
Mutations in RAS genes, which cause tumor growth in about a quarter of all cancer patients, are among the most infamous cancer drivers. Scientists have solved the molecular structure of SHOC2, a RAS-pathway protein, and two other proteins (that it binds to). The SHOC2-MRAS-PP1C (“SMP”) complex, a three-protein assembly, regulates the RAS signaling pathway and [..]
Read More
Researchers have developed a new, lighter convolutional neural network (CNN) model for facial expression recognition. The findings describe an Xception-based model that balances training speed, memory usage, and recognition accuracy. The original Xception model has 71 layers and can load a pre-trained version of the network trained on over a million images from the ImageNet [..]
Read More
Researchers have created a self-calibrated photonic chip that builds bridges between data superhighways, revolutionizing the connectivity of current optical chips and replacing bulky 3D optics with a wafer-thin slice of silicon. This development can warp-speed the global advancement of artificial intelligence and offers significant real-world applications such as: autonomous vehicles that interpret their surroundings rapidly [..]
Read More
A novel somatostatin-receptor (SSTR) targeting peptide — 18F-SiTATE — has provided excellent imaging in meningioma patients, identifying bone involvement and lesions previously undetected on standard morphological imaging. The PET imaging agent, 18F-SiTATE, has a longer half-life and can be produced in large quantities by a cyclotron, which offers significant logistical advantages over the 68Ga-labeled ligands [..]
Read More
A new single-mode optical fiber made from sapphire rather than the usual silica can withstand temperatures of over 2000°C as well as high levels of radiation. Although the fiber’s length is currently limited to 1 cm, the technique used to construct it could be extended up to several meters, making it useful for remote sensing [..]
Read More
