
Engineers have achieved a remarkable feat in imaging technology by developing a novel technique that harnesses the enigmatic power of quantum entanglement to capture high-fidelity 3D images of microscopic objects. This groundbreaking approach, dubbed Quantum Multi-Wavelength Holography, offers a unique way to “see” in infrared without needing expensive infrared cameras, all while providing unprecedented depth [..]
Read More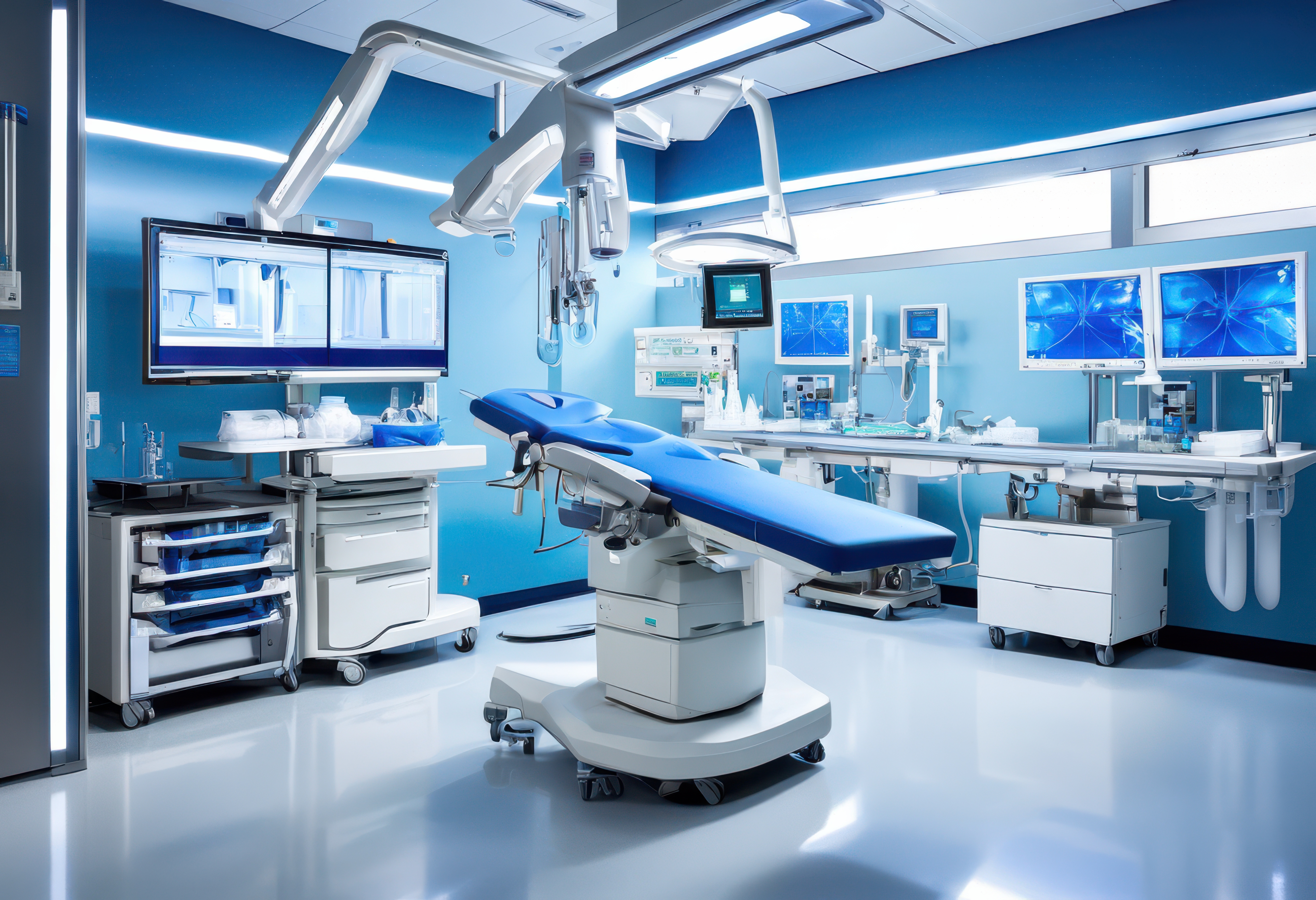
A groundbreaking advancement in optical technology promises to transform how we visualize the inside of the human body. Researchers have successfully developed an ultra-thin optical imager, offering a less invasive approach to acquiring high-resolution images from within internal organs and tissues. This innovation holds immense potential for early and precise disease detection, providing crucial insights [..]
Read More
As artificial intelligence (AI) data centers grapple with the ever-increasing demands for bandwidth to shuttle massive datasets between GPUs and memory, the limitations of traditional copper interconnects are becoming increasingly apparent. Startups are stepping up to address this bottleneck by developing innovative optical interconnects that can be integrated directly onto standard GPU and memory chiplets, [..]
Read More
After decades of frustration, scientists have successfully refined cryogenic electron microscopy (cryo-EM) by utilizing ultracold liquid helium to achieve remarkably high-resolution images of protein structures. This breakthrough overcomes a long-standing issue that paradoxically resulted in fuzzier images when using liquid helium compared to the warmer liquid nitrogen temperatures. The findings pave the way for electron [..]
