High-performance mid-infrared laser diodes have been made for the first time directly on silicon substrates suitable for microelectronics. The new lasers may make the widespread creation of low-cost sensors for real-time, precise environmental sensing for air pollution tracking, food safety analysis, and pipe leak detection possible. Most optical chemical instruments rely on the interaction of [..]
Read More
Concerns about the potential effects of plastic coatings in optoelectronic devices have begun to surface as the environmental cost of plastic microparticles and nanoparticles has become increasingly obvious. A research team suggests one potential response: Use fish scales to create the pictures. The team focused on the transparent plastic films that are used in a [..]
Read More
The study of vehicle-to-vehicle (V2V) positioning is crucial to the safety of autonomous cars. Global positioning system (GPS) has gained popularity as an option because it is inexpensive and simple to use. Researchers have suggested a reliable vehicle-to-vehicle (V2V) positioning technique based on visible light transmission that uses a monocular camera. (VLC). The baseline, which [..]
Read More
Scanning probe microscopy (SPM) has revolutionized materials science, nanotechnology, chemistry, and biology by making it possible to map surface properties and manipulate surfaces with atomic precision. These accomplishments, though, still require ongoing human supervision; completely automated SPM is still a work in progress. Researchers present a machine learning-based artificial intelligence system for autonomous SPM operation. [..]
Read More
Biological engineers have developed a multi-tissue model on a specialized microfluidic platform seeded with human cells, enabling them to research the interactions between various organs and the immune system. The study team investigated the function of circulating immune cells in ulcerative colitis and other inflammatory diseases using this model, also known as “organ-on-a-chip” or “physiome [..]
Read More
In science and technology, terahertz waves are becoming more and more significant. They allow us to examine the characteristics of potential materials, evaluate the effectiveness of automotive paint, and try envelopes. But producing these surges is still difficult. Researchers have now created a germanium component that produces brief terahertz pulses with an advantageous quality: the [..]
Read MoreApart from AR and VR, there are recent developments in wearable technology. According to a project, a novel approach to the design of the light-emitting fabric could create luminous clothing that is softer and more comfortable to wear. The porous structures and non-planar surfaces of the fabrics have previously prevented the production of wearable e-textiles [..]
Read More
A research team has reported a technique for creating metamolecules with two independently controllable subwavelength meta-atoms. Thanks to this two-parametric control, the metamolecule can be completely controlled regarding amplitude and the phase of the light – light modulator. The group proposed a graphene-based active metasurface that could independently regulate the amplitude and phase of mid-infrared [..]
Read More
Researchers have created a method that combines optics and magnetic particles that can test 100 samples of patients who may be infected with the virus and cut the diagnostic time to around 15 minutes after realizing that current methods of coronavirus diagnosis take about an hour. By joining the virus’ RNA to a fluorescent molecule [..]
Read More
Scientists have observed light traveling through a unique substance without reflections. The photonic crystal substance comprises two pieces with subtly different perforation patterns. Light can move along the border between these two regions uniquely because it is “topologically protected” and does not reflect flaws. The light follows the boundary without any issues, even when it [..]
Read More
Using a particular kind of light beam (polarization of light) to stimulate certain exotic materials has led a team of scientists to discover that an identically asymmetrical pattern can be produced and measured at will in these materials. In this instance, the “handedness” phenomenon—known as chirality—occurs in the abundance of electrons within the substance rather [..]
Read More
According to project managers, Galahad, a Horizon 2020 research project creating an OCT platform for enhanced early glaucoma screening, has successfully finished its job. The three-year program to create ultra-high resolution polarization-sensitive optical coherence tomography, called Galahad, from Glaucoma Advanced, LAbel-free High resolution Automated OCT Diagnostics, has ended. (UHR-PS-OCT). By utilizing only OCT volumes focused [..]
Read More
The results of a successful demonstration of a lensless on-chip microscopy platform by a biomedical engineering lecturer at a university have been published in Lab on a Chip. He claims that his ptychography platform offers a low-cost alternative for disease detection while removing several of the most prevalent issues with traditional optical microscopy. The platform [..]
Read More
Semiconductor quantum dots (QDs) may power various optical devices that produce light in the near- and mid-infrared (IR) spectral ranges. But basic physical constraints reduce the power of IR-emitting QDs. According to Fermi’s golden rule, the quantum yield of such QDs declines at longer wavelengths as the radiative emission rate falls, while nonradiative recombination channels [..]
Read More
Using pseudo-random speckle patterns to image targets is efficient (high-resolution imaging), but most approaches require bulky, expensive, complex, and slow machinery. A smaller device capable of generating random speckles is required to apply this technique to biomedical imaging, such as ultra-thin endoscopy or in vivo neural imaging. A group of scientists demonstrated using a multimode [..]
Read More
While living tissue significantly attenuates and scatters visible light, attenuation, and scattering are less for two spectral regions at slightly longer wavelengths. The first and second near-infrared (NIR) windows refer to these frequencies. Although labels emitting in the NIR-II band are challenging, this band is especially attractive. A group of scientists has created an organic [..]
