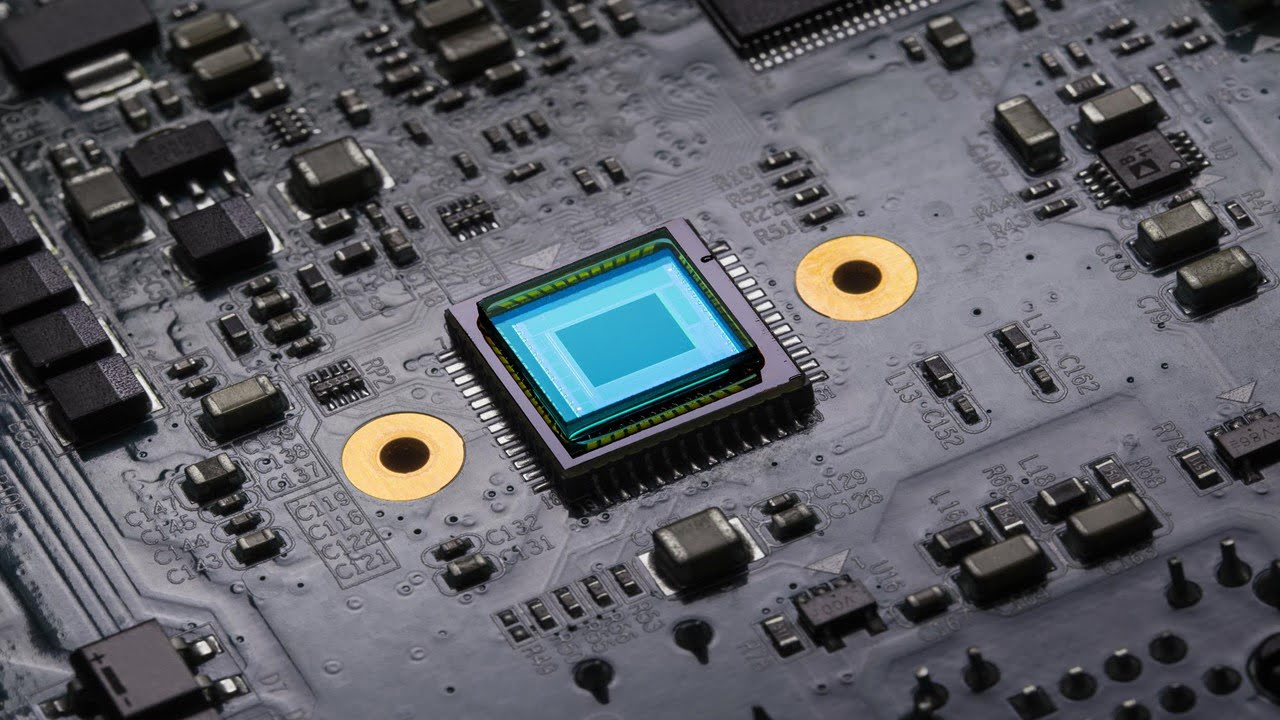
Researchers have created the first completely integrated, non-dispersive infrared (NDIR) gas sensor, made possible by metamaterials, specially engineered synthetic materials. The optical gas sensor is among the smallest NDIR sensors ever made, needs little energy to operate, and has no moving parts. The sensor is perfect for new Internet of Things and smart house gadgets [..]
Read More
To improve the detection of pathogens with difficult-to-distinguish molecular fingerprints, such as HIV and viruses that cause respiratory tract infection, sensors in diagnostic tools require nanoscale light manipulation. However, there is no way to make these light manipulation devices without damaging the sensors. Recognizing this, researchers created 3D plasmonic nanoarrays, light manipulation devices that can [..]
Read More
Many specialists believe that a second quantum revolution is about to occur globally. The transistor and the laser were made possible by energy quantization, and the ability of humans to control individual atoms and electrons has the potential to revolutionize a variety of sectors, from communications and energy to medicine and defense. The quantum computer, [..]
Read More
The Nobel Prize-winning innovation of super-resolution microscopy, which allows imaging below the diffraction limit of light, has enabled some breathtakingly sharp views of tiny biological structures. However, it is not something you would find in a typical biology lab; instead, it necessitates sometimes using complex and expensive tools and extensive image post-processing. Researchers have developed [..]
