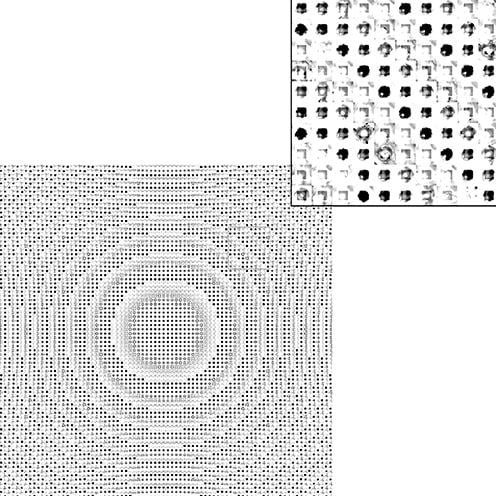
Researchers have developed a new mathematical technique that quickly determines the ideal makeup and arrangement of millions of individual, microscopic features on a metasurface, to generate a flat lens that manipulates light in a specified way. Previous work attacked the problem by limiting the possible patterns to combinations of predetermined shapes, such as circular holes [..]
Read More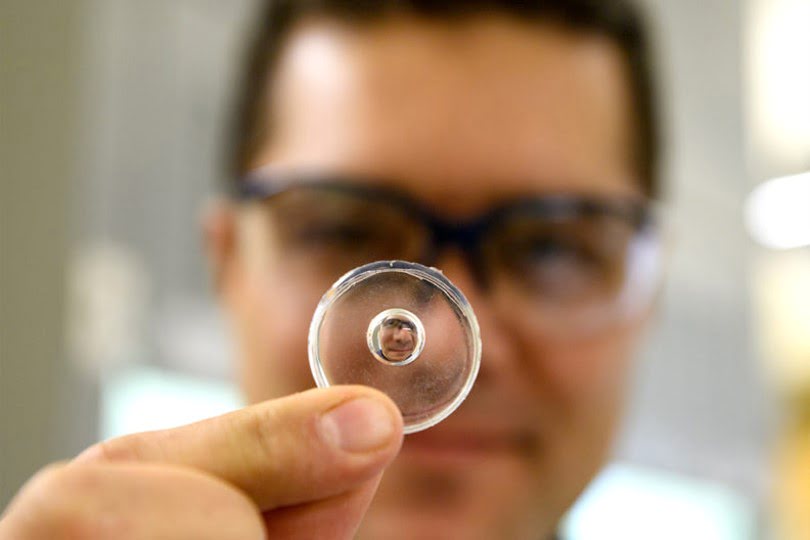
Researchers have developed a low-cost, easy way to make custom lenses that could help manufacturers avoid the expensive molds required for optical manufacturing. The researchers developed a liquid mold from droplets that they can manipulate with magnets to create lenses in a variety of shapes and sizes. High-quality lenses are increasingly used in everything from [..]
Read More
Researchers have developed a new biopsy technique that uses pulses from two kinds of lasers to take pictures of microscopic biological structures. The new biopsy technique, called ultraviolet-localized mid-infrared photoacoustic microscopy, or ULM-PAM, develops images of the microscopic structures found in a piece of tissue by bombarding the sample with both infrared and ultraviolet laser [..]
Read More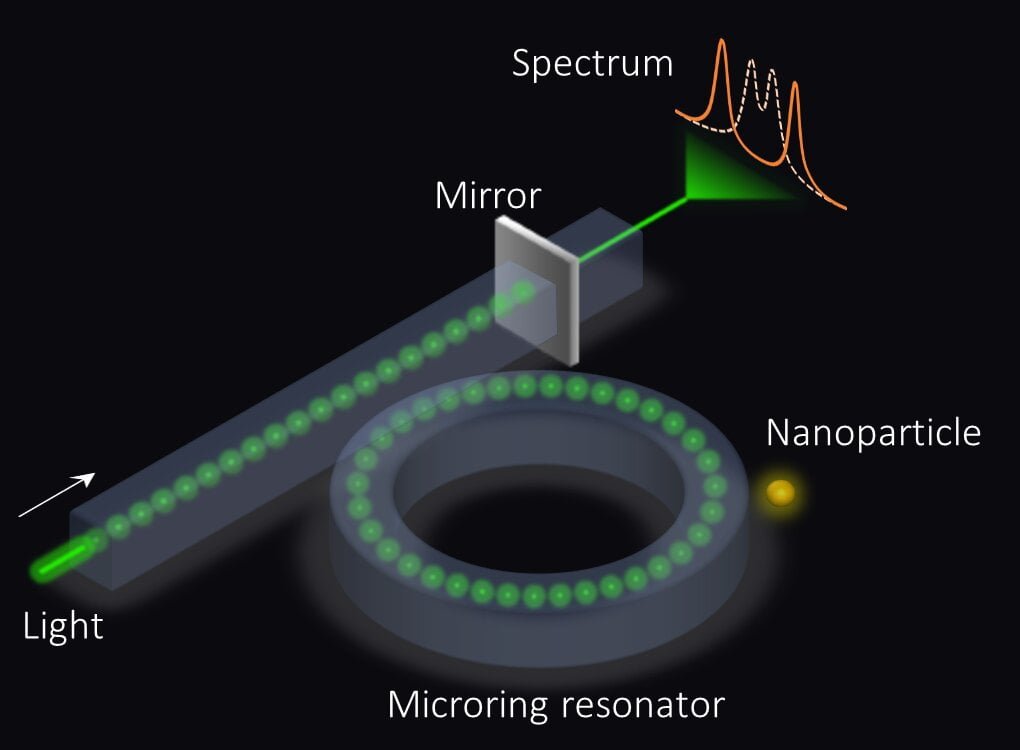
Physicists and engineers propose a new type of sensor. They are based on the new notion of exceptional surfaces: surfaces that consist of exceptional points. In order to understand the meaning of exceptional points, consider an imaginary violin with only two strings. In general, such a violin can produce just two different tones — a [..]
