
Using a particular kind of light beam (polarization of light) to stimulate certain exotic materials has led a team of scientists to discover that an identically asymmetrical pattern can be produced and measured at will in these materials. In this instance, the “handedness” phenomenon—known as chirality—occurs in the abundance of electrons within the substance rather [..]
Read More
According to project managers, Galahad, a Horizon 2020 research project creating an OCT platform for enhanced early glaucoma screening, has successfully finished its job. The three-year program to create ultra-high resolution polarization-sensitive optical coherence tomography, called Galahad, from Glaucoma Advanced, LAbel-free High resolution Automated OCT Diagnostics, has ended. (UHR-PS-OCT). By utilizing only OCT volumes focused [..]
Read More
The results of a successful demonstration of a lensless on-chip microscopy platform by a biomedical engineering lecturer at a university have been published in Lab on a Chip. He claims that his ptychography platform offers a low-cost alternative for disease detection while removing several of the most prevalent issues with traditional optical microscopy. The platform [..]
Read More
Researchers have equipped a normal optical microscope with infrared (IR) capabilities to perform digital biopsies for cancer diagnosis. They developed digital biopsies that did better than cutting-edge infrared microscopes. They closely correlated with conventional pathology procedures by combining IR measurements with high-resolution optical images and machine learning methods. The benefit is that the chemistry and [..]
Read More
These quickly expanding industries, including big data centers, Industry 4.0, and personalized healthcare, have one thing in common: they require miniaturized photonic components. These integrated or miniature photonic parts provide methods for sensing, transmitting, and processing data. Integrated photonic component production, alignment, and assembly technologies are constantly developing. Markets and manufacturers are frequently tiny, making [..]
Read More
Noise is a constant issue in traditional sensing techniques, particularly in systems designed to notice changes in their environment that are barely larger or smaller than the noise in the system. Scientist Said Rodriguez devised a solution after running into this issue in his tests with interacting photons. In a paper, he shows how noise [..]
Read More
Scientists have been working to create processors that operate on light instead of electric currents for many years. Finding an appropriate nonlinear process to perform the optical equivalent of a transistor’s switching has proven to be one of the biggest challenges. But now, a joint research effort thinks it may have the solution: a specially [..]
Read More
In many cases, by forming nanostructures on the surface, direct laser processing of material surfaces is a powerful method for changing those materials’ optical (light absorption) and electrical properties. The aspect of random chance that affects the size and geometry of the small-scale structures themselves has made it difficult to regulate precisely those surface modifications [..]
Read More
Semiconductor quantum dots (QDs) may power various optical devices that produce light in the near- and mid-infrared (IR) spectral ranges. But basic physical constraints reduce the power of IR-emitting QDs. According to Fermi’s golden rule, the quantum yield of such QDs declines at longer wavelengths as the radiative emission rate falls, while nonradiative recombination channels [..]
Read More
Using pseudo-random speckle patterns to image targets is efficient (high-resolution imaging), but most approaches require bulky, expensive, complex, and slow machinery. A smaller device capable of generating random speckles is required to apply this technique to biomedical imaging, such as ultra-thin endoscopy or in vivo neural imaging. A group of scientists demonstrated using a multimode [..]
Read More
The creation of 3-D images and range detection has been proven by researchers using stacked, transparent graphene photodetectors in conjunction with image processing methods. The feasibility of a 3D camera that can deliver superior three-dimensional imaging while calculating how far things are from the lens has been established by researchers. Robotics, autonomous vehicles, and 3-D [..]