Read More
A research team has created a low-cost colloidal quantum dot photodetector that can sense long-wave infrared (IR) light and may eventually replace more expensive commercially available options. According to the researchers, the new technology closes a gap in the photodetection spectrum and may be helpful for environmental monitoring, food inspection, and gas analysis. With silicon [..]
Read More
Non-line-of-sight imaging (NLoS), which is the task of recovering image data from objects hidden from direct observation or hidden by corners, can be approached in several ways, frequently requiring techniques to recover data from highly scattered or diffuse optical signals. In recent years, methods for reconstructing images using the intrinsic spatial correlations encoded in scattered [..]
Read More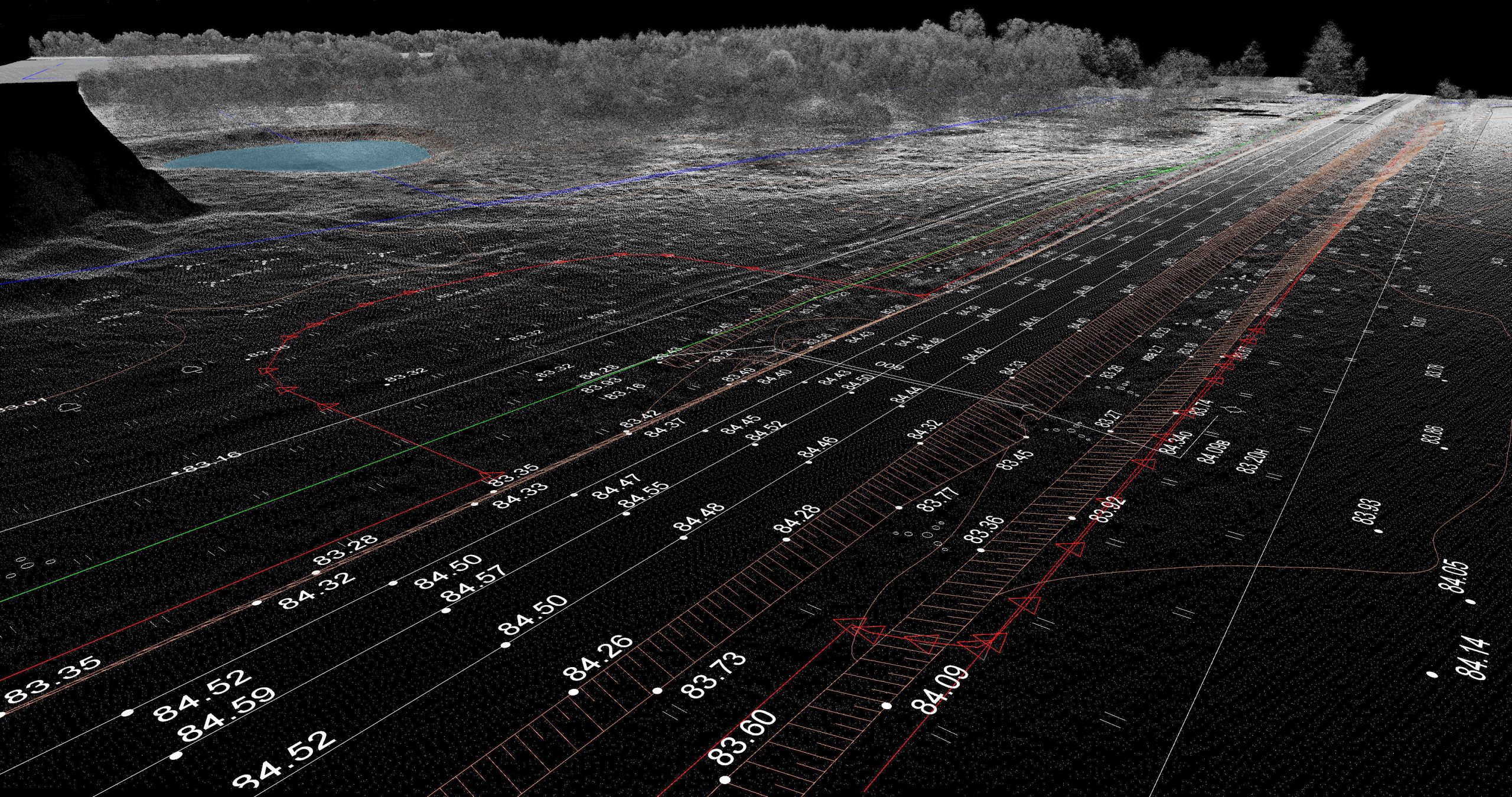
Particularly when it comes to a 3-D scanner in cutting-edge technology, faster is sometimes better. Researchers are working to create a 3-D lidar sensor that is portable and simple to use, with uses in autonomous vehicles, robots and drones, security systems, and more. In a field where speed is frequently valued above other factors, researchers [..]
Read More
Accurate identification and segmentation of choroidal neovascularization (CNV) are crucial for detecting and treating exudative age-related macular degeneration. (AMD). Cross-sectional and en-face imaging of CNV is possible with PR-OCTA or projection-resolved optical coherence tomographic i.e., OCT angiography. Due to the persistence of residual artifacts, CNV segmentation and detection remain challenging even with PR-OCT Angiography. In [..]
Read More