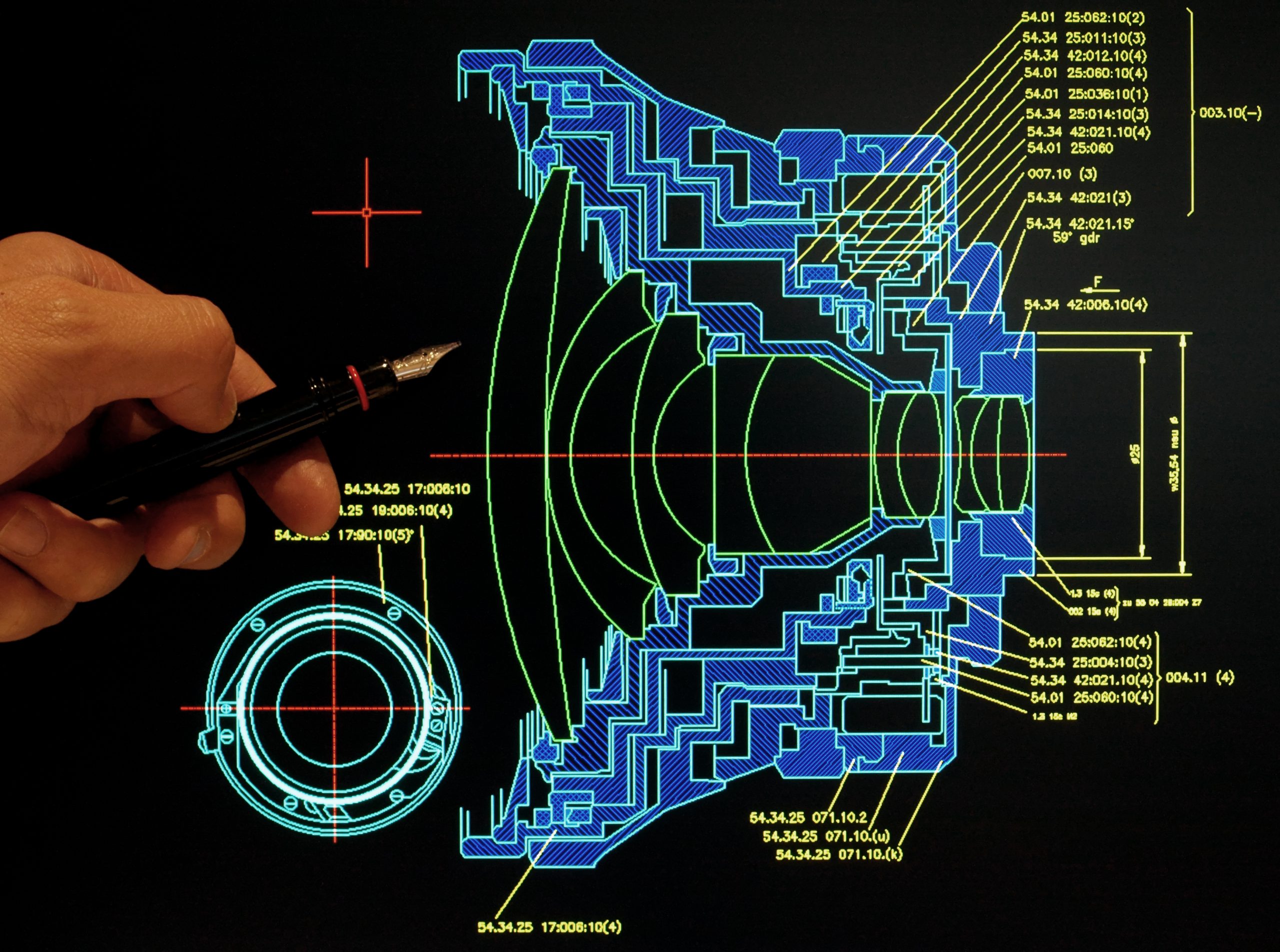
Nanowires, materials with 1000 times the diameter of a human hair and fascinating physical properties, have the potential to enable significant advances in a wide range of fields, from energy harvesters and sensors to information and quantum technologies. Their minuscule size, in particular, may enable the development of smaller transistors and miniaturized computer chips. However, [..]
