
A group of experimental physicists developed a device that behaves like a memristor while acting on quantum states and encoding and transmitting quantum information. The device is a quantum memristor. Creating such a device is difficult because the dynamics of a memristor defy usual quantum behavior. The physicists have overcome the challenge by using single [..]
Read More
The bright-field (BF) optical microscope is a traditional bioimaging tool that has been recently tested for depth discrimination during the evaluation of specimen morphology. However, existing approaches require dedicated instrumentation or extensive computer modeling. Now, researchers have developed a direct method for three-dimensional (3D) imaging in BF microscopy, applicable to label-free samples, where they use [..]
Read More
Researchers have calculated the maximum theoretical limit for optoelectronic devices, the point at which the laws of quantum mechanics prevent microchips from becoming any faster. Optoelectronics are the fastest devices globally — systems that use light to control electricity. The new study outlines the limit for optoelectronics by calculating the speed at which the most potent [..]
Read More
A fast-evolving understanding of materials and physical processes is critical to security applications. Febetrons generate X-rays to photograph objects moving at extremely high speeds as part of a detonation and allow the measurement of their position, velocity, shape, and internal density profiles. Powering the Febetrons are capacitor modules. Researchers have developed a new “K-module” device [..]
Read More
Researchers have developed a temperature sensing method using naturally occurring atom-like defects in diamonds. The defects, known as Nitrogen-Vacancy (NV) defects, are naturally occurring flaws in diamonds (two adjacent carbon atoms replaced by a nitrogen atom and a hole). They are easy to obtain and have unusual quantum and nonlinear optical properties. Among them is [..]
Read More
A new MRI innovation that makes cancerous tissue glow in medical images could help doctors more accurately detect and track cancer progression over time. The MRI innovation creates images in which cancerous tissue appears to light up compared to healthy tissue, making it easier to see. This new technology has promising potential to improve cancer [..]
Read More
In-sensor computing allows image sensors with internal computing capabilities to reduce communication latency and power consumption for machine vision in distributed systems and robotics. Because of its tunable electrical and optical properties and amenability for heterogeneous integration, two-dimensional semiconductors have several advantages in creating intelligent vision sensors. Researchers have developed a multipurpose infrared image sensor [..]
Read More
Dual-detection impulsive vibrational spectroscopy (DIVS) is a Raman spectroscopy technique. It permits monitoring two types of vibrational signals simultaneously. It offers ultrafast, real-time spectral detection over the low-frequency, or terahertz area of the Raman spectrum and the fingerprint region at a rate of 24,000 spectra per second. The fingerprint and terahertz spectral areas provide complementary [..]
Read More
Increasing the acquisition speed of three-dimensional volumetric imaging is essential – particularly in biological imaging – to unveil specimens’ structural dynamics and functionalities in detail. In conventional laser scanning fluorescence microscopy, volumetric images are constructed from optical sectioning images sequentially acquired by changing the observation plane, limiting the acquisition speed. Researchers have developed a novel [..]
Read More
Researchers have significantly improved micro-computed tomography, specifically imaging with phase contrast and high brilliance x-ray radiation. They have developed a new micro-structured optical grating and combined it with new analytical algorithms. The new approach makes it possible to depict and analyze the microstructures of samples in greater detail and investigate a broad spectrum of samples. [..]
