Many specialists believe that a second quantum revolution is about to occur globally. The transistor and the laser were made possible by energy quantization, and the ability of humans to control individual atoms and electrons has the potential to revolutionize a variety of sectors, from communications and energy to medicine and defense. The quantum computer, [..]
Read More
The Nobel Prize-winning innovation of super-resolution microscopy, which allows imaging below the diffraction limit of light, has enabled some breathtakingly sharp views of tiny biological structures. However, it is not something you would find in a typical biology lab; instead, it necessitates sometimes using complex and expensive tools and extensive image post-processing. Researchers have developed [..]
Read More
A team of researchers at the Dresden University of Technology (TU Dresden; Dresden, Germany) has developed a self-calibrating lensless endoscope that produces 3D images of objects smaller than a single cell. Without a lens or any optical, electrical, or mechanical components, the tip of the endoscope measures 200 µm across. As a minimally invasive tool [..]
Read More
The protein aggregates known as beta-amyloid plaques, which develop in the brains of Alzheimer’s patients, impair numerous brain processes and have the potential to destroy neurons. They may also compromise the blood-brain barrier, a protective buffer between the bloodstream and the brain. Engineers have now created a tissue model that mimics the effects of beta-amyloid [..]
Read More
Since rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is an autoimmune disease in which the patient’s immune system attacks the lining of their joints, it is generally accepted that aggressive therapy administered within the first three months of the onset of symptoms enhances long-term outcomes for those with RA. Due to the pain, swelling, and damage caused by this [..]
Read More
According to the researchers, new two-photon microscopy can capture video of brain activity 15 times more quickly than was previously thought feasible, revealing voltage changes and neurotransmitter release over sizable regions and simultaneously monitoring hundreds of synapses. The new tool, known as scanned line angular projection microscopy, or SLAP, increases the efficiency of data gathering [..]
Read More
For the first time, researchers used a powerful microscopy technique in conjunction with automated image analysis algorithms to distinguish between healthy and metastatic cancerous tissue without using invasive biopsies or contrast dye. This novel non-invasive imaging approach could one day assist doctors in detecting cancer metastasis that is otherwise difficult to detect during operations using [..]
Read More
Researchers have demonstrated that Raman spectroscopy, an optical technique, can distinguish between benign and cancerous thyroid cells. The new study demonstrates Raman spectroscopy’s potential for improving thyroid cancer diagnosis, the ninth most common cancer in the United States, with over 50,000 new cases diagnosed yearly. The promising results indicate that Raman spectroscopy has the potential [..]
Read More
Researchers have created thin coatings that react mechanically and chromatically to specific vapors, drawing inspiration from the chameleon’s skin’s adaptive iridophores, or nanophotonic structures. According to the experts, the resulting “structural-color actuators” could be used for “sensing, communication, and disguise” in soft robotics. These actuators can move and change color in response to changes in [..]
Read More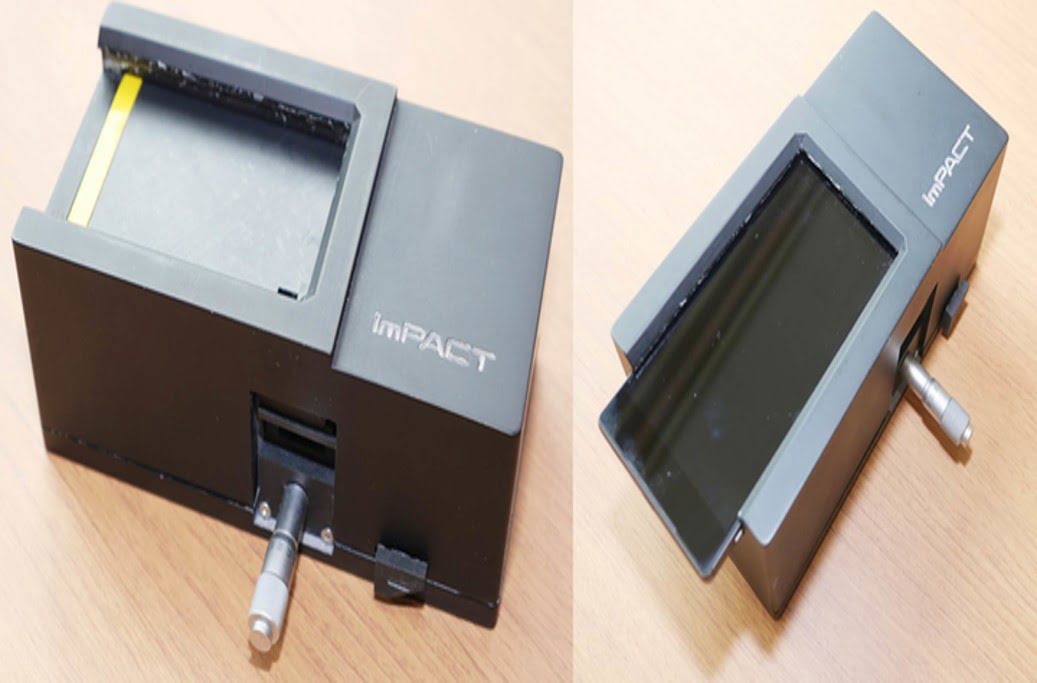