Scientists studied the implementation of neutron transmutation doping (NTD) to manipulate electron transfer. NTD is a controllable in-situ substitutional doping method. It utilizes the nuclear reactions of thermal neutrons with the nuclei of the atoms in semiconductors. The process provides a new way to dope 2D materials intentionally without extra reagents. Even after fabrication, it [..]
Read More
Researchers have developed a highly accurate and sensitive virus detection method using Raman spectroscopy, a portable virus capture device, and machine learning. The device could enable real-time virus detection and identification to help battle future pandemics. The new virus detection method is label-free and not aimed at any specific virus, thus enabling researchers to identify [..]
Read More
Researchers have developed a curvelet-based algorithm to quickly measure and reconstruct whole-brain vasculature and brain blood flow in mice. The work could enable future research into the neurovascular mechanisms underlying conditions like Alzheimer’s disease. The new approach deploys ultrasound technology to produce whole-brain images of animal microvasculature in just a few seconds. Instead of averaging [..]
Read More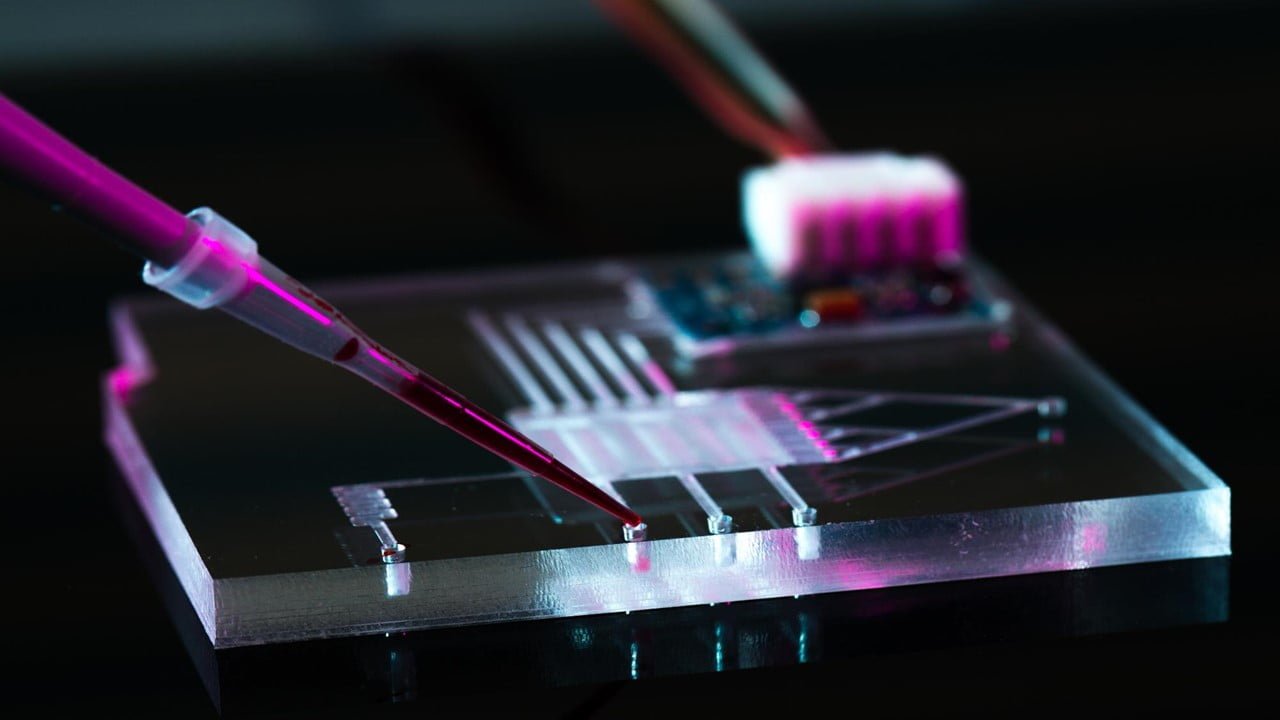
Microfluidic devices use tiny spaces to manipulate very small quantities of liquids and gasses by taking advantage of the properties they exhibit at the microscale. They have demonstrated usefulness in applications from inkjet printing to chemical analysis. They have great potential in personalized medicine, where they can miniaturize many tests that now require a full [..]
Read More
Researchers have developed a new way to 3D-print glass microstructures that is faster and produces objects with higher optical quality, design flexibility, and strength. The researchers expanded the capabilities of a 3D-printing process they developed three years ago — computed axial lithography (CAL) — to print much finer features and to print in glass. They [..]
Read More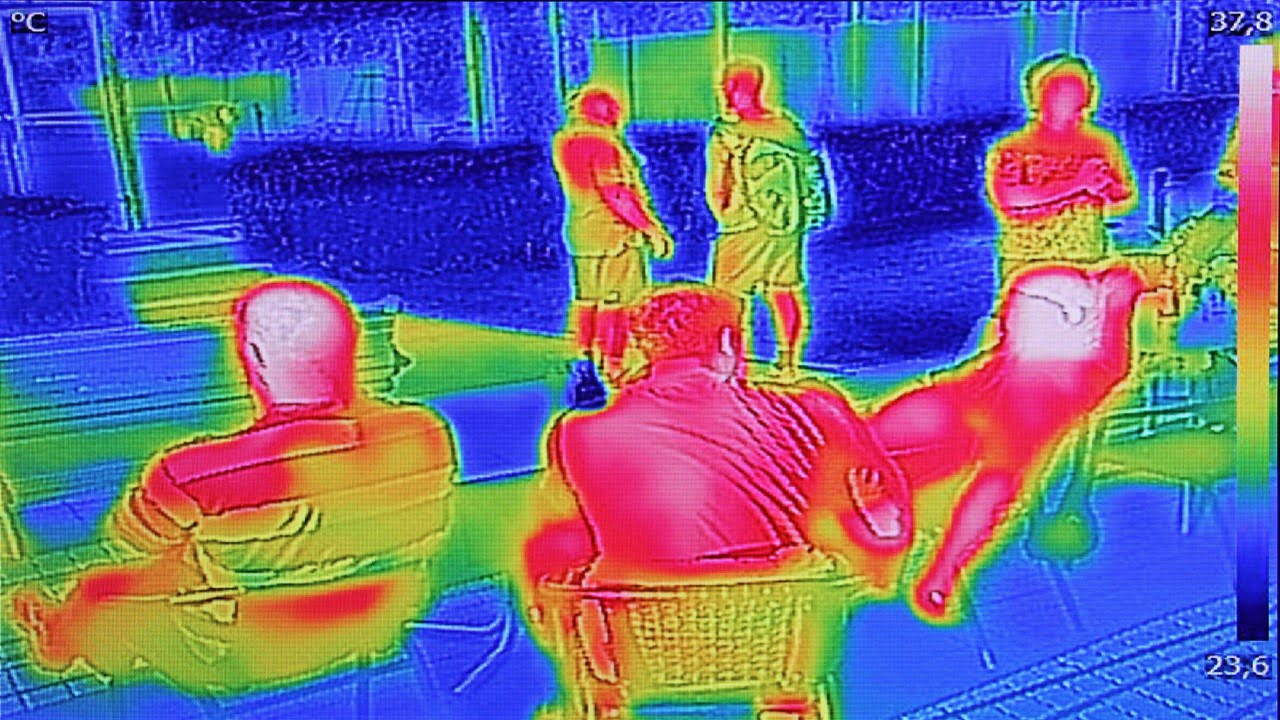