Read More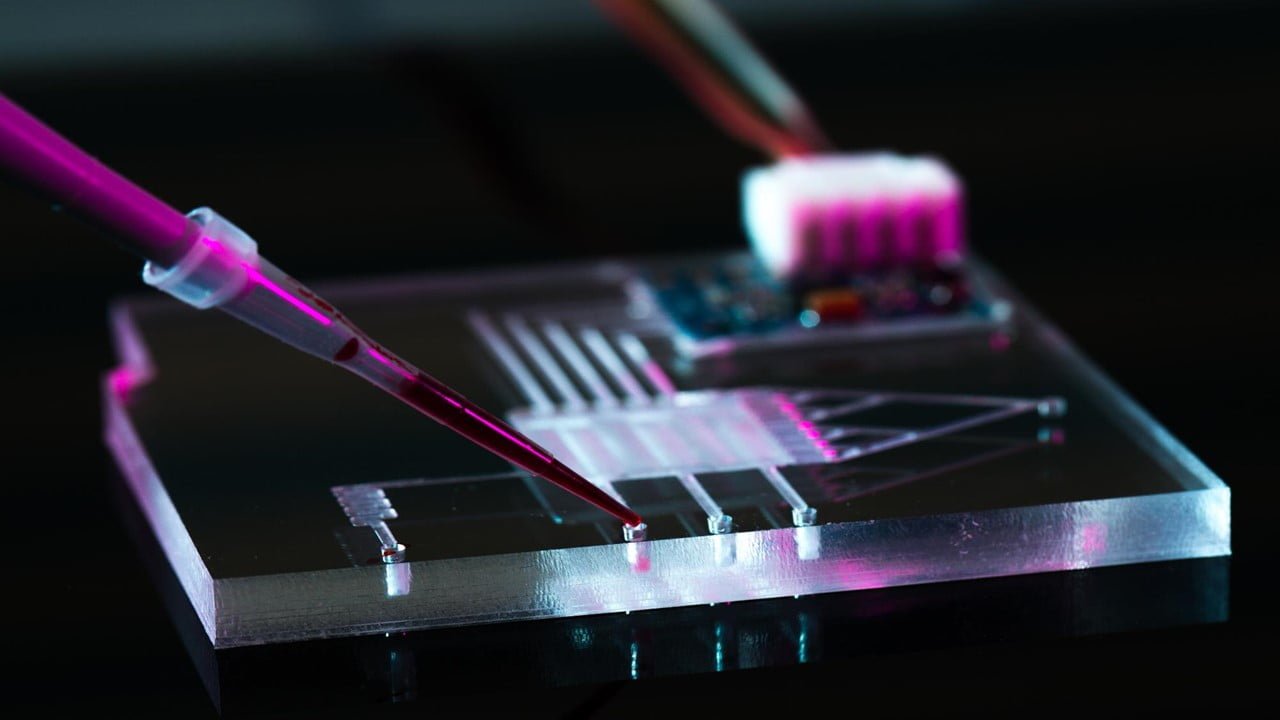
A research team developed a technique that uses condensation to noninvasively refill liquid marbles with water. The method could improve the viability of applications such as drug delivery. It could also establish improved opportunities for the droplet-size microreactors to see use in opto- and microfluidics. Liquid marbles are droplets of solution that wrap in a [..]
Read More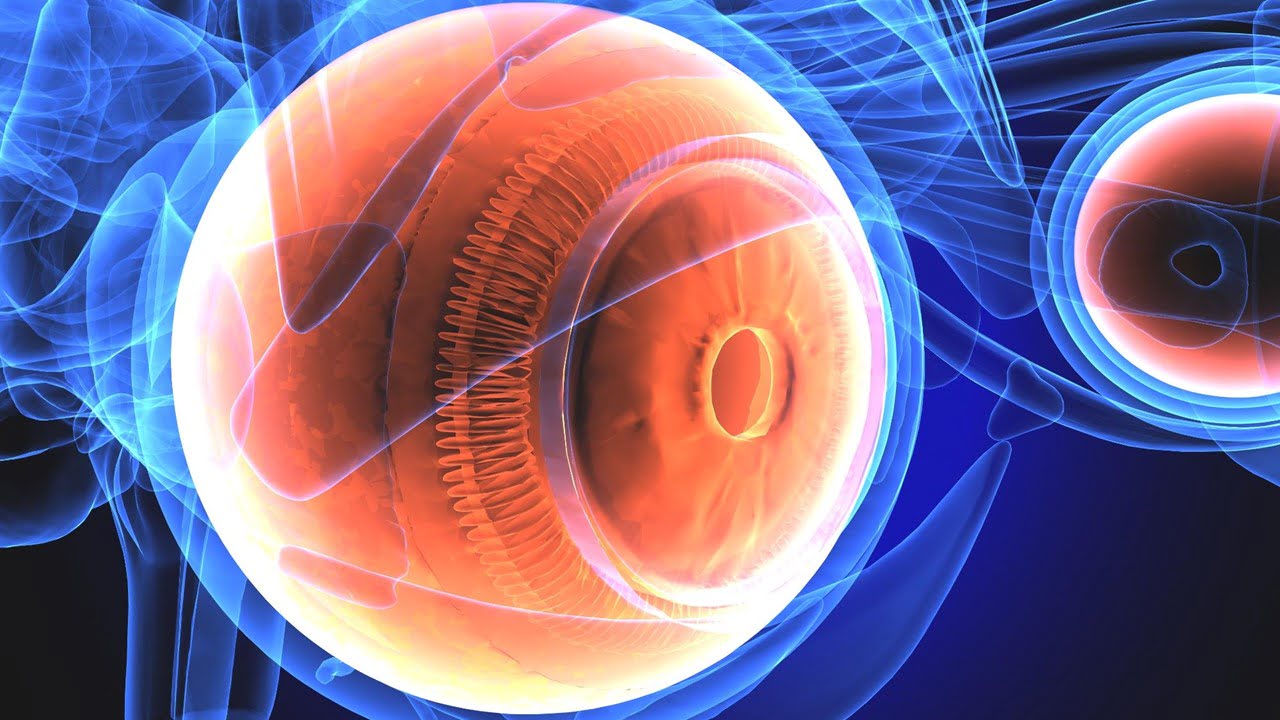
A study on ground squirrels shows, not only do mitochondria produce bioenergy in the cone-shaped photoreceptors in the retina of the eye, they also act as micro-lenses that redirect light to the tapering outer reaches of these cells where light is converted into electrical signals. The finding provides a clearer picture of the evolution and [..]