Read More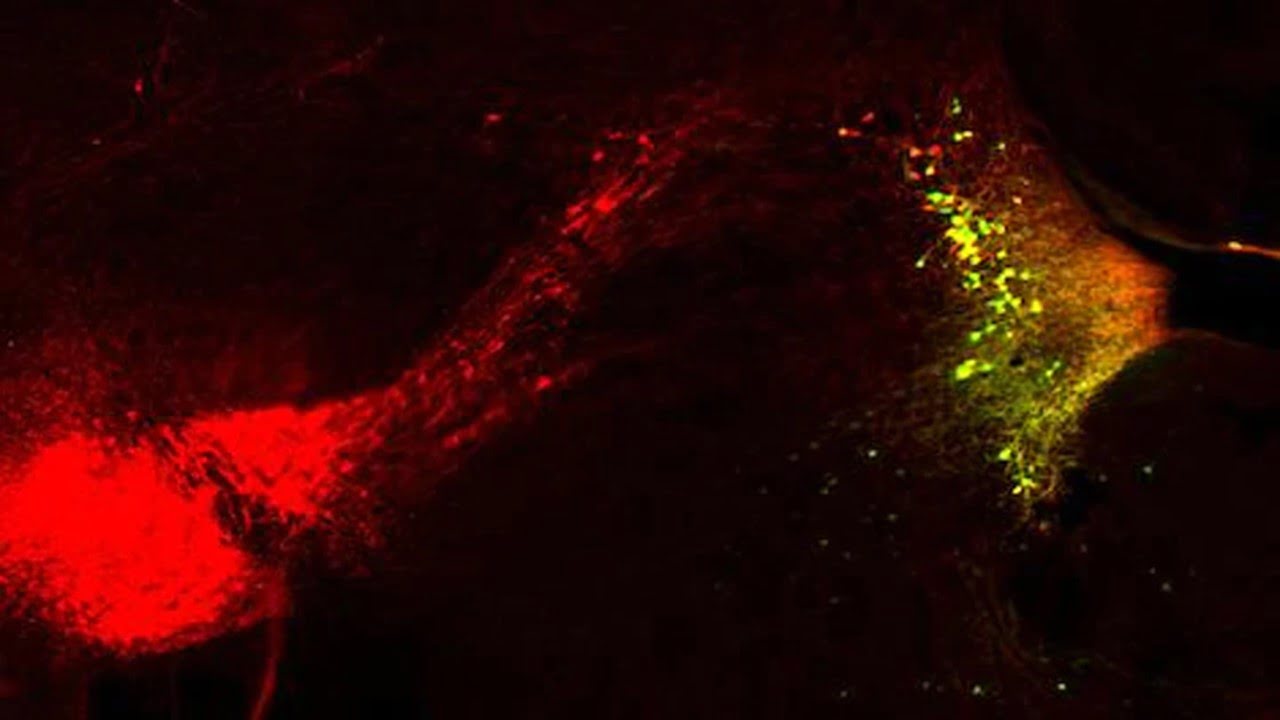
Sustained concentration (also known as vigilance) produces a different type of memory than a momentary startle, and these differences are linked to different signaling molecules in mice brains. Researchers used optogenetics neuroscience to help visualize these dynamics in the living mouse brain, observing fast and slow molecular pathways that support memory function. These processes occur [..]
Read More
While living tissue significantly attenuates and scatters visible light, attenuation, and scattering are less for two spectral regions at slightly longer wavelengths. The first and second near-infrared (NIR) windows refer to these frequencies. Although labels emitting in the NIR-II band are challenging, this band is especially attractive. A group of scientists has created an organic [..]
Read More
The diagnosis of sepsis must be made quickly, but the tests presently used to do so can take up to 72 hours. Researchers have created an optical detector that can diagnose sepsis in minutes instead of several days. The portable biosensor uses digital plasmonic imaging, in which nanoparticles have improved. An optical metasurface made of [..]
Read More
A research team has created a low-cost colloidal quantum dot photodetector that can sense long-wave infrared (IR) light and may eventually replace more expensive commercially available options. According to the researchers, the new technology closes a gap in the photodetection spectrum and may be helpful for environmental monitoring, food inspection, and gas analysis. With silicon [..]
Read More
Non-line-of-sight imaging (NLoS), which is the task of recovering image data from objects hidden from direct observation or hidden by corners, can be approached in several ways, frequently requiring techniques to recover data from highly scattered or diffuse optical signals. In recent years, methods for reconstructing images using the intrinsic spatial correlations encoded in scattered [..]