Read More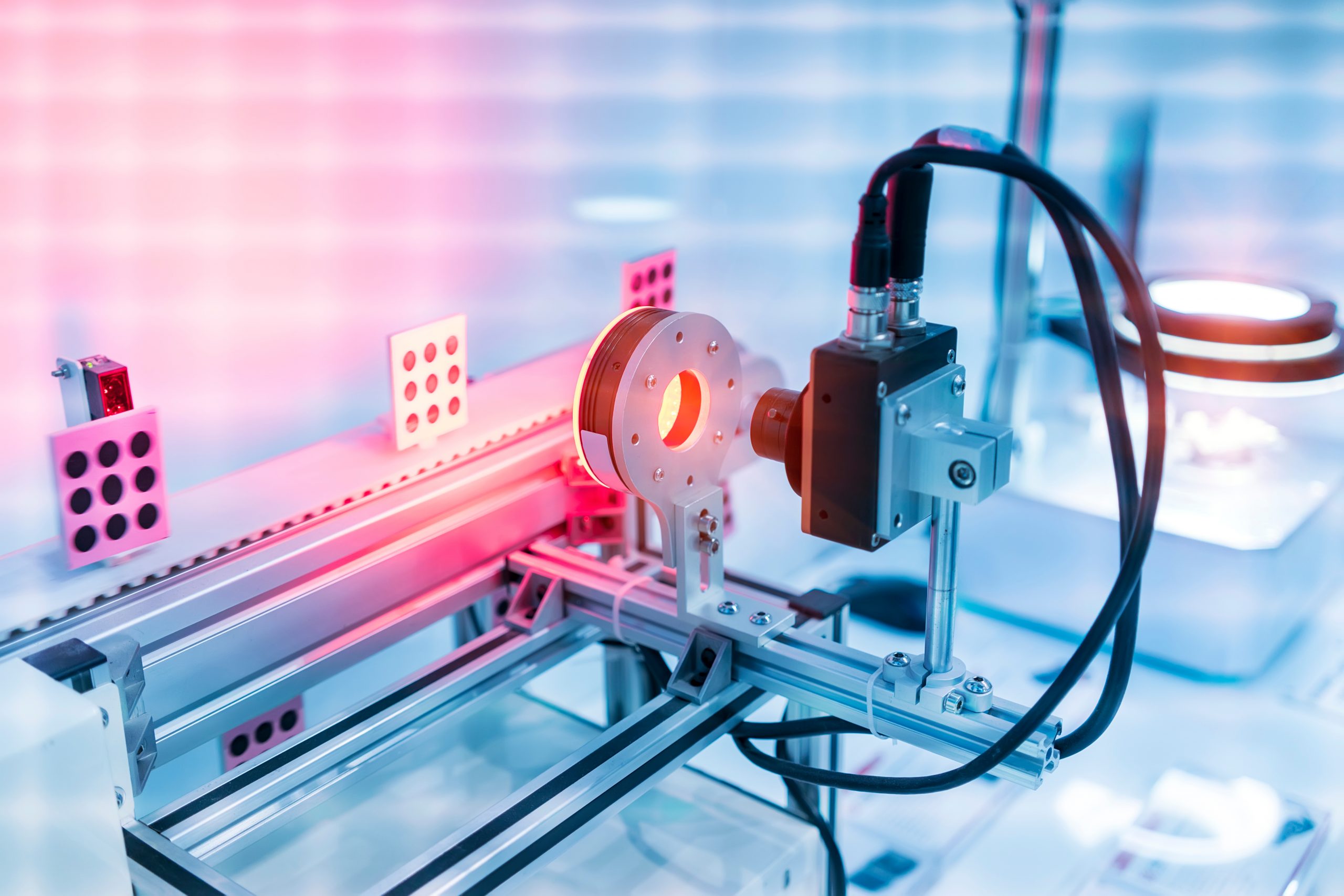
When a germinating seed is placed on its side, some roots bend earthward immediately, while others turn more slowly. Plant roots must be directed toward gravity for water and nutrients to be available. Understanding these directional mechanisms could help improve agriculture and ensure food security as global climate changes. A new study used machine vision [..]
Read More
New cardiology discoveries rely heavily on medical imaging. Researchers use cardiac imaging techniques to detect signs of artery disease that would not have been visible to doctors otherwise. The more tools we have to combat heart disease, the better. According to the CDC (Centers for Disease Control and Prevention), it is still the leading cause [..]
Read More
Researchers have developed a new type of high-efficiency photodetector. The concept comes from the photosynthetic complexes plants use to turn sunlight into energy. The researchers used unique quasiparticles known as polaritons. The new detector generates the particles in an organic thin film. Photodetectors are used in cameras, optical communication systems, and many other applications to [..]
Read More
Organic light-emitting transistors (OLETs) are promising components for optoelectronics, smart display technologies, and electrically pumped lasers. They combine the light-emitting function of organic light-emitting diodes (OLEDs) and the current modulation (and signal amplification) function of organic field-effect transistors (OFETs) in a single device. High-mobility emissive organic semiconductors with tunable colors, which serve as the core [..]