Read More
Lenses play a crucial role in the quality of the images produced by a machine vision system since they determine the sharpness of the image on the camera sensor. As lenses transmit light the first consideration is the light wavelengths used, as this has a major influence on both chromatic aberration and light transmission. This [..]
Read More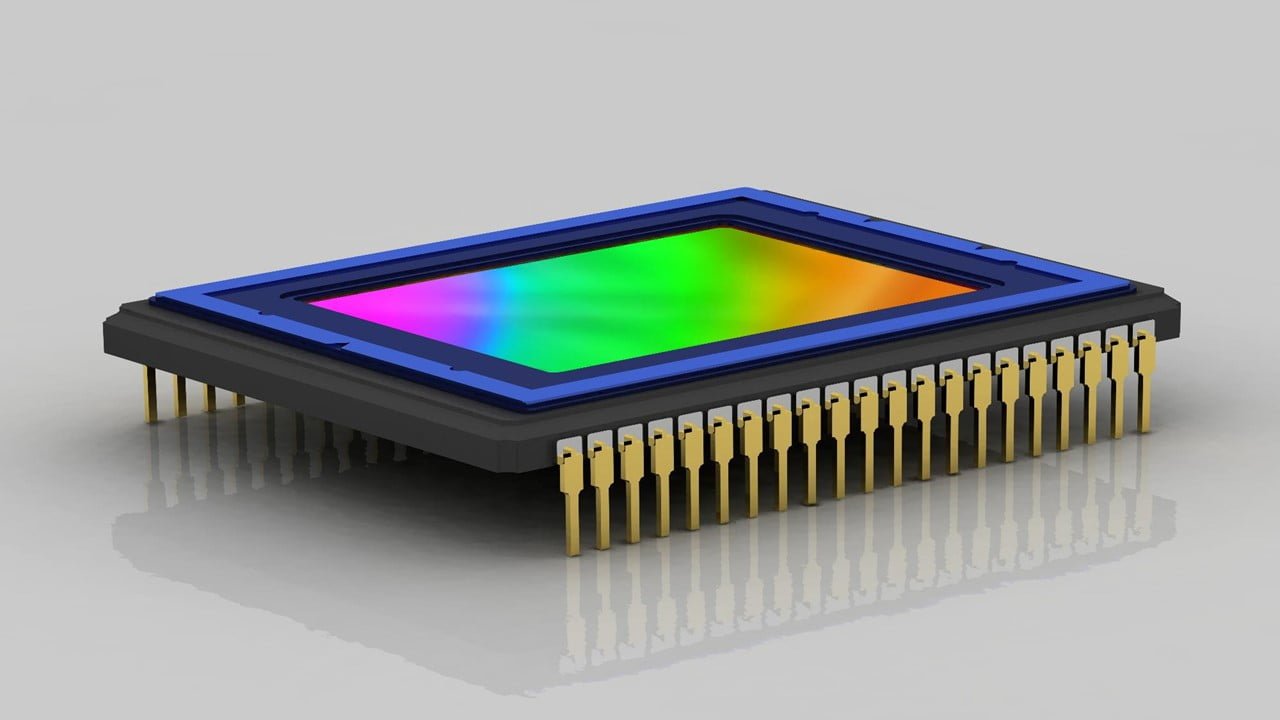
Raman spectroscopy is a powerful analytical technique that has been spotlighted for bacteria detection and diagnosis of diseases ranging from infection to cancer. However, as Raman signals are usually weak and can easily be swamped by interfering background signals, deploying Raman spectroscopy can be very challenging in the clinic. One solution to enhance the signals [..]
Read More
Researchers developed and tested a new blood vessel imaging approach that will allow investigators to capture images of blood vessels at different spatial scales, which will speed up imaging-based research in the lab. The “VascuViz” method, tested in mouse tissues, uses a quick-setting polymer mixture to fill blood vessels and make them visible in multiple [..]
