
Researchers have created a self-calibrated photonic chip that builds bridges between data superhighways, revolutionizing the connectivity of current optical chips and replacing bulky 3D optics with a wafer-thin slice of silicon. This development can warp-speed the global advancement of artificial intelligence and offers significant real-world applications such as: autonomous vehicles that interpret their surroundings rapidly [..]
Read More
A new holographic platform generates realistic holographic patient scenarios for training purposes. The first module covers common respiratory problems and emergencies. Mixed reality is becoming more popular as a method of simulator training. As institutions scale their procurement, there is a growing demand for platforms that provide utility and ease of mixed reality learning management. [..]
Read More
Researchers have shown that a new mid-infrared spectrometer can precisely measure the ratios of different forms of water — known as isotopologues — in atmospheric water vapor through open air in a little over 15 minutes. The new open-path mid-infrared dual-comb spectrometer (DCS) uses near-infrared femtosecond laser pulses and specially designed waveguides to create broadband [..]
Read More
2D semiconductor materials are making their way into optoelectronic devices — the sort used in telecommunication. These devices have started to surpass the performance of conventional switches made with silicon and III-V semiconductors (compounds with elements from columns III and V on the periodic table). Optical computing, an early approach that was later abandoned in [..]
Read More
Metamaterials are artificial composites that can interact with electromagnetic waves, including visible light. Our brains generate electromagnetic waves as they process information. The brain waves can trigger changes in metamaterials. Not exactly like telekinesis and telepathy in science fiction, but the research can have applications in real-life scenarios. In a study, researchers used a brainwave [..]
Read More
Researchers have developed a nonlinear optical crystal-based compact terahertz (THz)-microfluidic chip with several I-design meta-atoms for attomole (amol)-level sensing of trace amounts of solution samples. The I-design meta-atoms consist of metallic strips with micrometer-sized gaps sandwiched by other metallic strips, periodically arrayed in a row of 1 × 5 units. A point THz source (locally [..]
Read More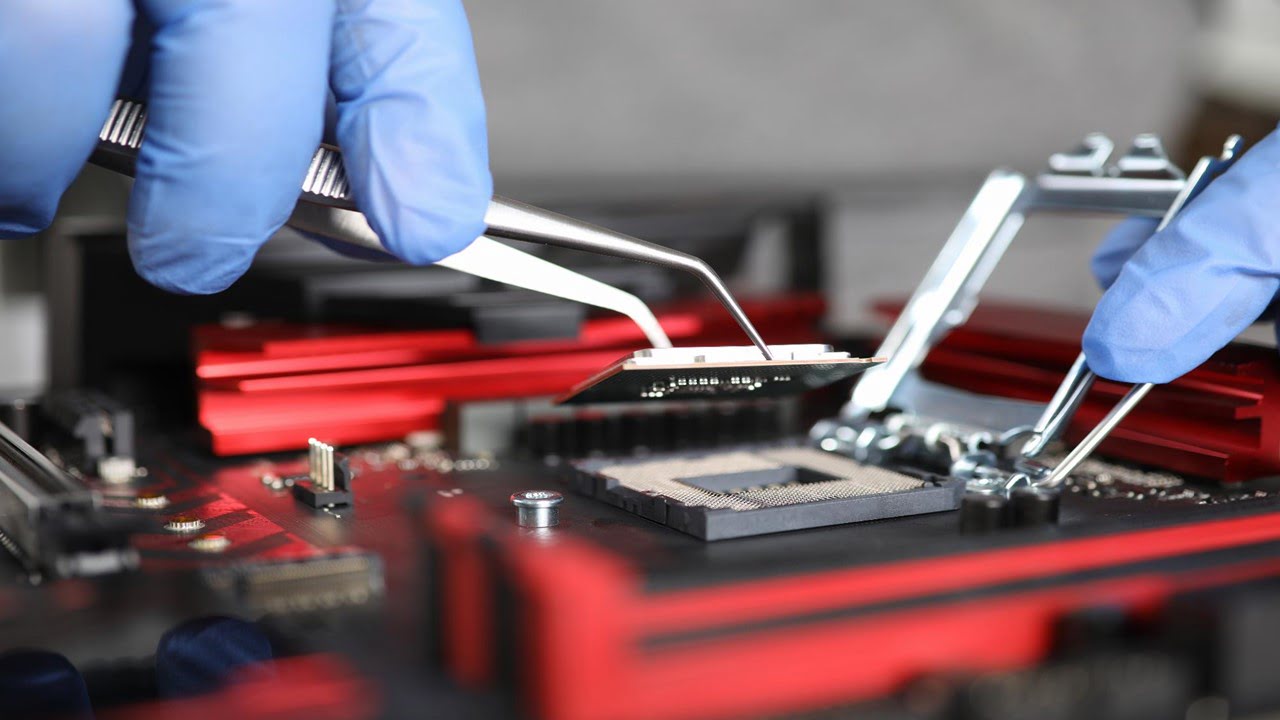
Lithium Niobate (LN) does not exist in the natural world and is a purely artificial inorganic material. It is composed of lithium, niobium, and oxygen. People usually refer to LN as a distorted perovskite type of crystal. LN has many unique features, such as a wide operational wavelength window, electro-optic (Pockels) effect, nonlinear optical polarizability, [..]