Read More
After decades of patient quantum computer science groundwork, the notion of “quantum computing” has, in the past several years, seen a surge in new activity and interest—not only in the lab, but at commercial firms, and even among the public at large. Spurring that new interest has been successful lab demonstrations of systems and simulations [..]
Read More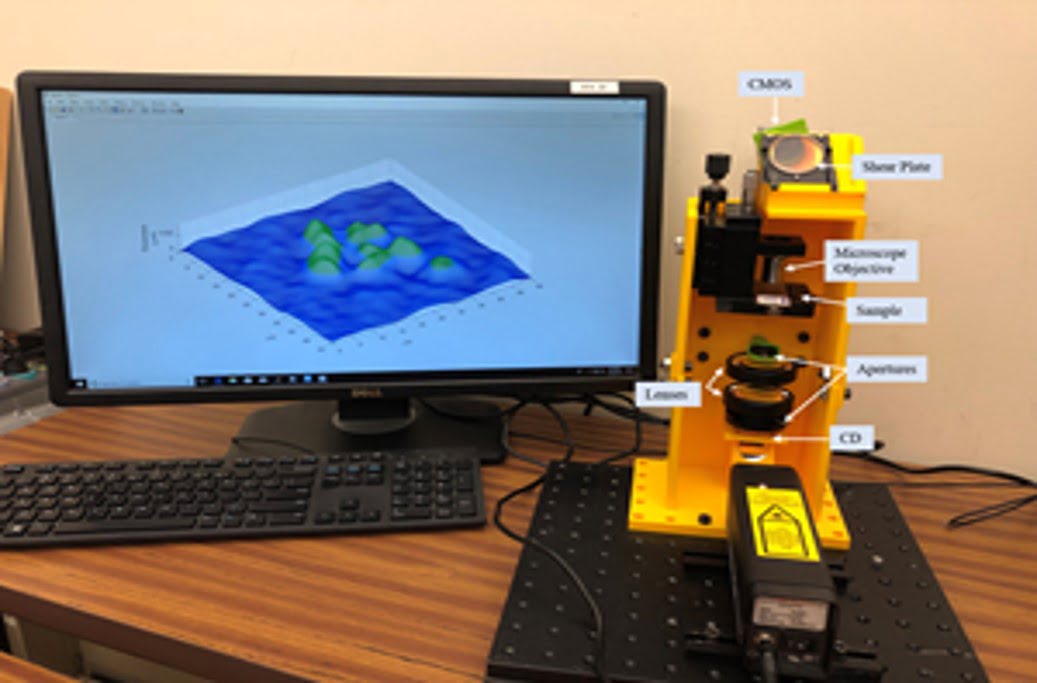
Researchers have made an inexpensive and portable high-resolution 3D printed microscope that is small and robust enough to use in the field or at the bedside. The high-resolution 3D images provided by the instrument could potentially be used to detect diabetes, sickle cell disease, malaria, and other diseases. The new microscope doesn’t require any special [..]
Read More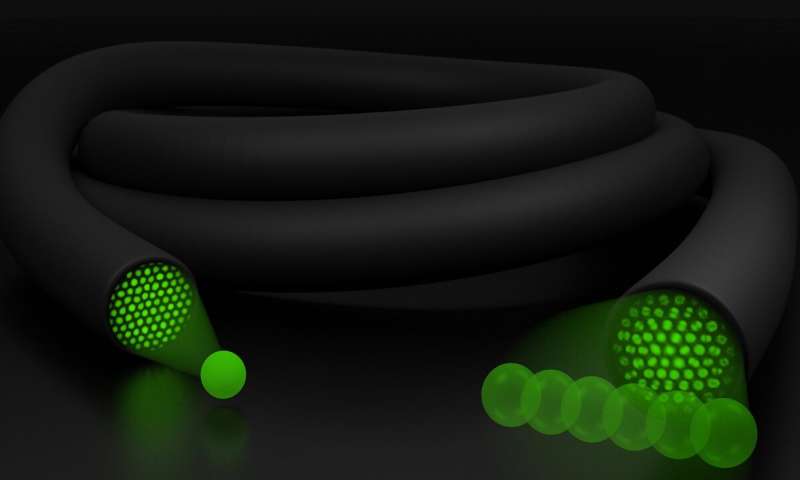
Researchers have shown that existing light field technology could be used to produce microscopic 3-D images of tissue inside the body, paving the way toward 3-D optical biopsies. Unlike normal biopsies where tissue is harvested and sent off to a lab for analysis, optical biopsies enable clinicians to examine living tissue within the body in [..]