A team of researchers has created and tested a miniaturized virus-scanning system that uses inexpensive components and a smartphone because current methods to detect viruses and other biological markers of disease are efficient but large and expensive (such as fluorescence microscopes). While current tools are accurate at counting viruses, they are often too laborious for [..]
Read More
It is critical for patients with kidney failure who require dialysis to remove fluid at the correct rate and stop at the correct time. This usually entails estimating how much water to remove and closely monitoring the patient for any sudden drops in blood pressure. There is currently no reliable, simple method for measuring hydration [..]
Read More
Building an adjustable zoom lens in a millimeter-thick cell phone, a miniaturized microscope, or the distal end of a medical endoscope necessitates complex lenses that can handle the entire optical spectrum and be electrically reshaped within milliseconds. Researchers have demonstrated an adjustable technique for manipulating light without the use of mechanical movement, resulting in devices [..]
Read More
The noninvasive imaging of body organs through turbid biological tissues like skin and muscle is made possible by a novel bio-imaging method that combines ultrasound and optical processes. This newly created optical imaging technique may replace the need for intrusive visual examinations using endoscopic cameras. To examine and identify symptoms of deep tissue disease, invasive endoscopic [..]
Read More
Astronomers may soon be able to view galaxies, stars, and planetary systems in exquisite detail thanks to researchers’ development of an ultra-sensitive light-detecting system. The terahertz sensor operates at room temperature, an advance over comparable technology that can only operate at or near minus 454 degrees Fahrenheit. The terahertz sensor generates images with extremely high [..]
Read More
Majorana photons, a new superclass of photons, may improve information on quantum-level transitions and brain images and their workings. A research team based their findings on that photons can take various forms while possessing important properties such as polarization, wavelength, coherence, and spatial modes. The team aimed to use a special super form of photons [..]
Read More
To detect train acceleration and vibration, researchers have created new sensors. The technology could be combined with artificial intelligence to stop serious train derailments and rail mishaps. According to the researchers, railway accidents cause serious injuries and occasionally yearly fatalities. The fiber optic accelerometers could detect real-time issues with the train or railway track and [..]
Read More
Researchers are developing a novel technique that may help magnetic memory systems use less energy and operate more quickly. The technique combines spintronic and photonic materials to manipulate the spin orientation of magnetic materials and uses ultrashort laser pulses to produce strong magnetic fields. They have developed a novel magneto-photonics effort to use light to [..]
Read More
Researchers have displayed a flexible, stretchable optical fiber that functions as a biocompatible temperature sensor by receiving light impulses from embedded upconversion nanoparticles. The research team thinks fiber might provide an intriguing platform for creating real-time wearable temperature sensors for robotics and personal health care. Wearable sensors must be pliable enough to bend and stretch [..]
Read More
A ground-breaking imaging technique created by researchers offers hope for cleaning up water by providing unexpected and crucial data about catalyst particles that can’t be obtained in any other manner. They have created a technique to capture images of catalytic nonfluorescent reactions, or processes that don’t produce light, on nanoscale particles. The new technique could [..]
Read More