Read More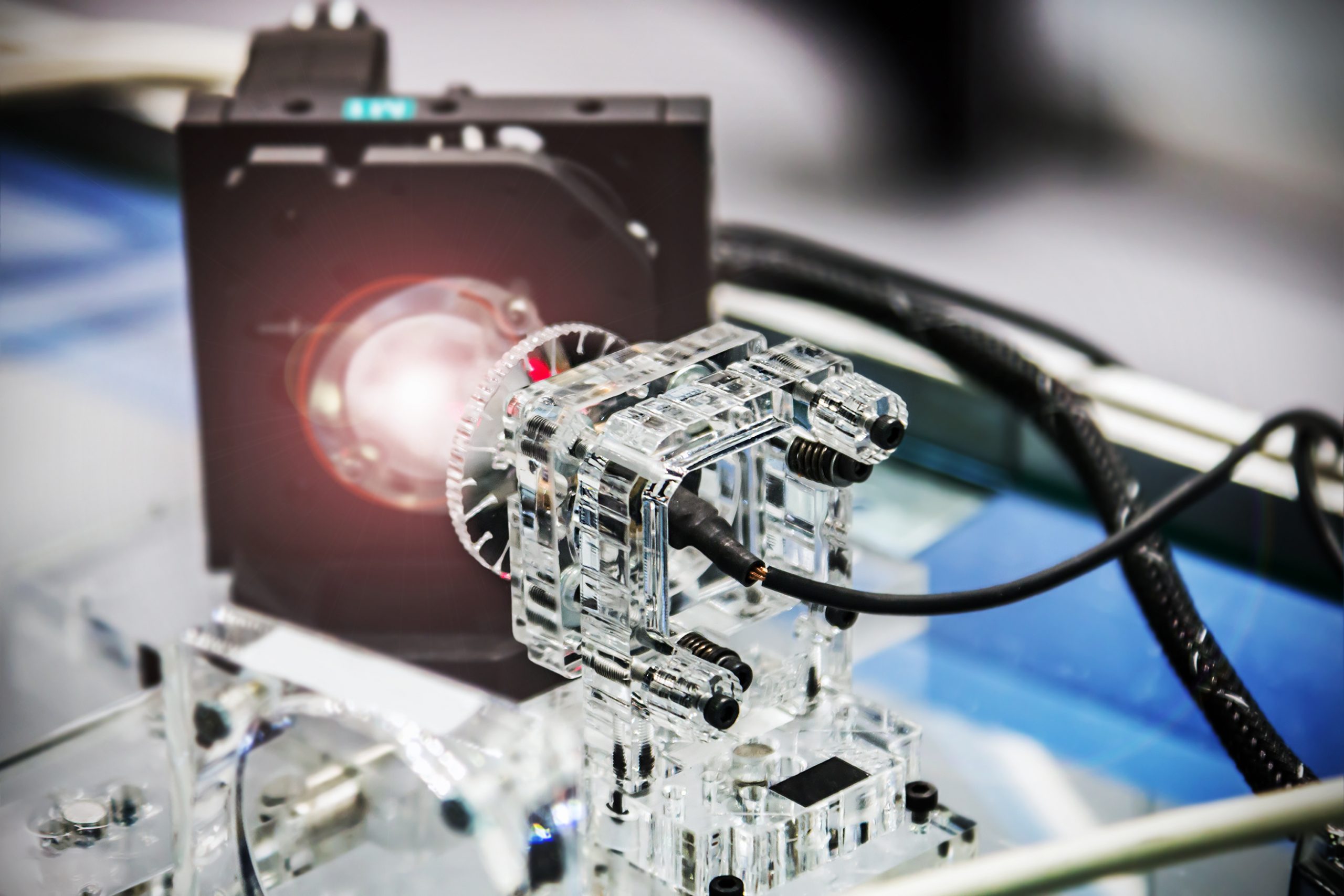
Researchers have created a method for turning a regular optical substance into a frequency doubler using light. The method could be used to investigate quantum-mechanical tunneling and build all-optical information processing devices. An optical phenomenon known as frequency doubling occurs in radially asymmetric materials with a second-order nonlinear susceptibility. One photon with a frequency twice [..]
Read More
To treat, identify, or keep track of GI disorders, a variety of medical devices can be inserted into the gastrointestinal system. Once they have completed their task, many of these must be removed through invasive surgery. Engineers have now devised a method to cause the internal decomposition of such devices when they are subjected to [..]