Read More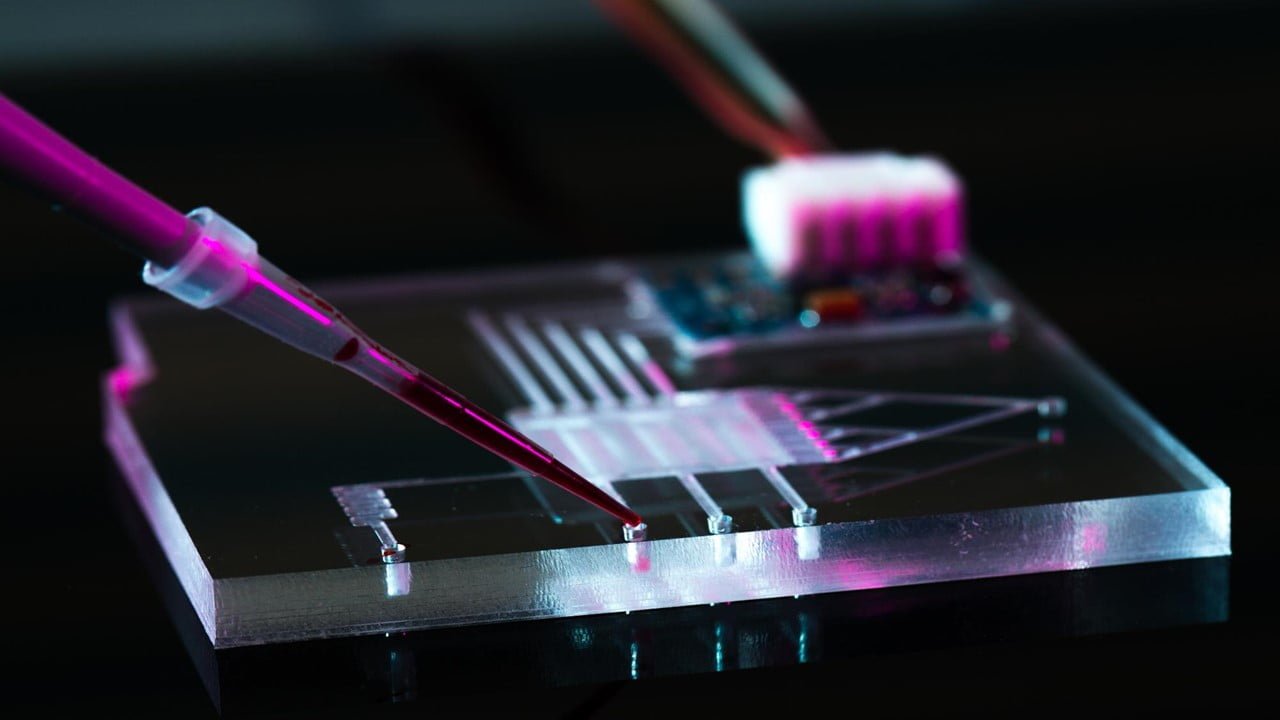
The protein aggregates known as beta-amyloid plaques, which develop in the brains of Alzheimer’s patients, impair numerous brain processes and have the potential to destroy neurons. They may also compromise the blood-brain barrier, a protective buffer between the bloodstream and the brain. Engineers have now created a tissue model that mimics the effects of beta-amyloid [..]
Read More
According to the researchers, new two-photon microscopy can capture video of brain activity 15 times more quickly than was previously thought feasible, revealing voltage changes and neurotransmitter release over sizable regions and simultaneously monitoring hundreds of synapses. The new tool, known as scanned line angular projection microscopy, or SLAP, increases the efficiency of data gathering [..]
Read More
For the first time, researchers used a powerful microscopy technique in conjunction with automated image analysis algorithms to distinguish between healthy and metastatic cancerous tissue without using invasive biopsies or contrast dye. This novel non-invasive imaging approach could one day assist doctors in detecting cancer metastasis that is otherwise difficult to detect during operations using [..]