Read More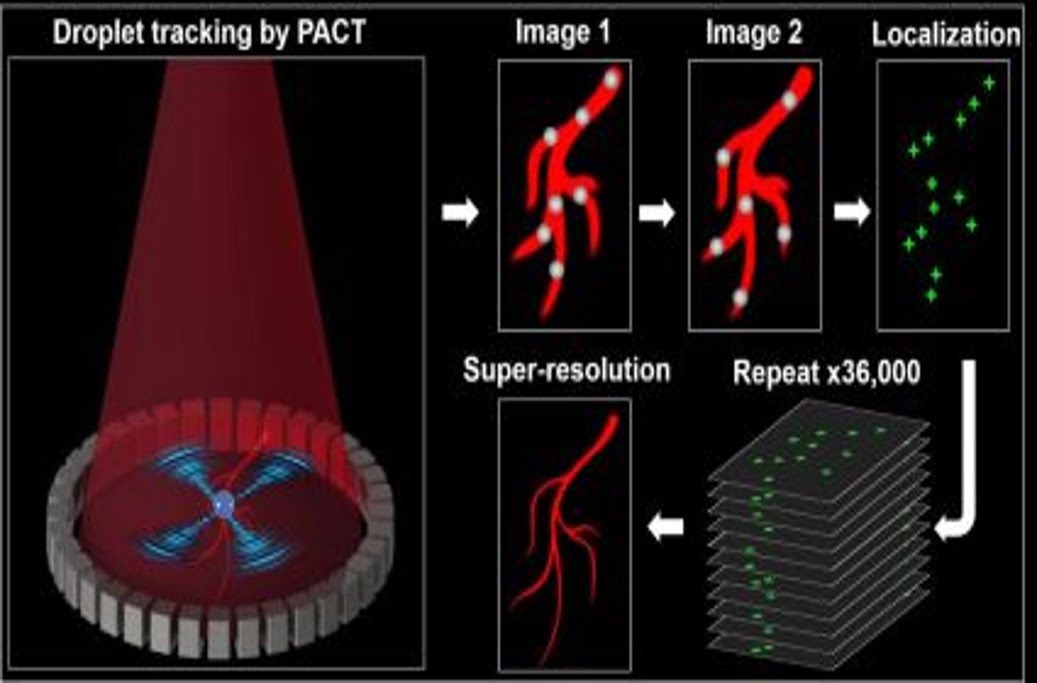
Researchers have developed a technique for in vivo super-resolution photoacoustic computed tomography (PACT) that breaks the acoustic diffraction limit by localizing the centers of single dyed droplets flowing in blood vessels. This technique has been shown to resolve brain blood vessels at a sixfold finer resolution. Photoacoustic computed tomography (PACT) is a noninvasive hybrid imaging [..]
Read More
Researchers have developed technology for microscopic imaging in living organisms. A miniaturized multiphoton microscopy device, which could be used in an endoscope in the future, excites the body’s own molecules to illuminate and enables cells and tissue structures to be imaged without the use of synthetic contrast agents. It is often necessary to examine tissue [..]
Read More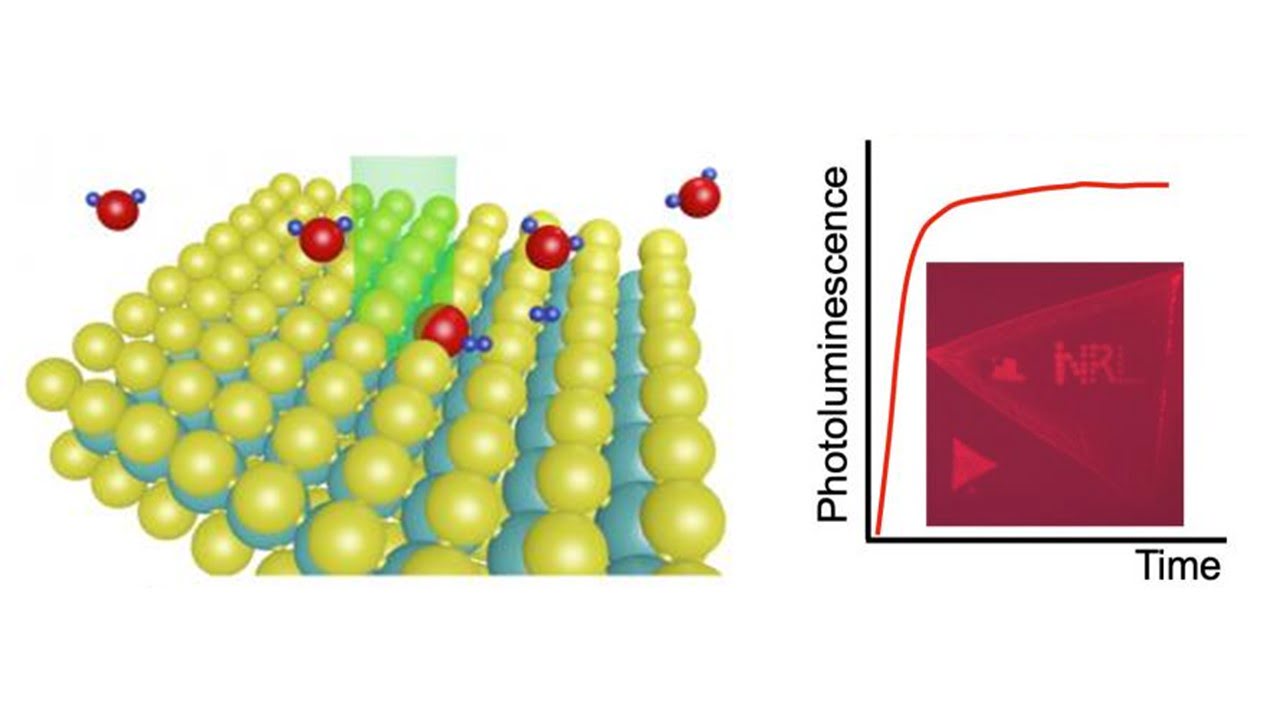
Scientists have discovered a new laser processing method to passivate defects in next-generation optical materials to improve optical quality and enable the miniaturization of light-emitting diodes and other optical elements. From a chemistry standpoint, they have discovered a new photocatalytic reaction using laser light and water molecules. The research enables the integration of high-quality, optically [..]