Read More
Although the electronic states of a material‘s surface are only 2D, they contain a wealth of interesting physics. These states, which differ from the bulk of the material, dominate many phenomena, including electrical conduction, magnetism, and catalysis. They are responsible for nontrivial surface effects observed in topological materials and systems with strong spin-orbit interaction. Surface [..]
Read More
Scientists must study the processes inside an operating battery to understand battery failures. The observations guide the development of faster-charging and longer-lasting batteries. Current techniques to study battery materials are complicated and expensive. They are not quick enough to capture the rapid changes in electrode materials. To understand battery failures, the researchers studied micrometer-sized rod-like [..]
Read More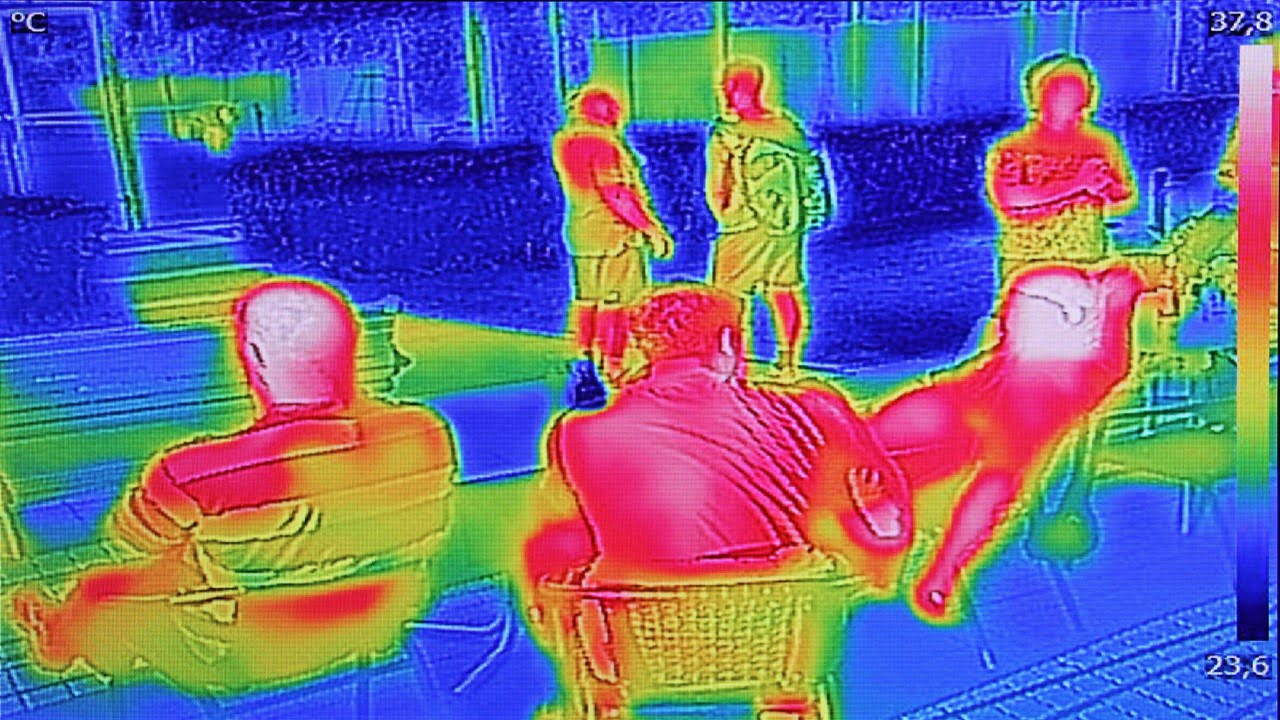
The surface temperature of a solar panel and the appearance of hotspots directly impact its efficiency. Researchers have developed a novel method for estimating the power efficiency of an on-field solar photovoltaics (PV) system based on data obtained from thermal imaging and weather instruments using an unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV). This method is designed explicitly [..]
