
Synchrotron x-ray fluorescence microscopy can be used to measure the concentrations of different elements in cross-sections of the ear at extremely high resolution. This method could address many open questions in hearing medical diagnosis research. X-ray fluorescence microscopy uses synchrotron radiation to evoke emissions from many biologically relevant elements in the tissue. The intensity and [..]
Read More
Leading research teams in nanophotonics are creating optical transistors, which will be crucial parts of upcoming optical computers. Instead of using electrons to process information, these photonic devices use light to produce less heat and operate more quickly. For microelectronics engineers, the poor photon-to-photon interaction poses a significant challenge. Scientists developed a planar system to [..]
Read More
The number of COVID-19 cases has not yet hit its peak and supplies of essential personal protective equipment (PPE) such as N95 masks are dwindling, so medical communities are desperately looking for alternative solutions for disinfecting masks that healthcare workers are being forced to reuse. Medical optics solutions can prove very helpful in such conditions. [..]
Read More
A laser-based interferometer sensor that can quickly identify coronavirus from saliva or nasal swab at the site of infection is being developed by researchers. The researchers are working on a brand-new optical biosensor demonstrator that can quickly and painlessly identify COVID-19 in humans as soon as it enters the body. The sensor is far more [..]
Read More
For use with adaptive optical (AO) systems combined with big ground-based astronomical telescopes, artificial “guide stars” are created in the mesosphere at an altitude of about 90 km using lasers that emit light at the sodium line, which is a doublet at a wavelength of about 589 nm. Astronomers can use AO to rectify atmospheric [..]
Read More
Computed tomography (CT), which can find lung tumors, is regularly used to screen people at a high risk of lung cancer, such as heavy smokers. However, because it also detects benign nodules in the lungs, this test has a very high incidence of false positives. Researchers have created a urine test to diagnose lung cancer [..]
Read More
An advanced X-ray imaging technique called propagation-based phase-contrast CT (PB-CT) can produce diagnostic breast images of better quality than absorption-based CT (AB-CT) at glandular radiation doses similar to or lower than traditional mammography and digital breast tomosynthesis. (DBT). The technology is presently only suitable for synchrotron light sources, but as compact light sources develop, the [..]
Read More
High-performance mid-infrared laser diodes have been made for the first time directly on silicon substrates suitable for microelectronics. The new lasers may make the widespread creation of low-cost sensors for real-time, precise environmental sensing for air pollution tracking, food safety analysis, and pipe leak detection possible. Most optical chemical instruments rely on the interaction of [..]
Read More
Concerns about the potential effects of plastic coatings in optoelectronic devices have begun to surface as the environmental cost of plastic microparticles and nanoparticles has become increasingly obvious. A research team suggests one potential response: Use fish scales to create the pictures. The team focused on the transparent plastic films that are used in a [..]
Read More
The study of vehicle-to-vehicle (V2V) positioning is crucial to the safety of autonomous cars. Global positioning system (GPS) has gained popularity as an option because it is inexpensive and simple to use. Researchers have suggested a reliable vehicle-to-vehicle (V2V) positioning technique based on visible light transmission that uses a monocular camera. (VLC). The baseline, which [..]
Read More
Scanning probe microscopy (SPM) has revolutionized materials science, nanotechnology, chemistry, and biology by making it possible to map surface properties and manipulate surfaces with atomic precision. These accomplishments, though, still require ongoing human supervision; completely automated SPM is still a work in progress. Researchers present a machine learning-based artificial intelligence system for autonomous SPM operation. [..]