Read More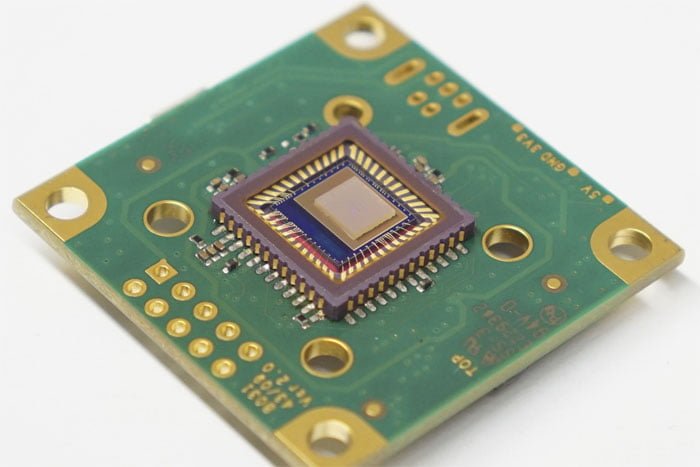
Engineers have developed a compact, single-shot, free-space-coupled spectrometer with hyperspectral imaging capabilities. The miniaturized spectrometer is fabricated on top of and integrated with a CMOS chip. The device measures 200 microns on each side. It can lie directly on a sensor from a typical digital camera. The miniaturized spectrometer and hyperspectral imager are based on [..]
Read More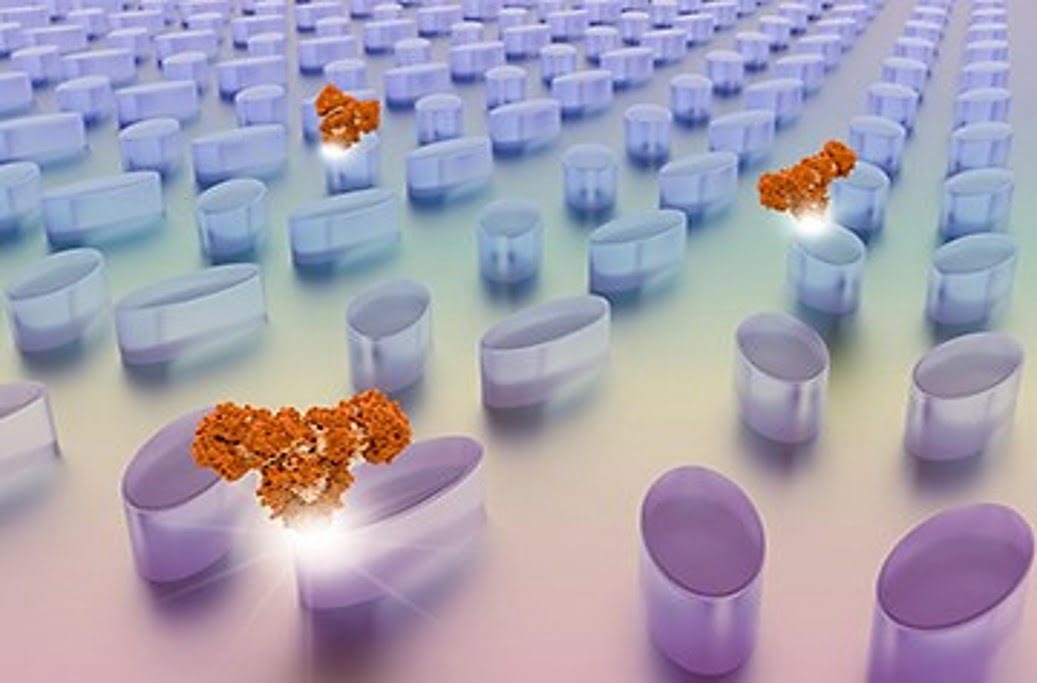
Researchers have combined the physics of dielectric metasurfaces and hyperspectral imaging to create an ultrasensitive, label-free biosensing platform. The platform can detect and analyze samples at spatial concentrations of less than three molecules per square micron. It could ultimately enable compact portable diagnostics for personalized medicine. It could also offer a route to high-throughput, high-resolution [..]
Read More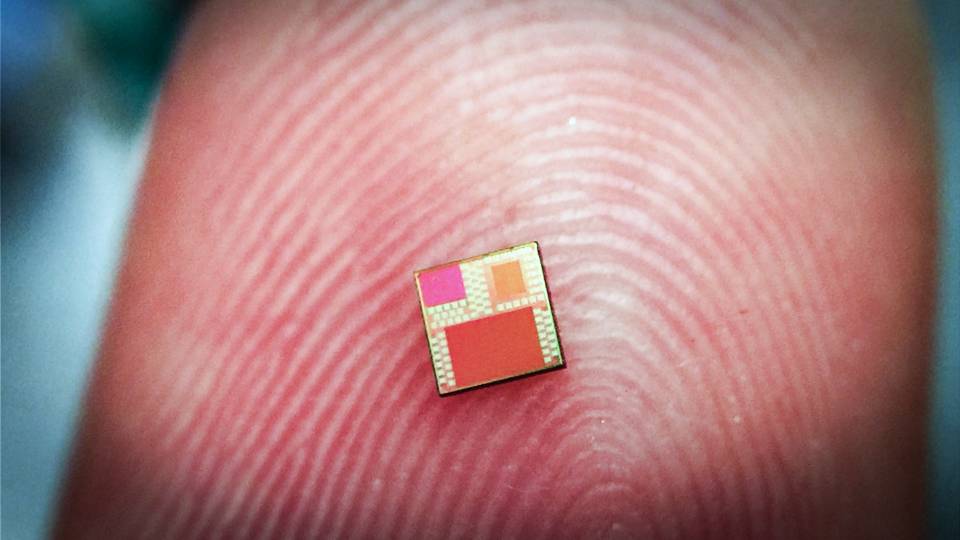
Researchers have developed silicon chip technology similar to that found in personal computers and mobile phones to function as biosensors. It is an essential step toward performing medical diagnoses using handheld devices. The technology eliminates all complex and bulky optical instrumentation used in diagnostic labs by using tiny metal layers embedded in a microchip. As [..]