Read More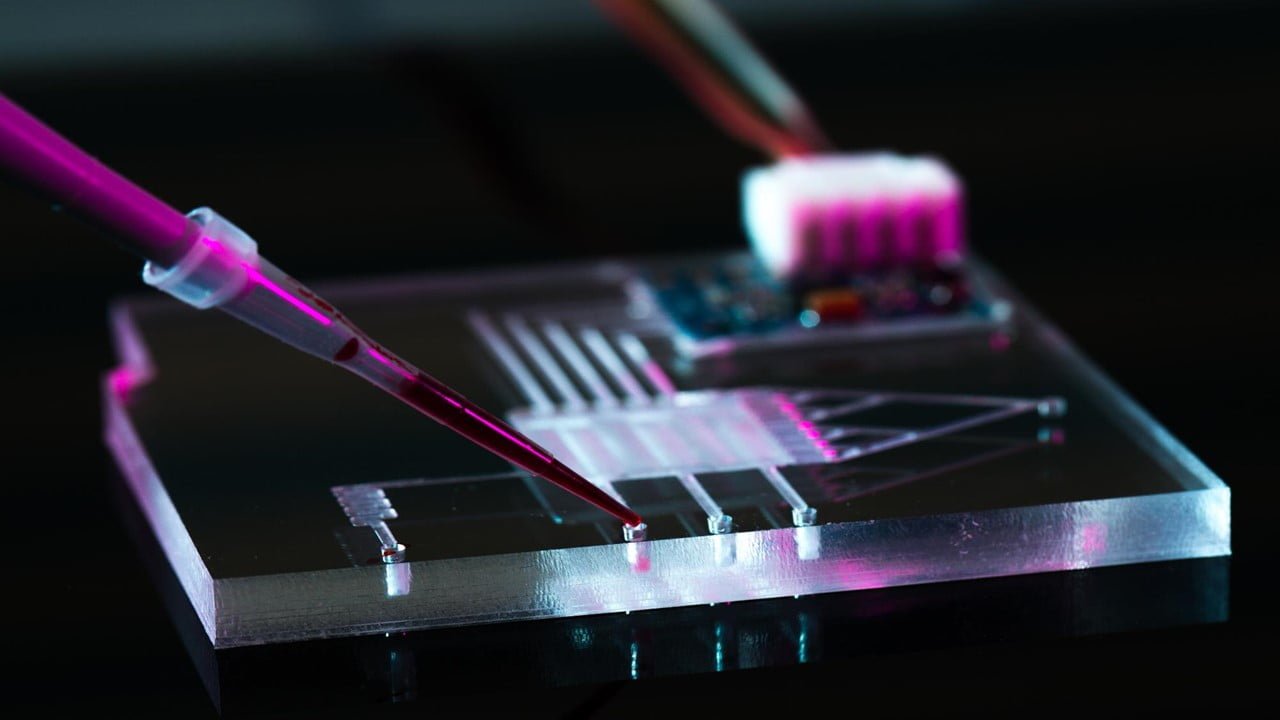
Light-induced charged slippery surfaces (LICS), which regenerate charge when illuminated, have the potential to pave the way for next-generation interfacial materials and microfluidics. A copolymer, tiny liquid metal particles, and lubricant-trapping microstructures make up the new material. It has the potential to be used in lab-on-a-chip devices, biological diagnostics, and chemical analysis. Slippery lubricant-infused porous [..]
Read More
Bioactive glass, a specific mixture of sodium oxide, calcium oxide, silicon dioxide, and phosphorus pentoxide, is now used as an orthopedic treatment to restore damaged bone and repair bone defects. Bioactive glass is a material you put into your body, and it begins to dissolve, telling cells and bone to become more active and produce [..]
Read More
Engineers have created a switch, one of the most fundamental components of computing, using optical rather than electronic components. The advancement could help in pursuing ultrafast all-optical signal processing and computing. Optics has the potential to revolutionize computing by allowing it to do more at faster speeds and with less power. However, one of the [..]
Read MoreA new study looks at conjugating 2D perovskites with optically active transition metal dichalcogenides (TMDs). The study can improve optoelectronic device performance and extend the functionalities of the perovskites. Despite their structural differences, 2D perovskites and TMDs can form clean interfaces due to van der Waals interactions between the stacked layers. Using accurate first-principles calculations, [..]
Read More
Researchers have been experimenting with ways to reach people as VR technology improves, becomes cheaper, and more accessible – everything from treating PTSD to performing operas. Visual artists are the most recent to wonder how technology might push the boundaries of their field, looking for new ways to express themselves and share their work. However, [..]
Read More
Carbon-based materials have enormous potential for constructing a sustainable future; however, material scientists require tools to properly analyze their atomic structure, which determines their functional properties. One of the tools used for this is X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), but the results can be challenging to interpret. Now, researchers have created the XPS Prediction Server, a [..]
Read More
Respiratory motion can influence the efficacy and safety of radiation therapy in the thorax and abdomen. Free-breathing 4D-MRI is a promising alternative to 4D-CT for motion management in MRI-guided linac treatments, providing excellent soft-tissue contrast with no ionizing radiation. High-quality MR images free of motion artifacts can distinguish lesions from normal tissue. MRI techniques, however, [..]