Read More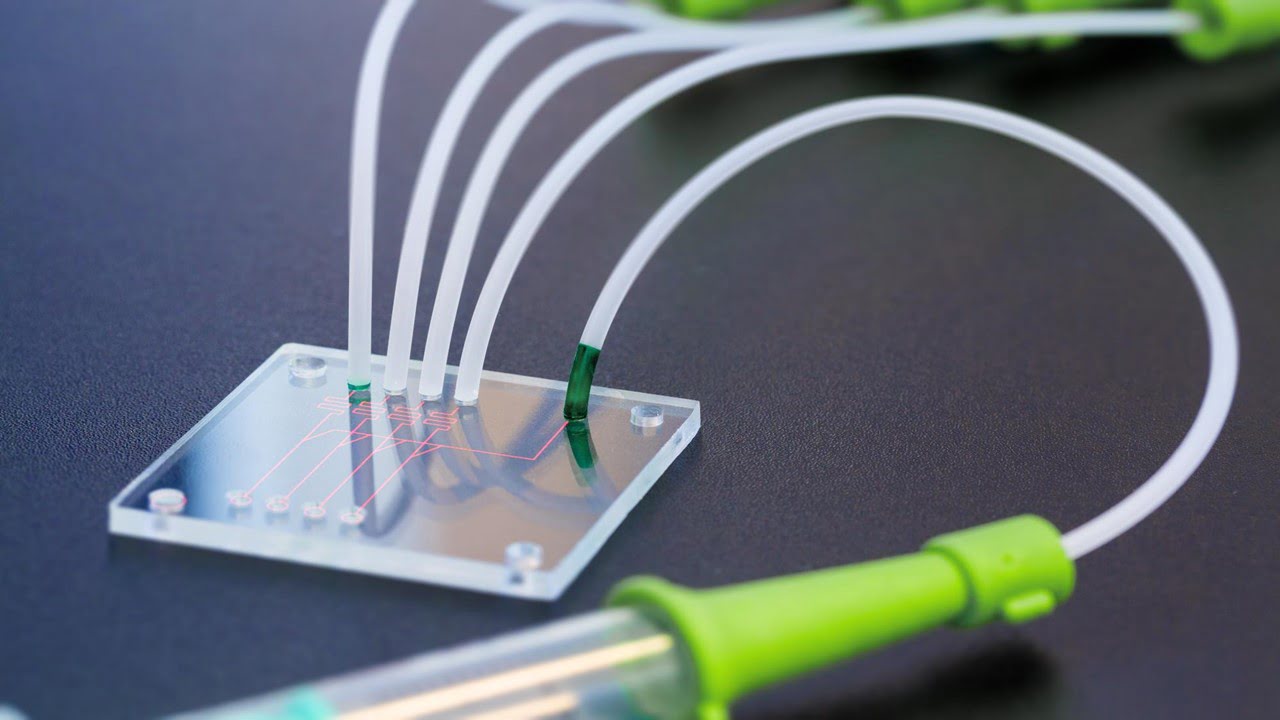
Biological engineers have developed a multi-tissue model on a specialized microfluidic platform seeded with human cells, enabling them to research the interactions between various organs and the immune system. The study team investigated the function of circulating immune cells in ulcerative colitis and other inflammatory diseases using this model, also known as “organ-on-a-chip” or “physiome [..]
Read More
In science and technology, terahertz waves are becoming more and more significant. They allow us to examine the characteristics of potential materials, evaluate the effectiveness of automotive paint, and try envelopes. But producing these surges is still difficult. Researchers have now created a germanium component that produces brief terahertz pulses with an advantageous quality: the [..]
Read MoreApart from AR and VR, there are recent developments in wearable technology. According to a project, a novel approach to the design of the light-emitting fabric could create luminous clothing that is softer and more comfortable to wear. The porous structures and non-planar surfaces of the fabrics have previously prevented the production of wearable e-textiles [..]
Read More
A research team has reported a technique for creating metamolecules with two independently controllable subwavelength meta-atoms. Thanks to this two-parametric control, the metamolecule can be completely controlled regarding amplitude and the phase of the light – light modulator. The group proposed a graphene-based active metasurface that could independently regulate the amplitude and phase of mid-infrared [..]
Read More
Researchers have created a method that combines optics and magnetic particles that can test 100 samples of patients who may be infected with the virus and cut the diagnostic time to around 15 minutes after realizing that current methods of coronavirus diagnosis take about an hour. By joining the virus’ RNA to a fluorescent molecule [..]
Read More
Scientists have observed light traveling through a unique substance without reflections. The photonic crystal substance comprises two pieces with subtly different perforation patterns. Light can move along the border between these two regions uniquely because it is “topologically protected” and does not reflect flaws. The light follows the boundary without any issues, even when it [..]
Read More
To treat a type of red-green color blindness called deuteranomaly, researchers have put metasurfaces, ultra-thin optical components, with commercially available high-tech contact lenses. People who experience different types of color blindness may find the new customizable contact lenses easy and comfortable. Additionally, the quality of plastic optical lenses can be enhanced by this research. Simple [..]
Read More
A recently released report from several German trade and research organizations argues that photonic technologies can represent “a driver of global sustainability,” and that the application of these technologies can prevent some 2.92 billion tons of annual CO2 emissions by 2030. Those avoided emissions, according to the study, would “correspond to at least 11% of [..]
Read More
Lasers that switch on and off billions of times per second are the backbone of optical communications networks, but this feat is only possible at certain laser frequencies. A team of researchers has now taken a step towards extending this frequency range by using sound waves to modulate the emission of a terahertz (THz) quantum [..]
Read More