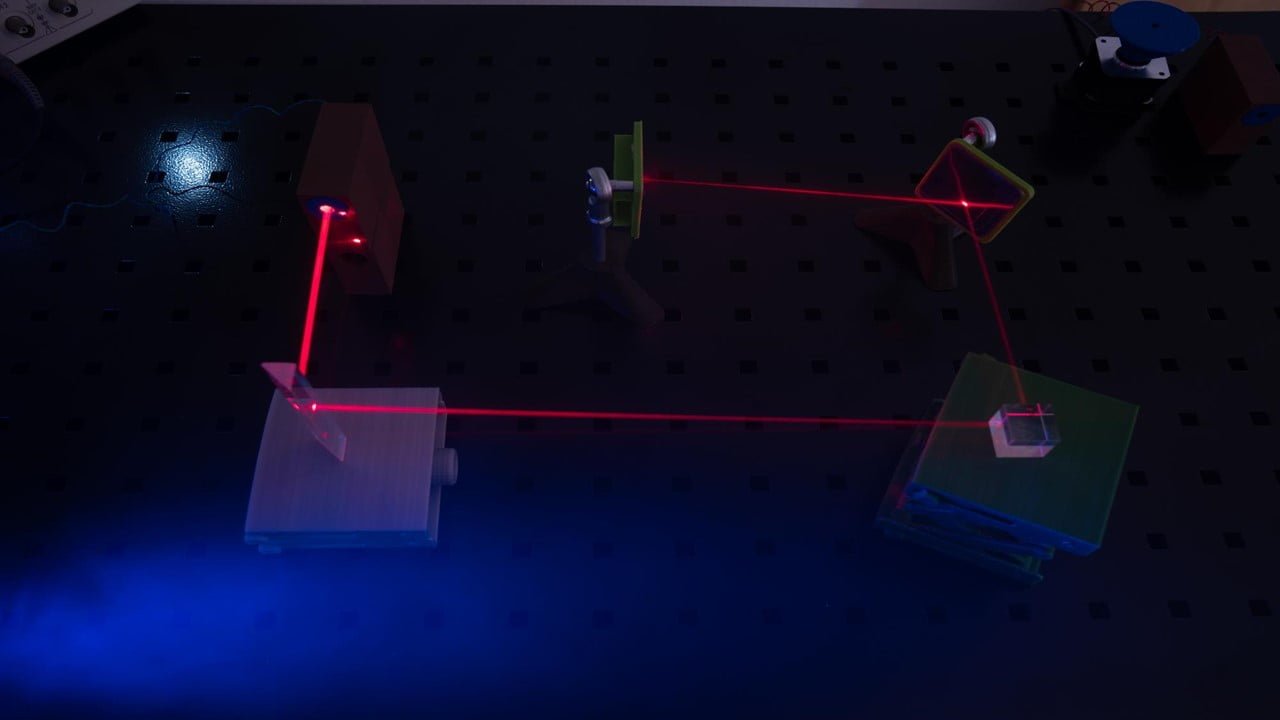
Despite being widely accepted, the physics of optical waves has some fundamental aspects that are debatable. One of these effects, the anomalous behavior of focused light fields, is being studied in a new light, a quantum light. Quantum light with a well-defined photon number behaves differently than standard focused laser beams, according to researchers. This [..]