Read More
Researchers have built erbium-doped waveguide amplifier (EDWA) based on silicon nitride (Si3N4) photonic integrated circuits of a length up to a half-meter on a millimeter-scale footprint. The device generates a record output power of more than 145 mW. It provides a small-signal net gain above 30 dB, translating to over 1000-fold amplification in the telecommunication [..]
Read More
Researchers have developed a nanofluidic scattering microscopy technique to study biomolecules in their natural state. When developing medicines and vaccines, it is crucial to study individual proteins’ behavior and interaction with each other. The new microscopy method can help find the most promising candidates at an early stage. The technique also has the potential for [..]
Read More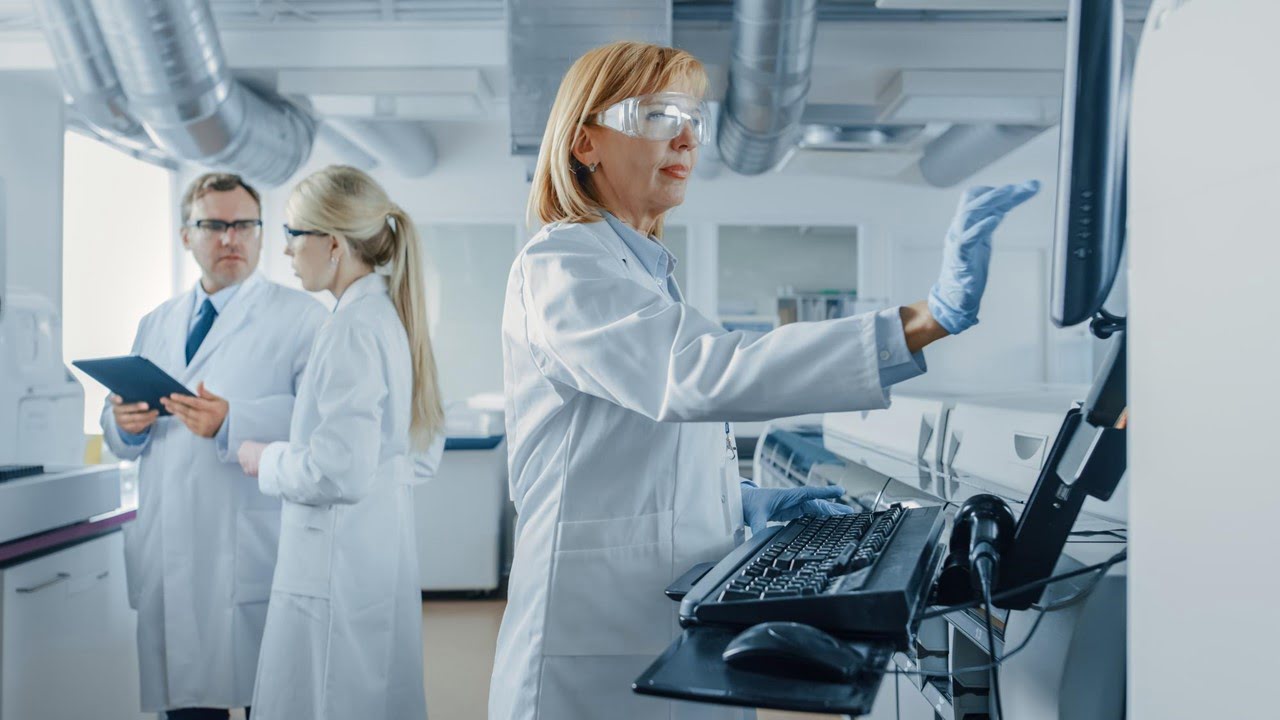
Imaging techniques are essential in cancer diagnosis and treatment, but their use remains limited in prostate cancer surgeries. Systematic prostate biopsies locate cancerous tissue and guide treatment. While magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) can yield greater insight into tumor characteristics, the extent to which it improves treatment outcomes needs a national scale. The new research demonstrates [..]