Read More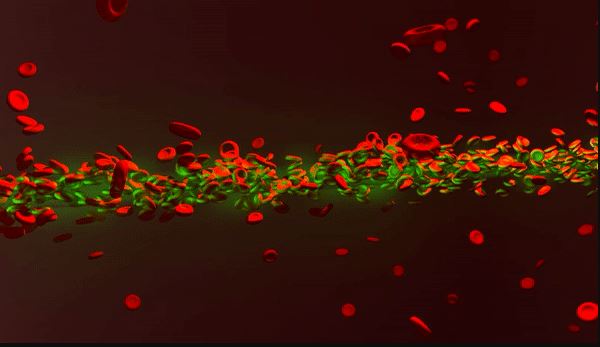
New photonic imaging tools can help to understand better the nonlinear behavior of laser light in human blood. A laser beam shining through red blood cell suspensions can become “self-trapped,” according to researchers. The process reduced light scattering to maintain the power of laser beams. The observed nonlinearity was affected by osmotic conditions and sample [..]
Read More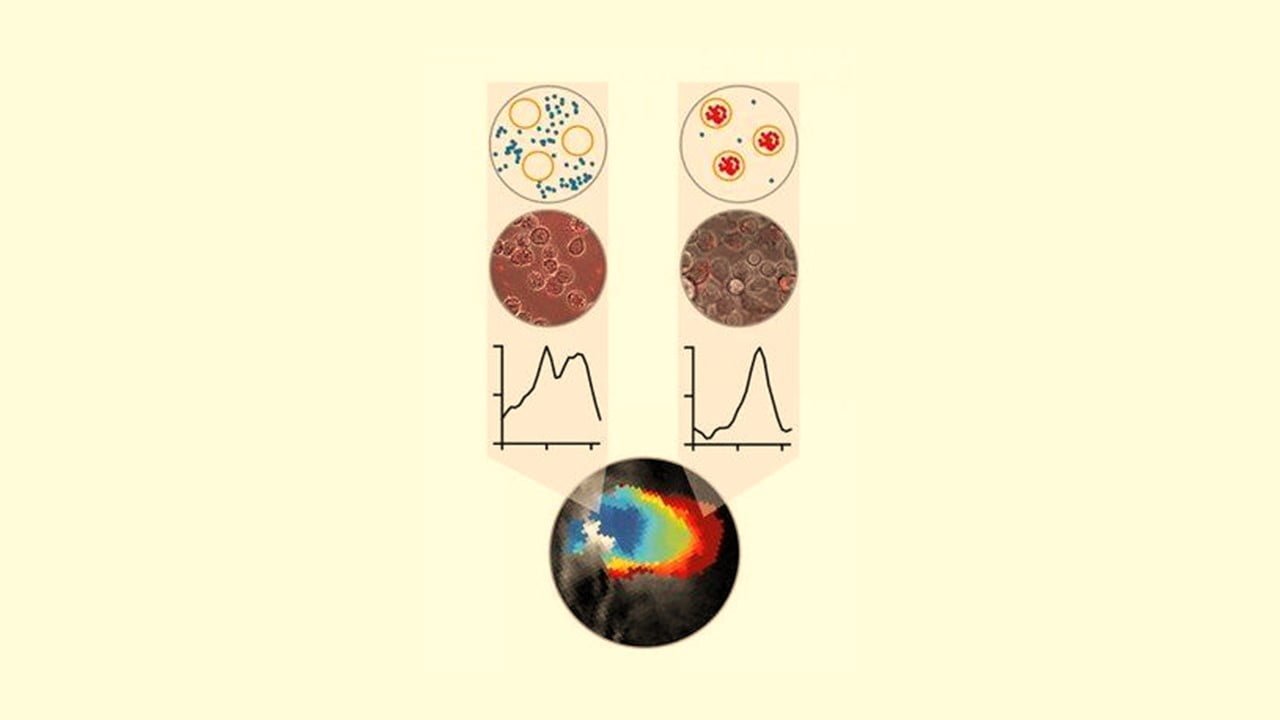
A group of researchers discovered that harmless purple bacteria from the genus Rhodobacter could visualize aspects of tumor heterogeneity in cancerous tumors. The researchers used these microorganisms to visualize immune system cells known as macrophages, which also play a role in tumor development, using optoacoustic imaging. The researchers developed the imaging technique that indicates where [..]