Read More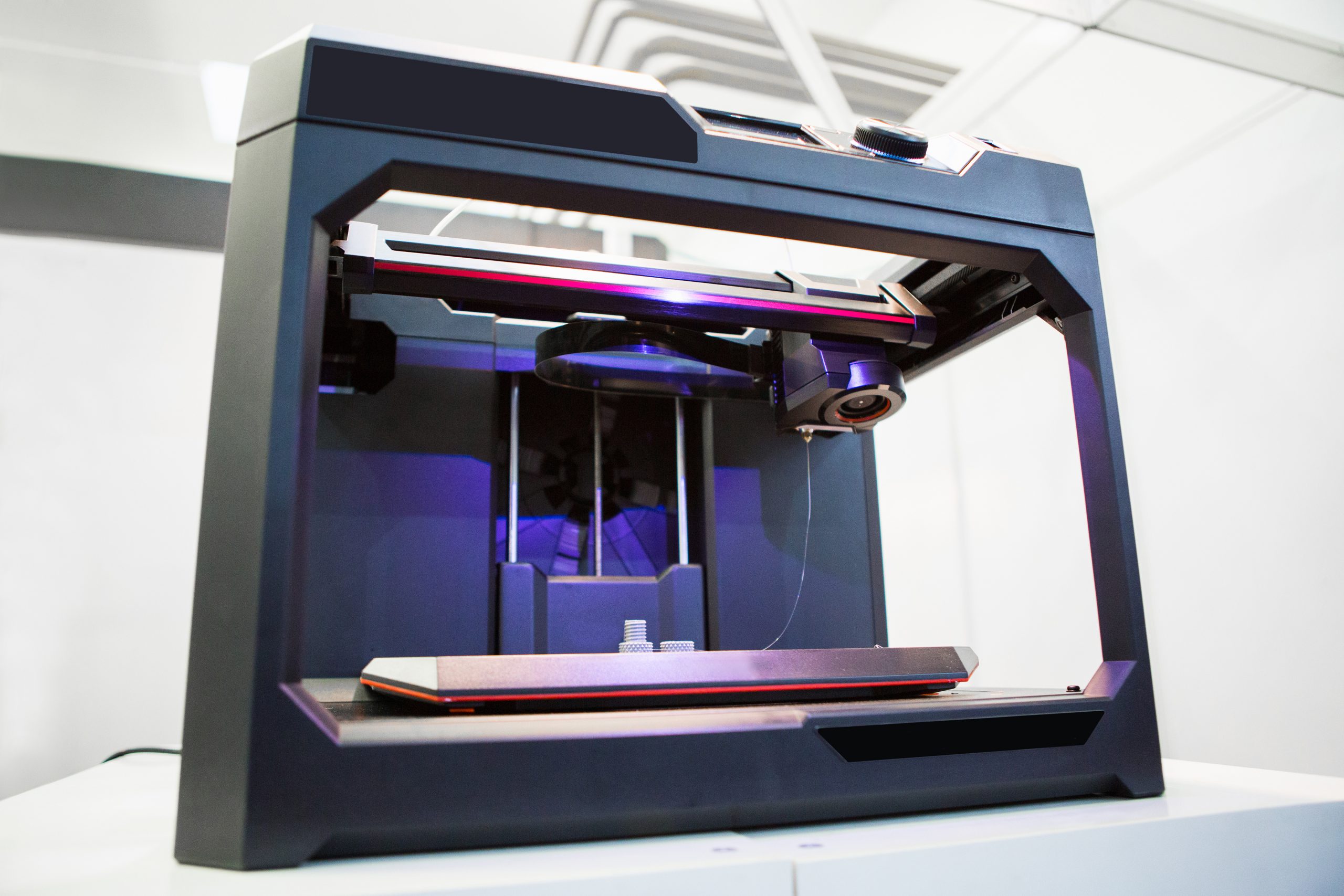
Additive manufacturing allows for the creation of novel, multifunctional lenses and components that have the potential to simplify and shrink traditional optical systems. Emerging 3D printing technology converts previously impossible optical component designs into optimized elements. It can improve medical instruments, research tools, communications systems, and consumer devices. The additive process in 3D printing prints [..]
Read More
Researchers have developed a new decoding method for orbital angular momentum (OAM) holography. Based on cross convolution, it significantly exceeds the upper limit of OAM holography’s information extraction rate. They designed an amplitude-modulated pattern called Amplitude Decoding Key (ADK) as a decoder for information extraction in OAM holography, starting with the spatial frequency domain. A [..]
Read More
With global energy-related carbon dioxide emissions reaching an all-time high in 2021, the need for clean energy is greater than ever. Solar energy is one such alternative to fossil fuels. Solar cells have been created using various materials, but selenium (Se) is popular because it is inexpensive, stable, and non-toxic. Its efficiency, however, is limited [..]
Read More
Risk stratification is essential for identifying high-risk individuals and disease prevention. Researchers investigated the potential of nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy-derived metabolomic profiles to provide information on multi-disease risk. They conducted the research in addition to conventional clinical predictors for the onset of 24 common conditions, including metabolic, vascular, respiratory, musculoskeletal, neurological, and cancer diseases. [..]