Read More
Researchers have demonstrated that Raman spectroscopy, an optical technique, can distinguish between benign and cancerous thyroid cells. The new study demonstrates Raman spectroscopy’s potential for improving thyroid cancer diagnosis, the ninth most common cancer in the United States, with over 50,000 new cases diagnosed yearly. The promising results indicate that Raman spectroscopy has the potential [..]
Read More
Researchers have created thin coatings that react mechanically and chromatically to specific vapors, drawing inspiration from the chameleon’s skin’s adaptive iridophores, or nanophotonic structures. According to the experts, the resulting “structural-color actuators” could be used for “sensing, communication, and disguise” in soft robotics. These actuators can move and change color in response to changes in [..]
Read More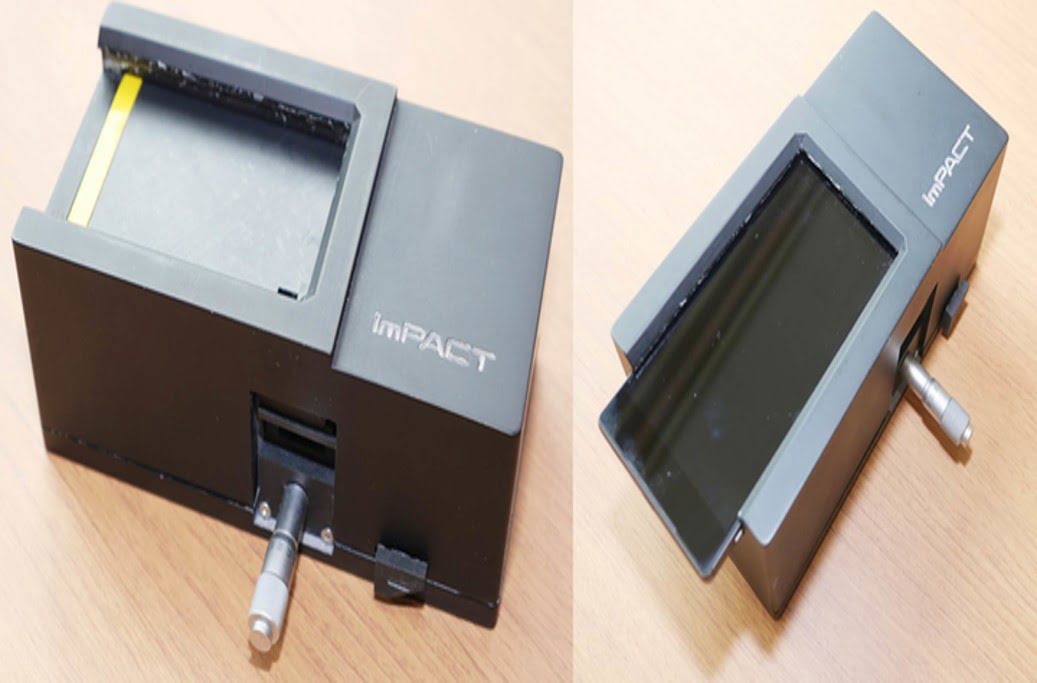
A team of researchers has created and tested a miniaturized virus-scanning system that uses inexpensive components and a smartphone because current methods to detect viruses and other biological markers of disease are efficient but large and expensive (such as fluorescence microscopes). While current tools are accurate at counting viruses, they are often too laborious for [..]
Read More
It is critical for patients with kidney failure who require dialysis to remove fluid at the correct rate and stop at the correct time. This usually entails estimating how much water to remove and closely monitoring the patient for any sudden drops in blood pressure. There is currently no reliable, simple method for measuring hydration [..]
Read More
Majorana photons, a new superclass of photons, may improve information on quantum-level transitions and brain images and their workings. A research team based their findings on that photons can take various forms while possessing important properties such as polarization, wavelength, coherence, and spatial modes. The team aimed to use a special super form of photons [..]
Read More
To detect train acceleration and vibration, researchers have created new sensors. The technology could be combined with artificial intelligence to stop serious train derailments and rail mishaps. According to the researchers, railway accidents cause serious injuries and occasionally yearly fatalities. The fiber optic accelerometers could detect real-time issues with the train or railway track and [..]
Read More