Read More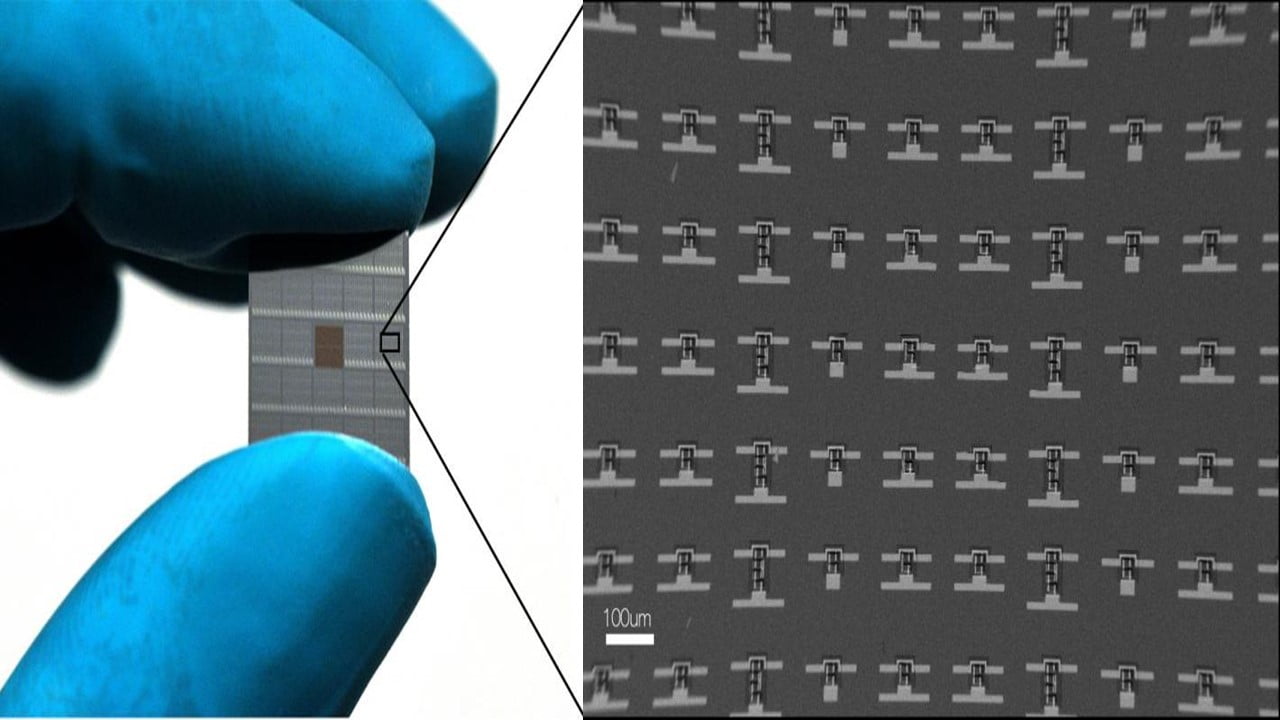
Using novel nanofabrication techniques, researchers have built micro-robots from silicon powered by solar cells. A 4-in. silicon wafer can help produce one million functional microscopic robots. The robots’ bodies form from a superthin rectangular skeleton of glass topped with a thin layer of silicon, into which the researchers have etched electronics control components and either two [..]
Read More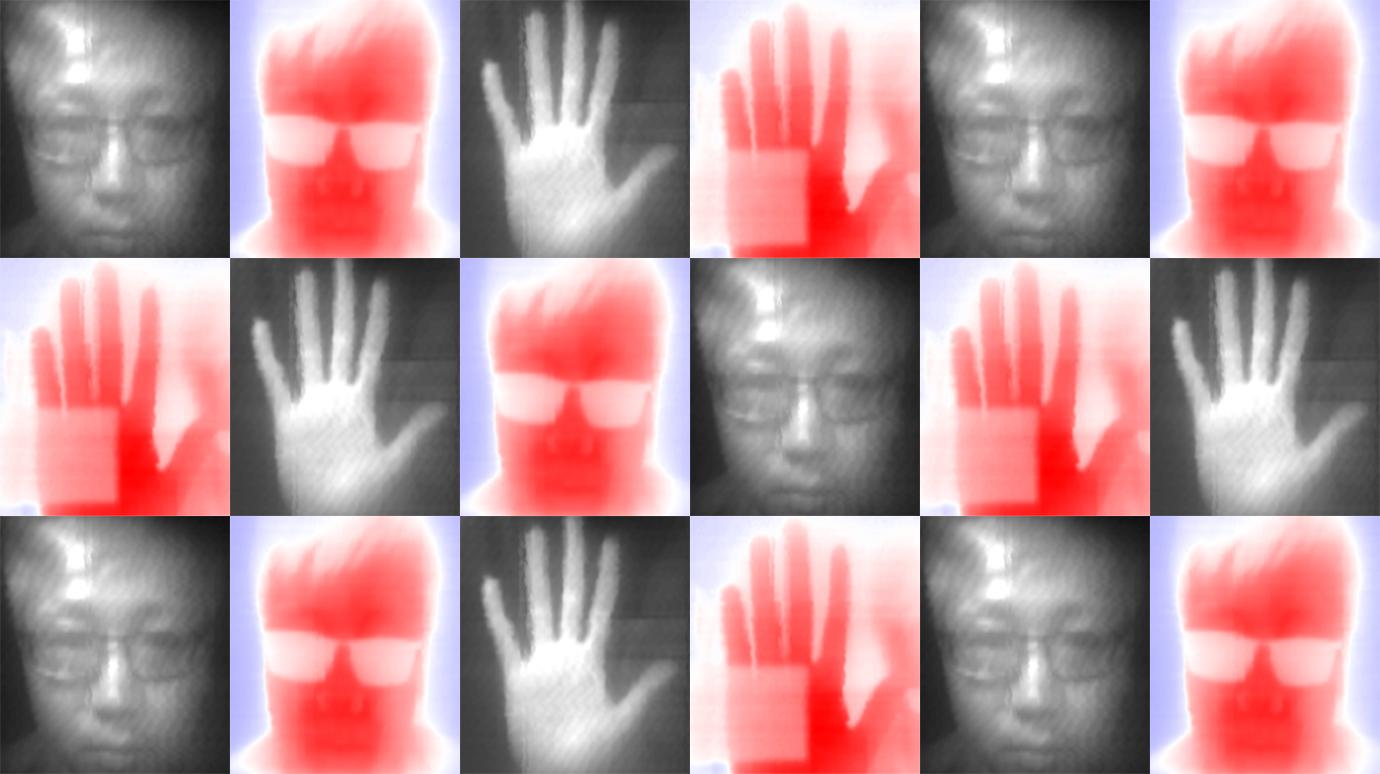
Infrared cameras can detect the invisible light emitted by plants as they photosynthesize, cool stars burn, and batteries heat up. Infrared light has less energy than visible light, making it more challenging to capture. A quantum dot technology breakthrough could one day lead to much more affordable infrared cameras, allowing infrared cameras for everyday consumer [..]
