
Researchers have developed a quantum sensing method using a nitrogen-vacancy (NV) center in single nanodiamond sensors, enabling the identification and evaluation of molecules in physiological in situ settings, a crucial goal in biological sciences. This method offers high sensitivity and biocompatibility. However, analyzing the movement of nanodiamonds in real cells reveals that they rotate at [..]
Read More
Modern computer models, such as those used in complicated, powerful AI applications, test the limits of classical digital computer operations. New computing architectures that mimic the operating principles of biological neural networks promise quicker, more energy-efficient data processing. A group of researchers has created an event-based architecture that uses photonic processors to transfer and analyze [..]
Read More
In medical diagnostics, artificial intelligence (AI) is already widely employed. In a realistic clinical environment, a research team studied how it benefits the diagnosis and management of pigmented skin lesions. The team evaluated the accuracy of two separate algorithms in smartphone applications in diagnosis and therapy suggestions to that of doctors in a study. The [..]
Read More
Low-frequency noise, ubiquitous in cities, roadways, and airports, can cause earaches, respiratory impairment, and irritation. Pingpong balls, typically hollow plastic balls, can assist in absorbing this noise, which is difficult to prevent due to its diverse sources and shapes. The researchers describe an acoustic metasurface that uses pingpong balls as Helmholtz resonators to provide low-frequency [..]
Read More
Rapid antimicrobial prescriptions are required when viable bacteria are in the blood or bacteremia, which can result in sepsis and bloodstream infection (BSI). Due to the lengthy nature of traditional antimicrobial susceptibility testing (AST), clinicians must rely on experience. In comparison to conventional approaches that take two days, researchers have created a BSI-AST chip for [..]
Read More
Because of its significant optical nonlinearity, wide transparency window, and strong electro-optic coefficient, thin-film lithium niobate (TFLN) presents a viable platform for integrated photonics. However, to fully utilize TFLN, additional lasers and photodetectors are necessary. Researchers merged a modified uni-traveling carrier photodiode wafer to improve bandwidth and responsiveness onto a TFLN wafer. LN waveguides and [..]
Read More
Using reconstruction methods, researchers created an MSOT scanner that gathers sound waves and translates them into images. MSOT imaging, a medical imaging technology, can potentially diagnose and assess various disorders. Its processing time could be more feasible in clinical settings. Fast and low-quality picture reconstruction is possible with MSOT imaging methods. Long processing periods are [..]
Read More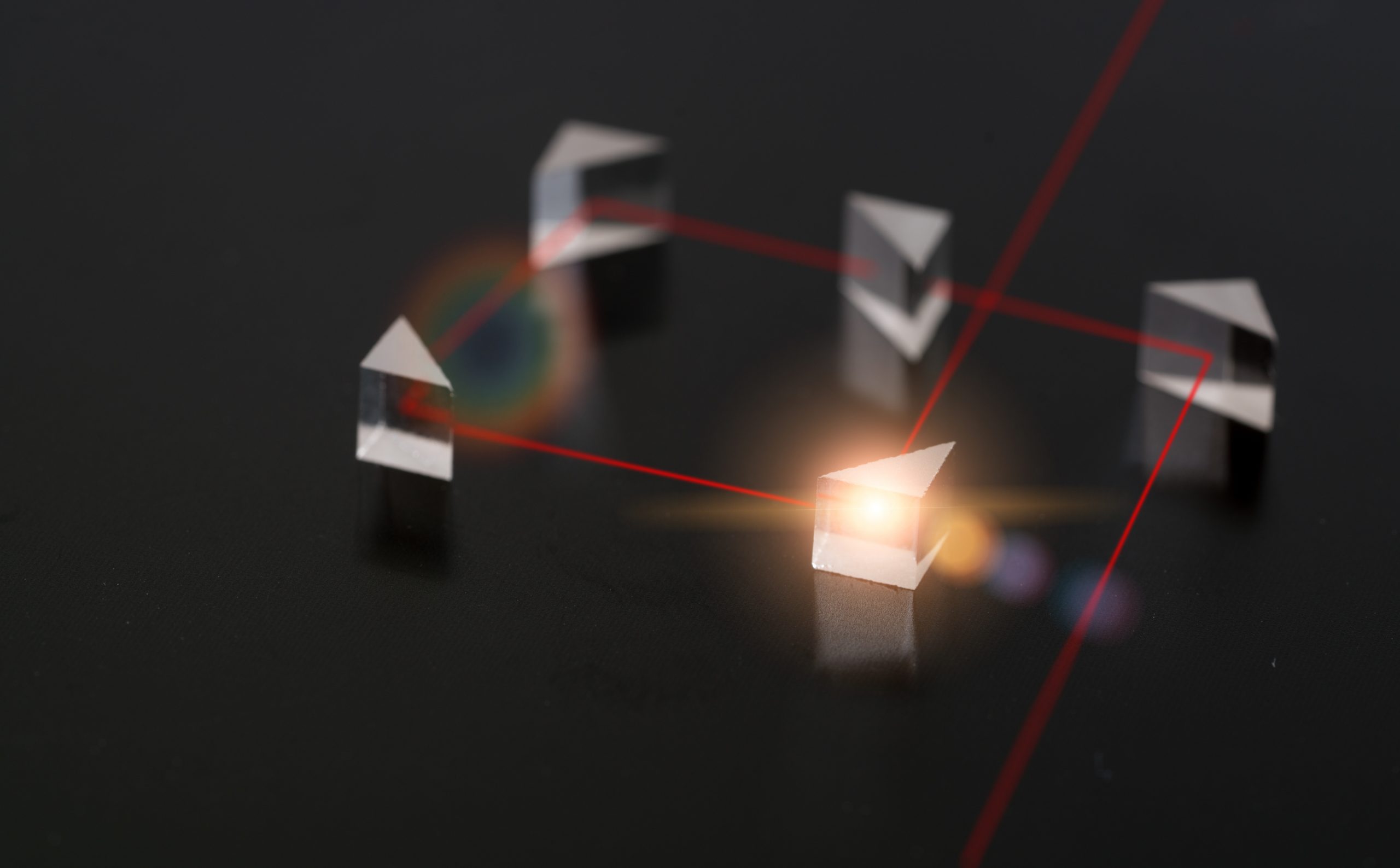
Researchers’ creation of a palm-sized, all-glass femtosecond laser cavity has opened a new path toward free-space femtosecond lasers. Its design defies standard procedures because of its exact component alignment and downsizing. The innovation consists of micromachining a holder for optical components and separating flexural elements into a glass substrate using a commercial femtosecond laser. Using [..]