Read More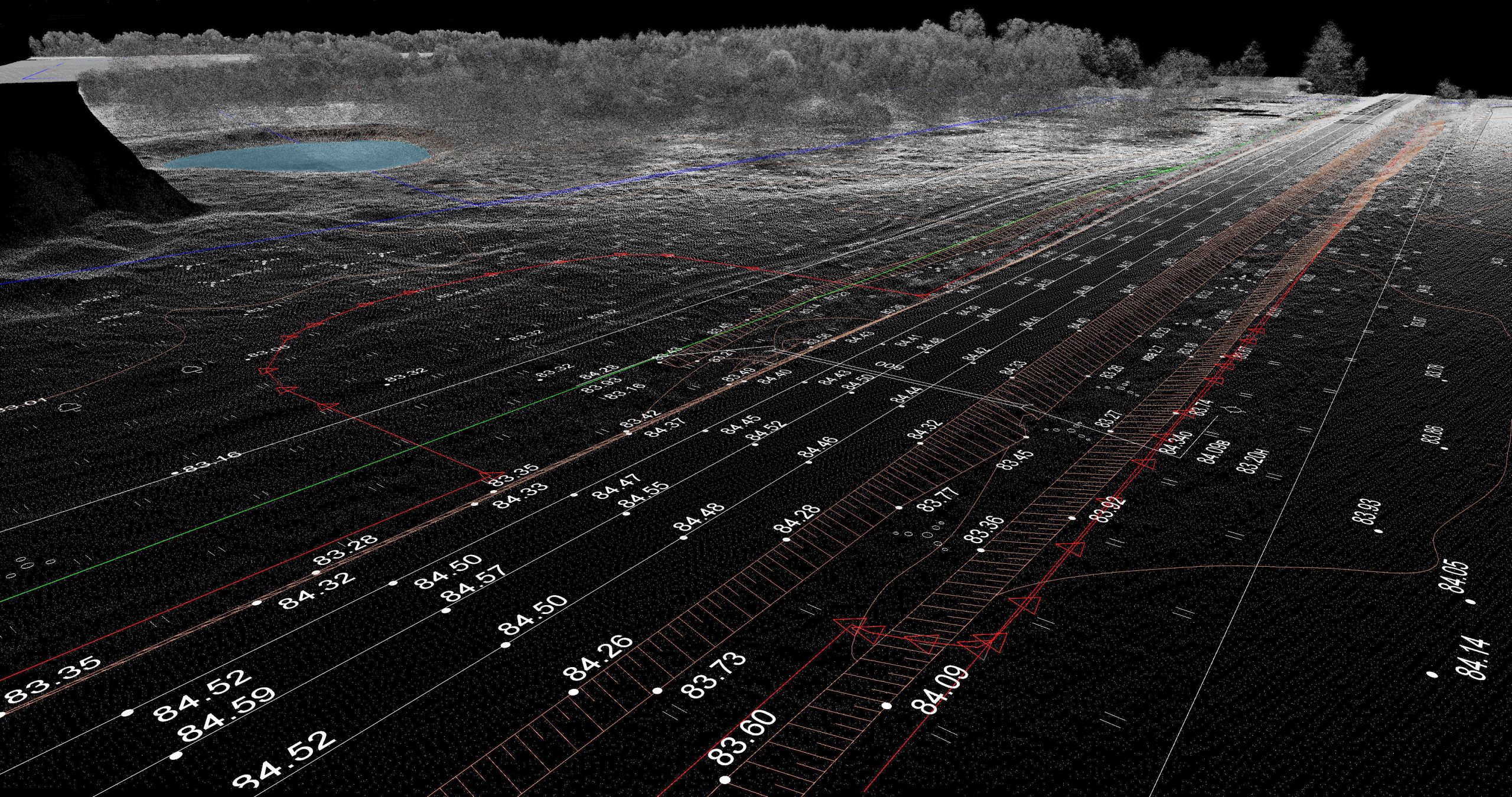
Particularly when it comes to a 3-D scanner in cutting-edge technology, faster is sometimes better. Researchers are working to create a 3-D lidar sensor that is portable and simple to use, with uses in autonomous vehicles, robots and drones, security systems, and more. In a field where speed is frequently valued above other factors, researchers [..]
Read More
Accurate identification and segmentation of choroidal neovascularization (CNV) are crucial for detecting and treating exudative age-related macular degeneration. (AMD). Cross-sectional and en-face imaging of CNV is possible with PR-OCTA or projection-resolved optical coherence tomographic i.e., OCT angiography. Due to the persistence of residual artifacts, CNV segmentation and detection remain challenging even with PR-OCT Angiography. In [..]
Read More