Read More
Using carbon nanotubes, a new strain-sensing smart skin monitors and detects damage in large structures. The coating detects surface deformation by stress by utilizing the fluorescent properties of nanotubes. As part of the S4 non-contact optical monitoring system, the multilayered coating can be applied to large surfaces — bridges, buildings, ships, and airplanes, to name [..]
Read More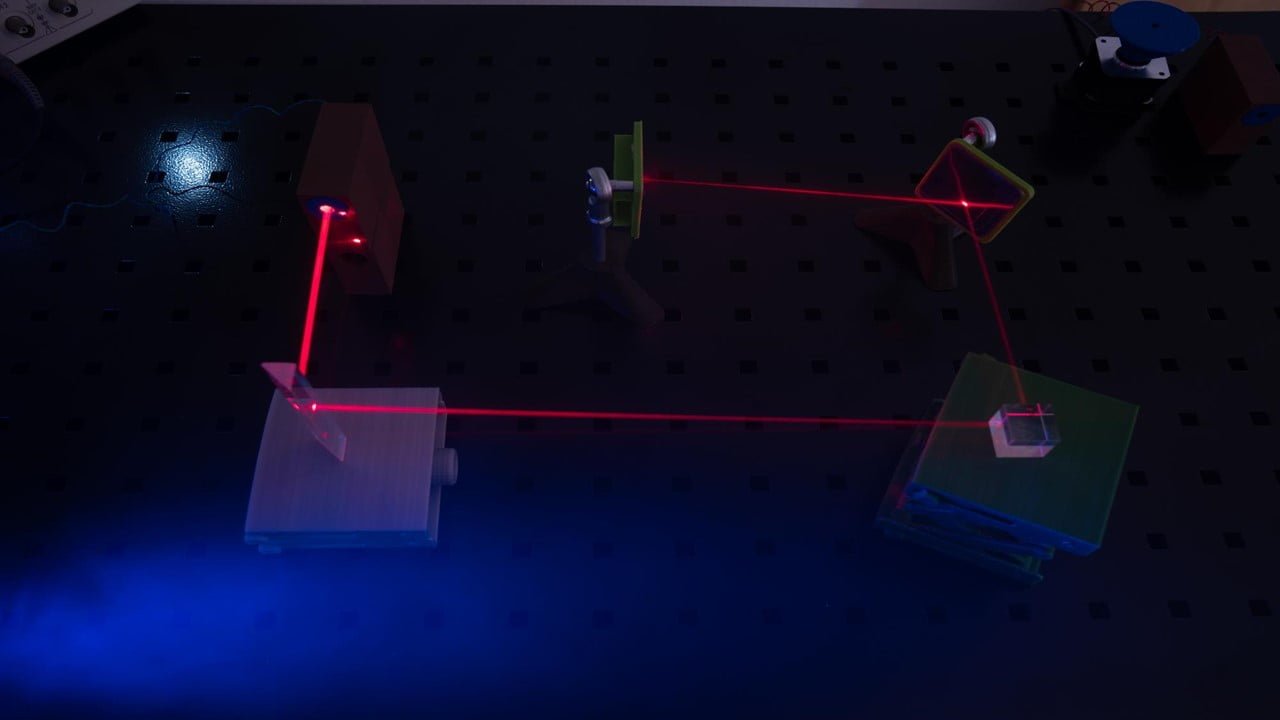
Detecting gases is critical for pollution monitoring, public safety, and personal health care. The sensors must be small, lightweight, inexpensive, and simple in various environments and substrates, such as clothing or piping. A research team has created the first highly customizable microscale gas sensing devices by combining laser writing and responsive sensor technologies. The challenge [..]
Read More
A new holographic platform generates realistic holographic patient scenarios for training purposes. The first module covers common respiratory problems and emergencies. Mixed reality is becoming more popular as a method of simulator training. As institutions scale their procurement, there is a growing demand for platforms that provide utility and ease of mixed reality learning management. [..]
Read More
Researchers have shown that a new mid-infrared spectrometer can precisely measure the ratios of different forms of water — known as isotopologues — in atmospheric water vapor through open air in a little over 15 minutes. The new open-path mid-infrared dual-comb spectrometer (DCS) uses near-infrared femtosecond laser pulses and specially designed waveguides to create broadband [..]
Read More
2D semiconductor materials are making their way into optoelectronic devices — the sort used in telecommunication. These devices have started to surpass the performance of conventional switches made with silicon and III-V semiconductors (compounds with elements from columns III and V on the periodic table). Optical computing, an early approach that was later abandoned in [..]
Read More