Read More
Polarimetric imaging, which considers the polarization of light in every pixel of an image, can provide a fuller view of an object than traditional cameras. Polarized light, made of electromagnetic waves, travels along a single plane or on a rotating plane. This technology can reveal information the human eye may miss, such as pointing out [..]
Read More
Researchers have created an optomechanical platform for superconducting circuits exhibiting high-fidelity quantum control and ultra-low quantum decoherence, the longest quantum state lifetime in a mechanical oscillator ever obtained results from their ground-breaking work with a “vacuum-gap drumhead capacitor,” opening up new possibilities in quantum computing and sensing. The challenge for optomechanical systems operating in the quantum [..]
Read More
Researchers have created a wearable optical device to detect bleeding during or after delivery early. This severe, profuse bleeding, responsible for about 30% of maternal fatalities worldwide, can be difficult to identify before it becomes an emergency. According to studies, the greatest strategy to avoid mortality from postpartum hemorrhage is to diagnose and treat the [..]
Read More
Scientists create computer models of the patient’s eyes to choose the best intraocular lenses and visual simulators for patients to experience what they would see with them. Researchers built computational eye models using the corneas of patients who had undergone LASIK surgery to understand better how conventional intraocular lenses and lenses intended to improve depth [..]
Read More
Researchers’ new technique, which enhances conventional machine vision and perception, is improving the field of robotics and autonomy. They have created heat-assisted detection and ranging, or HADAR. Conventional active sensors that gather three-dimensional data, such as LiDAR, radar, and sonar, have disadvantages such as interference and potential eye safety hazards. Conventional thermal imaging is a [..]
Read More
To enhance medical imaging, a group of researchers has created a novel method called quantitative photoacoustic tomography, or QPAT. QPAT is an imaging modality that combines optical tomography with ultrasonography, an imaging method that employs sound waves to view characteristics inside the body. It uses data on the strength of acoustic waves as detected on [..]
Read More
Two entangled light particles were seen in real-time by scientists using a first-of-its-kind method, giving rise to the striking quantum “yin-yang” sign. Future quantum experiments might be greatly accelerated by the new technique known as biphoton digital holography, which makes use of an ultra-high-precision camera. Two photons can become irrevocably linked by a relationship called [..]
Read More
Using a cascaded architecture of gas-filled hollow-core fiber (HCF), bare lithium niobate (LN) crystal plate, and a specially designed chirped periodically poled lithium niobate crystal (CPPLN), researchers have demonstrated four-octave-spanning intense ultraviolet-visible-infrared (UV-Vis-IR) full-spectrum laser source with the energy of 0.54 mJ per pulse. The HCF-LN system can produce an intense one-octave bandwidth mid-IR laser [..]