Read More
A novel somatostatin-receptor (SSTR) targeting peptide — 18F-SiTATE — has provided excellent imaging in meningioma patients, identifying bone involvement and lesions previously undetected on standard morphological imaging. The PET imaging agent, 18F-SiTATE, has a longer half-life and can be produced in large quantities by a cyclotron, which offers significant logistical advantages over the 68Ga-labeled ligands [..]
Read More
A new single-mode optical fiber made from sapphire rather than the usual silica can withstand temperatures of over 2000°C as well as high levels of radiation. Although the fiber’s length is currently limited to 1 cm, the technique used to construct it could be extended up to several meters, making it useful for remote sensing [..]
Read More
Scientists studied the implementation of neutron transmutation doping (NTD) to manipulate electron transfer. NTD is a controllable in-situ substitutional doping method. It utilizes the nuclear reactions of thermal neutrons with the nuclei of the atoms in semiconductors. The process provides a new way to dope 2D materials intentionally without extra reagents. Even after fabrication, it [..]
Read More
Researchers have developed a highly accurate and sensitive virus detection method using Raman spectroscopy, a portable virus capture device, and machine learning. The device could enable real-time virus detection and identification to help battle future pandemics. The new virus detection method is label-free and not aimed at any specific virus, thus enabling researchers to identify [..]
Read More
Researchers have developed a curvelet-based algorithm to quickly measure and reconstruct whole-brain vasculature and brain blood flow in mice. The work could enable future research into the neurovascular mechanisms underlying conditions like Alzheimer’s disease. The new approach deploys ultrasound technology to produce whole-brain images of animal microvasculature in just a few seconds. Instead of averaging [..]
Read More
Researchers have developed an enhanced version of optical coherence tomography (OCT scan) that can image biomedical samples at higher contrast and resolution over a wider 3D field of view than was previously possible. The new 3D microscope could be useful for biomedical research and enable more accurate medical diagnostic imaging. The researchers describe the new [..]
Read More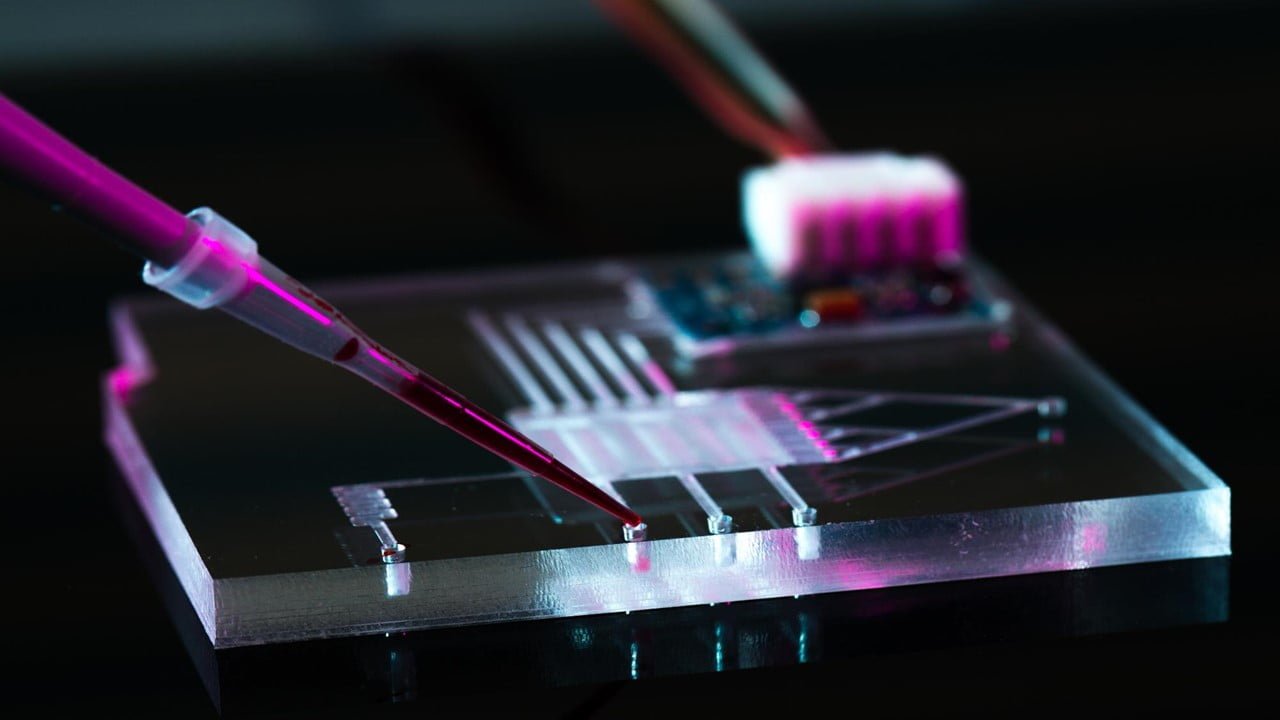
Microfluidic devices use tiny spaces to manipulate very small quantities of liquids and gasses by taking advantage of the properties they exhibit at the microscale. They have demonstrated usefulness in applications from inkjet printing to chemical analysis. They have great potential in personalized medicine, where they can miniaturize many tests that now require a full [..]