Read More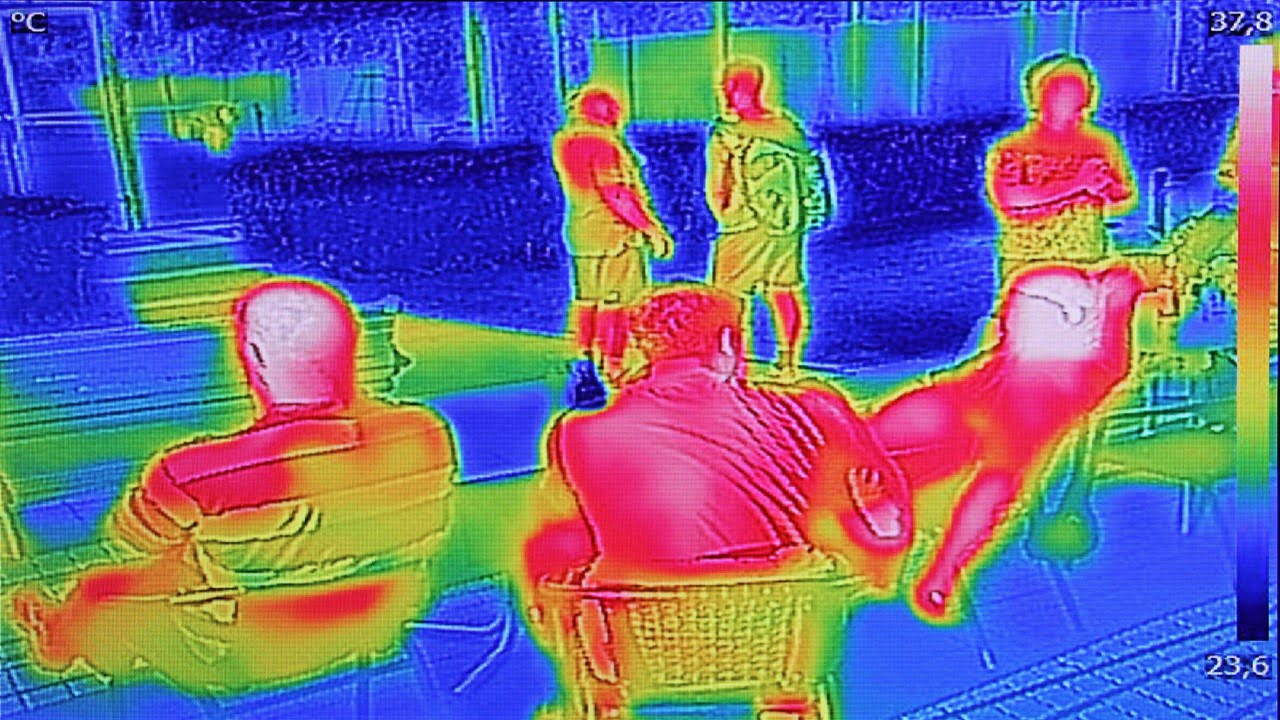
Researchers have invented a low-cost continuous fever screening system – SIFTER – based on an RGB-thermal camera. The system can automatically take temperature readings of people walking by, going about their own business, up to three meters away – no one has to stand in front of a camera for a few seconds to take [..]
Read MoreSince the earliest scientific developments, researchers have looked to nature as an inspiration source for designing novel functional devices. The so-called bioinspiration and biomimetic designs enabled the development of multifunctional sensors. Recently, researchers developed an ultrasensitive flexible optical waveguide sensor bioinspired in orb webs. They named it bioinspired multifunctional flexible optical sensor (BioMFOS). The multifunctional [..]
Read More
Nanopositioning systems move and arrange stages and samples with incredible precision at nanometer and sub-nanometer scales (motion control). They can position themselves within tens of nanometers and possibly even single-digit nanometers, making them ideal for applications requiring extremely precise measurement, such as space telescopes and microscopes. And the capabilities of nanopositioning systems go beyond that. [..]
Read More
Tunable focusing is a desirable property in many optical imaging and sensing technologies. Still, it traditionally requires bulky components that cannot be integrated on-chip and have slow actuation speeds. Integration of metasurfaces into electrostatic micro-electromechanical system (MEMS) architectures have recently shown promise in overcoming these challenges but has limited out-of-plane displacement range while requiring high [..]
Read More
The increasing demand for high-resolution and real-time recognition in radar applications has fueled the development of electronic radars with increased bandwidth, high operation frequency, and fast processing capability. However, the generation and processing of wideband radar signals place an additional hardware burden on complex and fast electronics, limiting its capability for high spatial resolution applications. [..]
Read More