Read More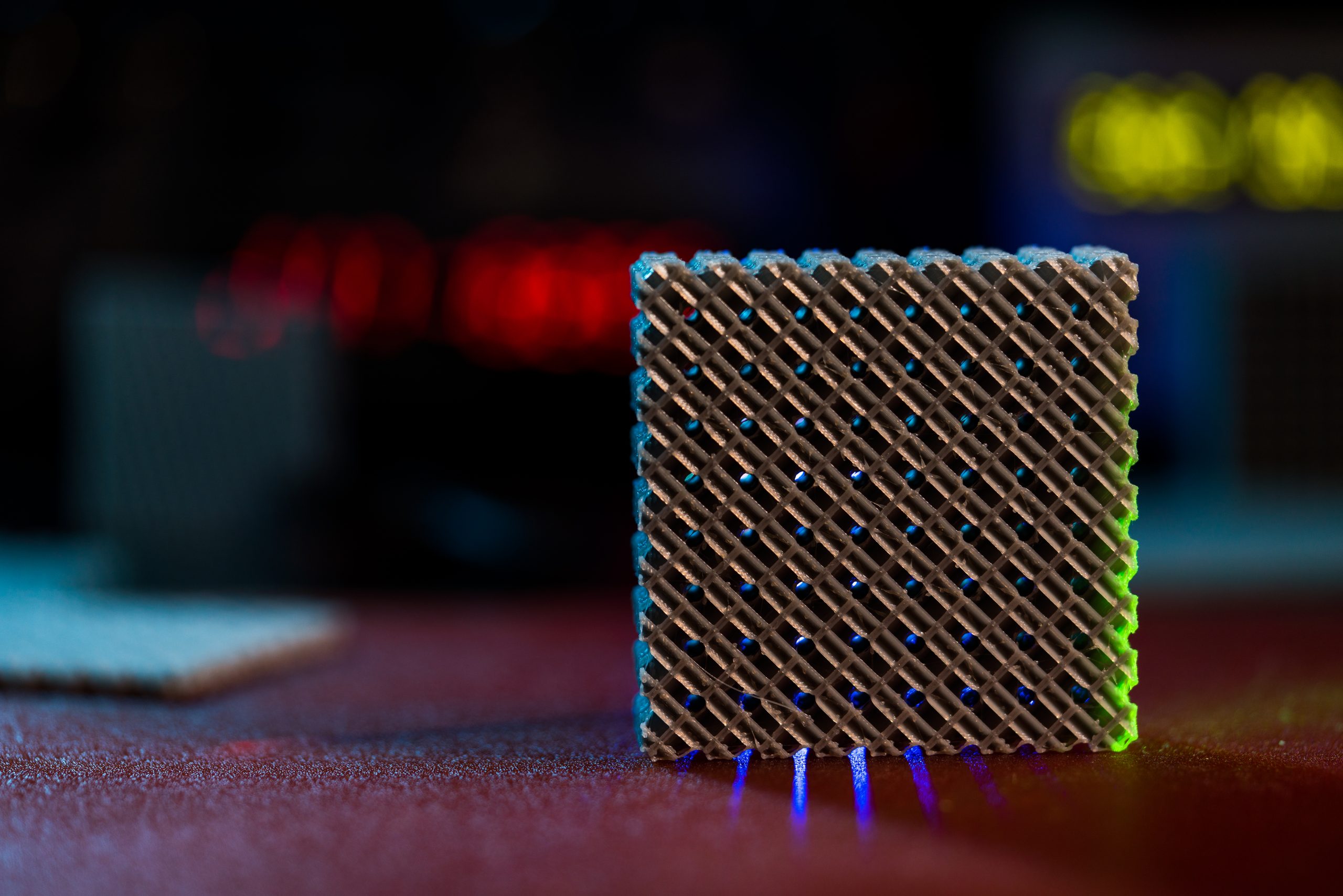
To minimize the thickness of a camera lens and enable the fabrication of a high-resolution and high aspect ratio metasurface, a team created a water-soluble mold. This development has the potential to completely change smartphone camera technology, despite difficulties, including high production costs and complicated procedures. Nanoimprint lithography and electron beam lithography are two important [..]
Read More
Recent patent approvals provide insight into anticipated improvements to future mixed-reality (MR) headsets. The patents highlight the commitment to user security and technical innovation by describing a multi-camera biometric imaging system and an automated selection procedure for the best biometric data. The patent for a multi-camera biometric imaging system describes the use of many cameras [..]
Read More
Researchers created a nanosecond-scale volatile modulation system combining a phase-change material as a breakthrough for optical computing. The requirement for processing capacity has risen due to developments in computer vision and autonomous driving. The power and size constraints on current optical computer circuits have prompted the development of nonvolatile integrated photonics. Phase-change materials (PCMs) have [..]
Read More
Because of their distinctive porous atomic structures, zeolites are utilized in various industrial applications as catalysts, ion exchangers, and molecular sieves. However, because of poor electron irradiation resistance, direct study of zeolitic local atomic structures by electron microscopy is challenging. Their essential structure-property correlations are, therefore, yet uncertain. Optimal bright-field scanning transmission electron microscopy (OBF [..]
Read More