Read More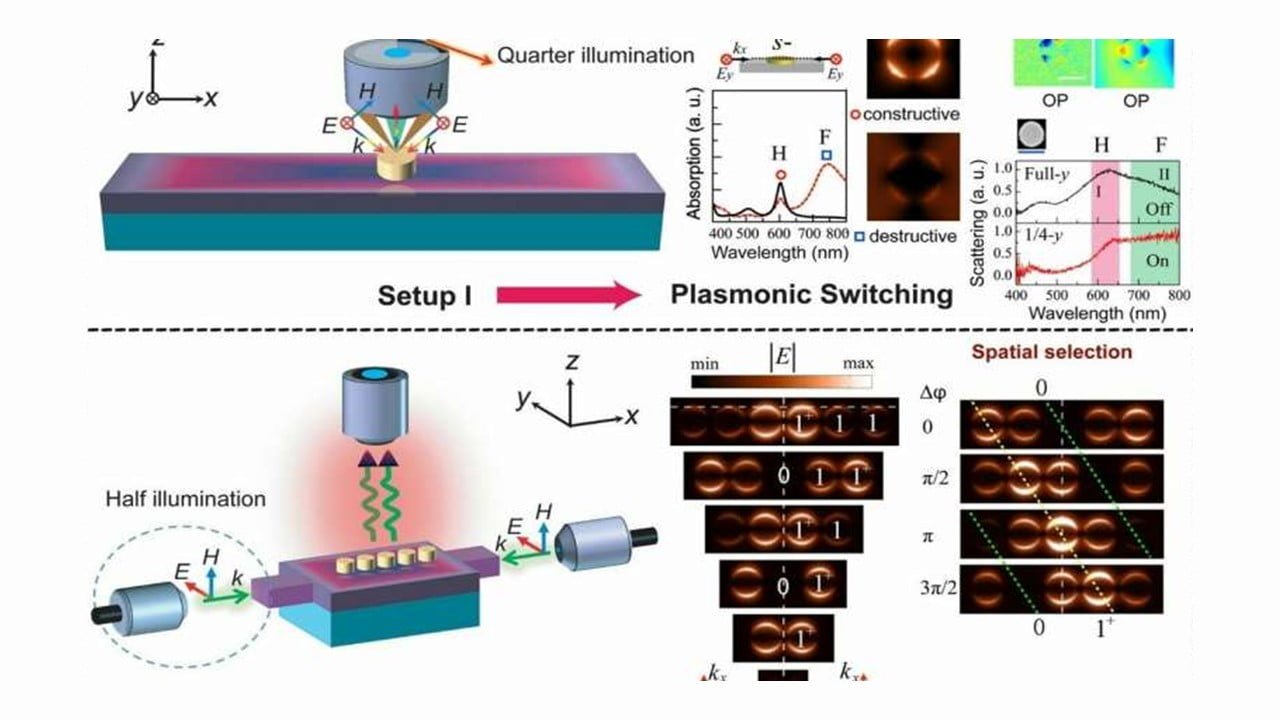
Digital holographic microscopy can reconstruct the images of 3D samples from a single hologram at a fraction of the size and cost of a standard bright-field microscope. It has enabled a plethora of hand-held holographic devices for biomedical diagnostics. Despite these benefits, holographic microscope images generally suffer from light interference-related spatial artifacts, which can limit [..]