Read More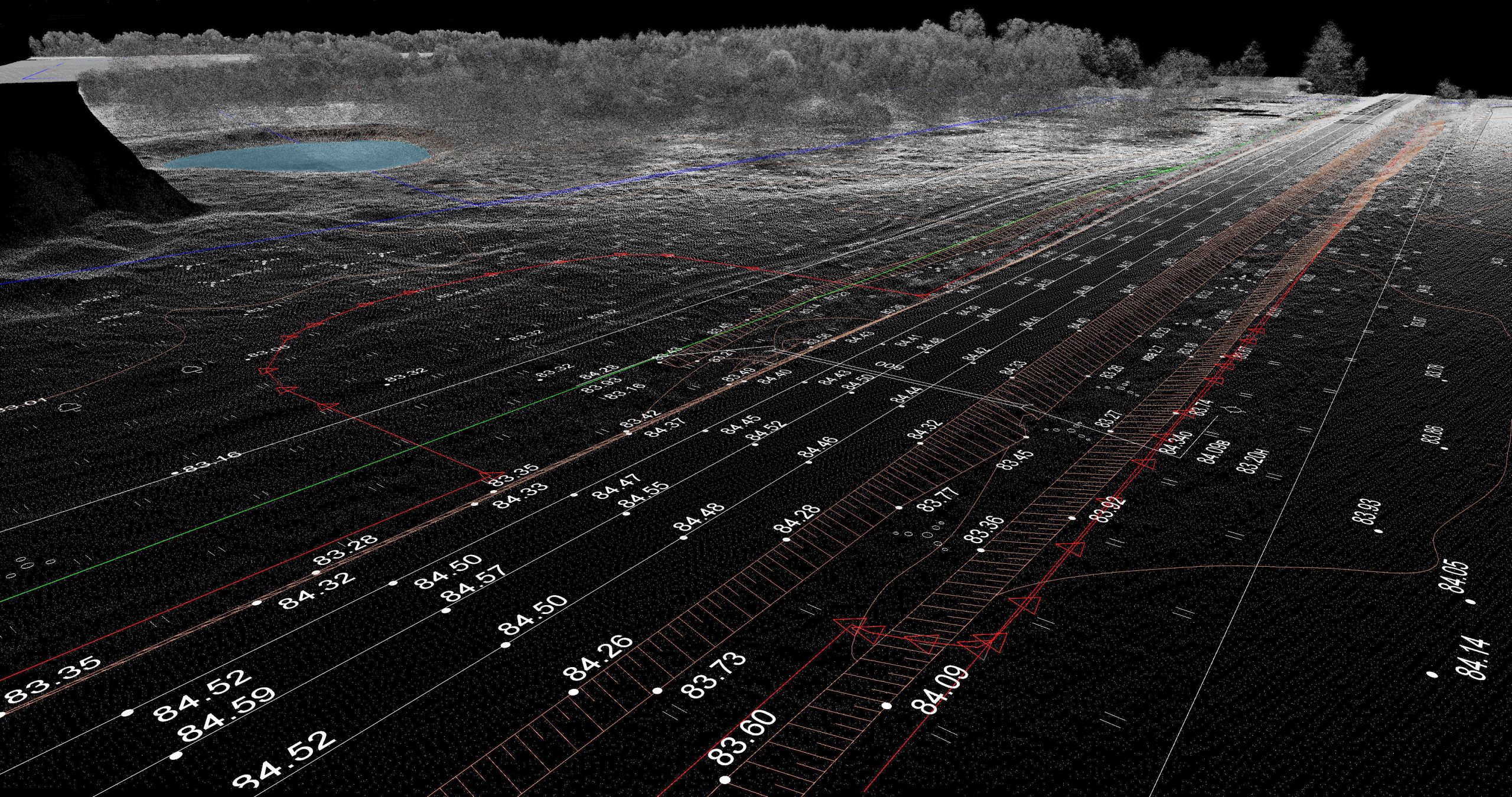
Researchers have developed a new laser-based technique that can perform LiDAR and remote chemical measurements at the same time. LiDAR (light detection and ranging) uses a laser to measure distances or ranges. Chemically sensitive LiDAR measurements could be useful for remote chemical mapping, detecting trace amounts of chemicals, monitoring industrial processes, and quality control. Researchers [..]
Read More
A new photonic chip could be a significant step toward enabling photonic quantum information processors. It can generate and measure quantum states of light in ways previously only possible with large and costly laboratory equipment. The chip is built with lithium niobate, a salt whose crystals have numerous applications in optics. On one side of [..]