High-performance wavelength discrimination in the long-wave infrared region (LWIR) of the electromagnetic spectrum (wavelength range from 8 microns to 12 microns) is desirable for civilian and military applications. Of particular importance is to achieve on-chip passive thermal imaging with spectral filters, allowing remote target recognition without requiring any light source for illumination since objects emit [..]
Read MoreTemperature monitoring with a high spatial and temporal resolution is vital in various disciplines, including industrial manufacturing, environmental protection, and healthcare monitoring. Because of their benefits of remote detection, minimum intrusion, tolerance to electromagnetic interference, and high resolution, optical-based sensors offer attractive alternatives for temperature monitoring in biological diagnostics. The luminous intensity, wavelength, peak width, [..]
Read More
Researchers have demonstrated, for the first time, light-induced thermomagnetic recording in a magnetic thin-film on silicon waveguides. The new writing technique is poised to enable miniature high-performance magneto-optical memories that don’t require bulky optics or mechanical rotation. The devices are nonvolatile — meaning that data is saved even when no power is supplied to the [..]
Read More
Consumers are looking for AR/VR glasses that are compact and easy to wear, delivering high-quality imagery with socially acceptable optics that don’t look like “bug eyes.” Researchers have developed a novel technology to deliver those attributes with maximum effect. The researchers imprinted freeform optics with a nanophotonic optical element called a metasurface. The metasurface is [..]
Read More
Exciton polaritons are hybrid particles that combine light and molecules of organic material, making them ideal vessels for energy transfer in organic semiconductors. Thanks to their photonic origins, they are both compatible with modern electronics and move speedily. However, they are difficult to control, and much of their behavior is a mystery. Researchers have found [..]