Read More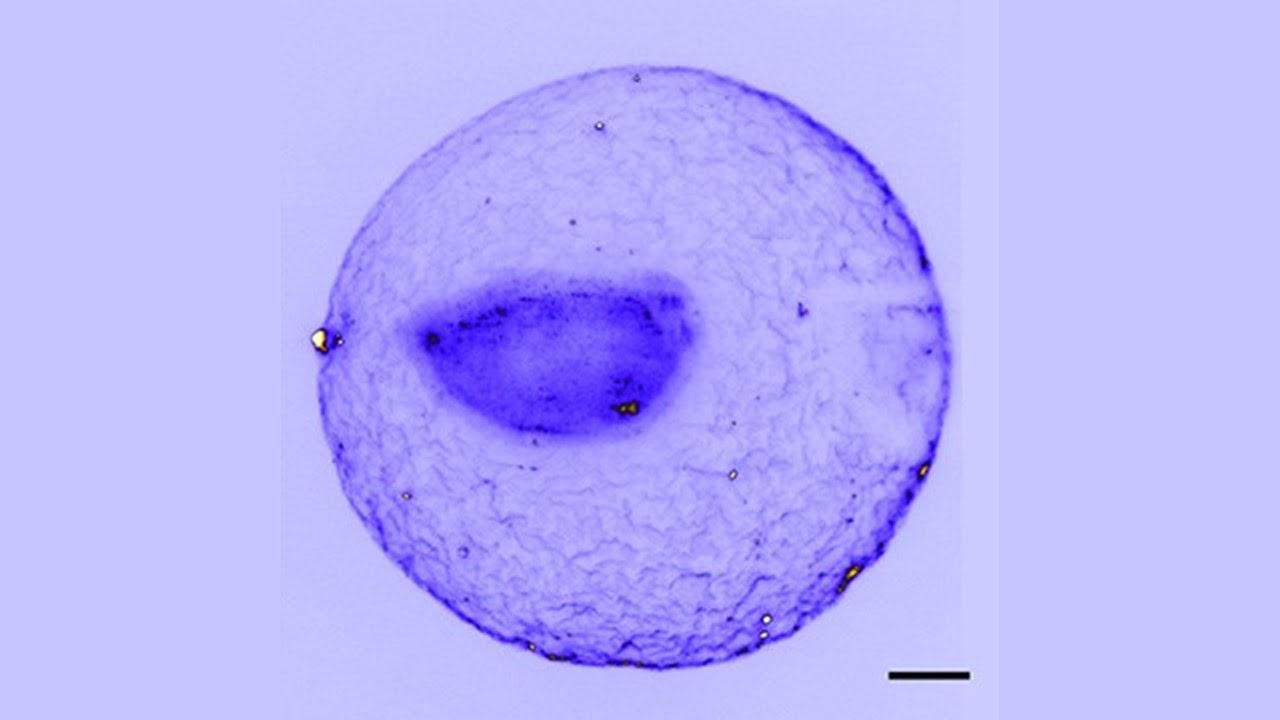
Light-sheet fluorescence microscopy (LSFM) can quickly generate stunning 3-D images of intact organs and tiny organisms like zebrafish and mouse brains. However, the samples must typically be immobilized in a stiff gel to obtain those images. This requirement limits the technique’s use in some studies of biological dynamics and aspects of drug discovery. A team [..]
Read More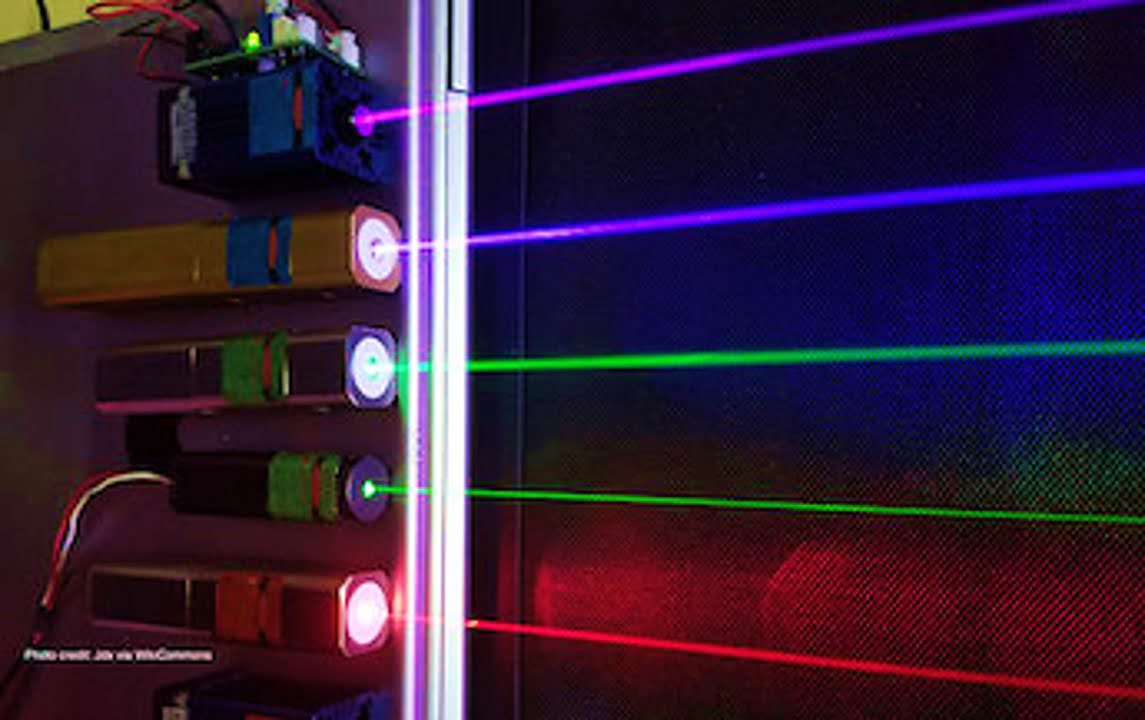
Quantum dots, semiconductor particles small enough to contain single electrons, are a promising laser light source for specific applications. Although careful selection of the semiconductor material can effectively tune the output of quantum dot lasers, structural flaws tend to split the output into multiple wavelengths. A group of researchers has proposed a possible solution in [..]
Read More