Read More
A progressive loss of central vision characterizes age-related macular degeneration (AMD). It is the commonest cause of blindness in the elderly. Intermediate AMD is a risk factor for progression to advanced stages categorized as geographic atrophy (GA) and neovascular AMD. However, rates of progression to advanced stages vary between individuals. Recent advances in imaging and [..]
Read More
Researchers have developed a new way to 3D-print glass microstructures that is faster and produces objects with higher optical quality, design flexibility, and strength. The researchers expanded the capabilities of a 3D-printing process they developed three years ago — computed axial lithography (CAL) — to print much finer features and to print in glass. They [..]
Read More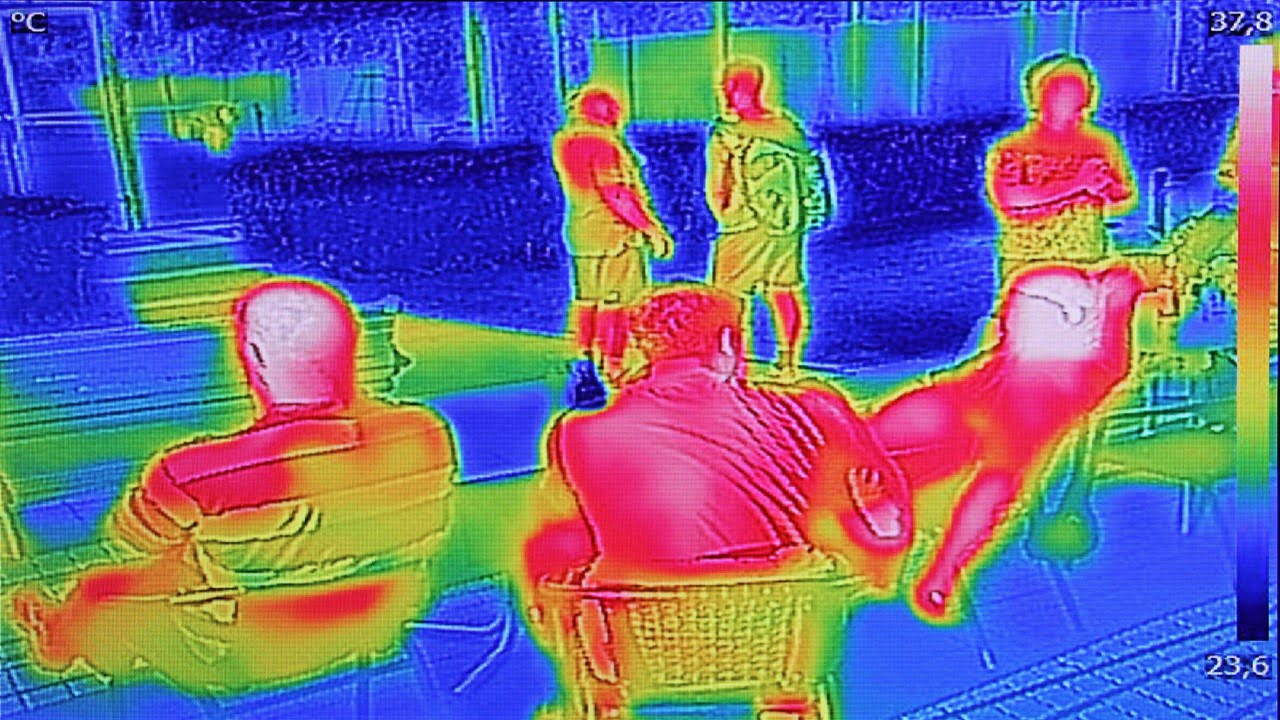
High-performance wavelength discrimination in the long-wave infrared region (LWIR) of the electromagnetic spectrum (wavelength range from 8 microns to 12 microns) is desirable for civilian and military applications. Of particular importance is to achieve on-chip passive thermal imaging with spectral filters, allowing remote target recognition without requiring any light source for illumination since objects emit [..]
Read More