Read More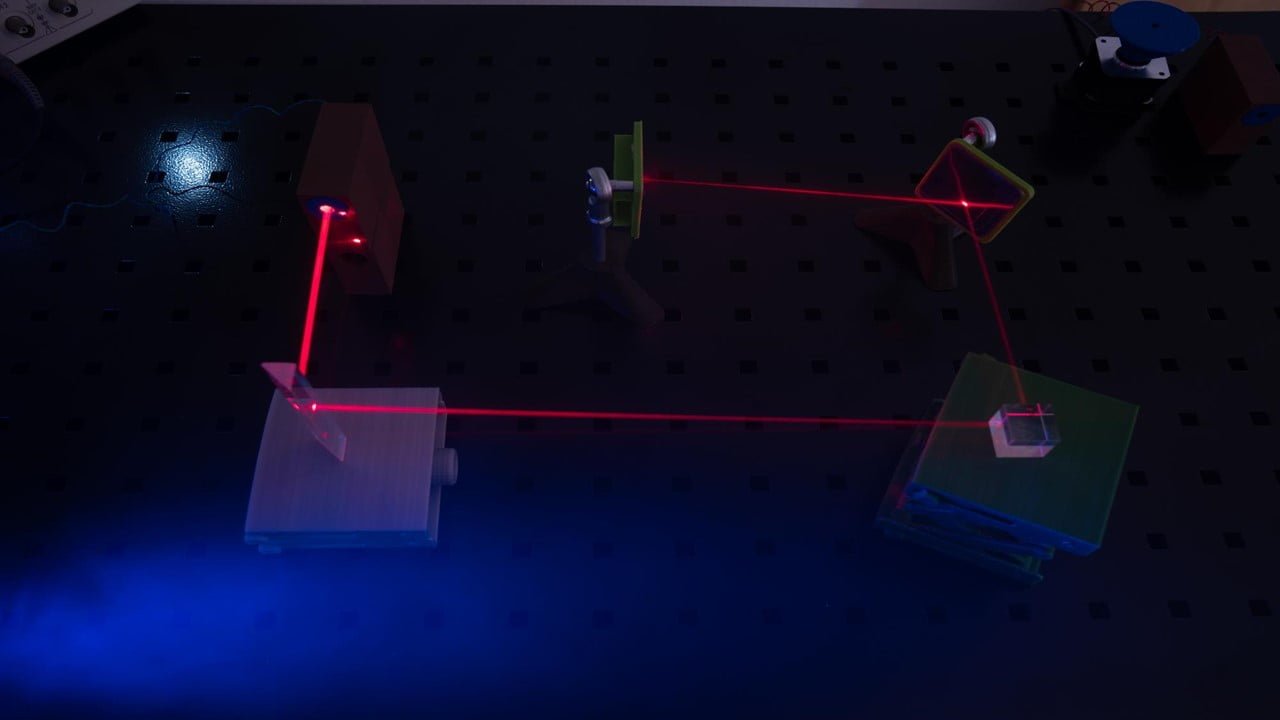
Researchers have developed a new laser ultrasound technique capable of performing on-demand characterization of melt tracks and detecting the formation of defects in a popular metal 3D printing process. The researchers propose a diagnostic using surface acoustic waves (SAW), generated by laser ultrasound, that can reveal tiny surface and sub-surface defects in laser powder bed [..]
Read More
Scientists have created a novel electromagnet that could help gadgets ranging from tokamaks (doughnut-shaped fusion reactors) to medical instruments that capture detailed human body images. Tokamaks rely on a central electromagnet, a solenoid, to generate electrical currents and magnetic fields that confine the plasma (a hot, charged state of matter made up of free electrons [..]
Read More
Atrial fibrillation (AF) is diagnosed with an electrocardiogram, the gold standard in clinics. However, sufficient arrhythmia monitoring takes a long time, and many of the tests take place in only a few seconds, which can miss arrhythmia. Researchers have developed a combined method to detect the effects of AF on atrial tissue. The researchers characterized [..]
Read More
Polarization holography is a newly researched field that has gained traction with the development of tensor theory. It primarily focuses on the interaction between polarization waves and photosensitive materials. The extraordinary capabilities in modulating light amplitude, phase, and polarization have resulted in several new applications, such as holographic storage technology, multichannel polarization multiplexing, vector beams, [..]
Read More
Researchers have developed a quick and cost-effective way to determine the age of malaria mosquitoes using mid-infrared spectroscopy. The new technology is vital for assessing the effectiveness of control interventions as only older mosquitoes can transmit the parasite. The scientists say that their approach could also help with other mosquito-borne and insect-borne diseases. The researchers [..]
Read More