Read More
Light Fidelity (LiFi) is a high-speed broadband mechanism that uses the light spectrum to transmit and receive data. The Visible Light Communication (VLC) technology uses an LED light to transmit data to a receiver, which can be installed in hotspots, laptops, or smartphones. Infrared signals are then sent back to the LED light by a [..]
Read More
Researchers have shown for the first time how cells across different tissue layers in the eye are affected in people with choroideremia – a rare genetic disorder that leads to blindness. The researchers combined traditional eye imaging techniques with adaptive optics, a technology that improves imaging resolution. The researchers used adaptive optics and indocyanine green [..]
Read More
Photons are essential in various current research fields and technologies, such as quantum state engineering, which is the foundation of all quantum photonic technologies. Metasurfaces are gaining attention as photon pair sources for quantum research. They can simultaneously transform photons in multiple degrees of freedom, including polarization, frequency, and path. Researchers have now taken another [..]
Read More
Researchers used a microfluidic device in the lab to simulate an embryonic heart, which resulted in the development of human blood stem cell “precursors,” which are stem cells on the verge of becoming blood stem cells. To create blood stem cells in laboratory dishes, researchers must first understand all of the processes that occur in [..]
Read More
Indium phosphide (InP) is an incredibly versatile material. Electronic circuits based on this compound semiconductor are among the fastest currently available, operating at frequencies far exceeding 100 gigahertz (for comparison, modern PC and laptop processors typically clock at 3-4 gigahertz). In photovoltaics, InP is an essential component of ultra-high-efficiency solar cells used in space applications [..]
Read More
Phase transitions, such as those between solids, liquids, and gases, occur in many substances and can occur quickly or slowly. For example, scientists intend to use phase transitions to control various materials’ electronic, structural, or magnetic properties as they change for use in new types of computer memories. In a new study, researchers could examine [..]
Read More
Researchers looked at the nucleus of cells inside connective tissues that were deteriorating due to tendinosis. Disease-related disruptions in the environments in which cells exist resulted in the re-organization of the genome – the sum of an organism’s DNA sequences – inside the cell’s nucleus, changing the way cells function and rendering them unable to [..]
Read More
Researchers have made strides toward improving the performance of mixture-based quarter-wave plate laser beam splitter (PLBS) coatings. Because of their unique optical properties, plate beam splitters find uses in quantum communication, measurement, and laser systems. The quarter-wave plate laser beam splitter must have a specific spectral performance in high-power laser systems. It also requires a [..]
Read More
Fundus photography is essential in ophthalmology to screen, diagnose, and manage eye diseases. Wide-field fundus photography has demonstrated its utility in the clinical management of eye diseases such as diabetic retinopathy (DR), age-related macular degeneration (AMD), glaucoma, hypertensive retinopathy, retinal detachments, and vascular pathologies (vascular occlusions, vasculitis, etc.) with ocular metastasis. Choroidal and retinal imaging [..]
Read More
Researchers have developed a new ultrasensitive optical sensing instrument that could benefit science, medicine, and engineering. It is known as a Mach Zehnder-Fabry Perot (MZ-FP) hybrid fiber interferometer. It combines the benefits of the two types of interferometers currently available, making it compact and highly sensitive. Interferometers are precision measuring devices that work by creating [..]
Read More
MRI, electroencephalography (EEG), and magnetoencephalography (MEG) have been the most widely used techniques to study brain activity for many years. A new study introduces a novel, AI-based dynamic brain imaging technology that can map rapidly changing electrical activity in the brain at high speed, high resolution, and low cost. The breakthrough follows more than 30 [..]
Read More
Researchers used the light-guiding properties of spider silk to create a sensor that can detect and measure tiny changes in the refractive index of a biological solution, such as glucose or other sugar solutions. The new light-based sensor could be useful for measuring blood sugar and other biochemical analytes in the future. Glucose sensors are [..]
Read More
Currently, ultrasound imaging necessitates using large, specialized equipment only available in hospitals and doctor’s offices. On the other hand, a new design could make the technology as wearable and accessible as buying Band-Aids at the pharmacy. A new ultrasound sticker, the size of a stamp, adheres to the skin and can provide continuous ultrasound imaging [..]
Read More