Read More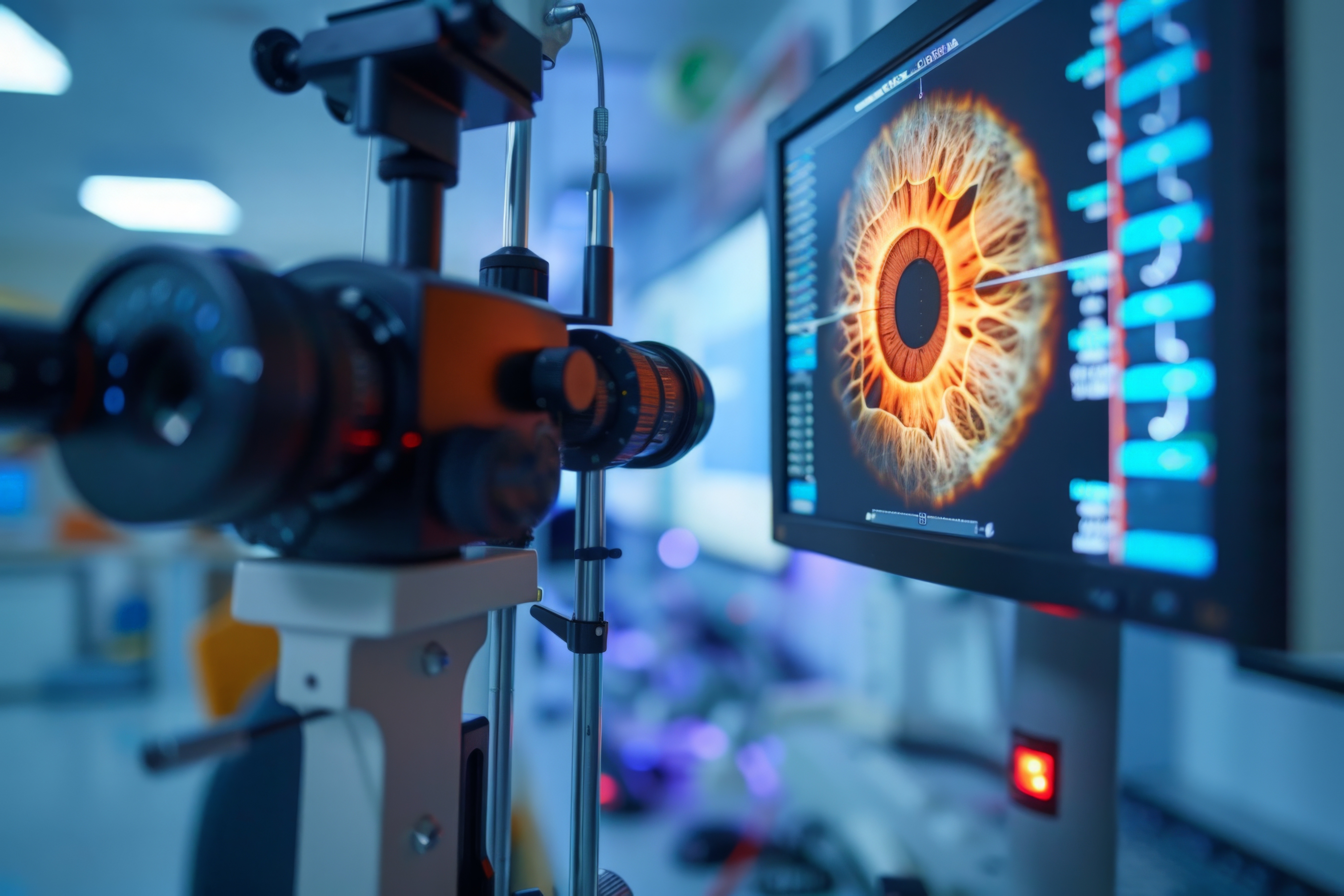
The intricate connection between the eye, particularly the retina and optic nerve, and the central nervous system (CNS) provides a unique and non-invasive pathway to understanding neurological health. Neuro-ophthalmology, a specialized field, capitalizes on this relationship to diagnose and manage a spectrum of systemic and neurological disorders that manifest within the visual pathway. Advanced diagnostic [..]
Read More
Physicists have achieved a significant milestone in integrated photonics with the creation of an on-chip compact laser capable of generating exceptionally bright, short pulses of light in the mid-infrared (mid-IR) spectrum. This wavelength range is highly valuable for applications such as gas sensing and spectroscopy but has historically been challenging to access with integrated devices. [..]
Read More
Researchers have pioneered a novel terahertz (THz) imaging technique that offers an unprecedented ability to non-destructively visualize and analyze the internal structures and properties of layered materials with remarkable clarity. This terahertz light breakthrough in THz photonics overcomes limitations of conventional imaging methods, opening up new avenues for quality control, material science research, and the [..]
Read More
The convergence of artificial intelligence (AI) and optics is ushering in a new era of enhanced digital security, offering innovative solutions to combat increasingly sophisticated cyber threats. By integrating AI algorithms with advanced optical technologies, researchers and developers are creating powerful defense mechanisms that operate at the physical layer, providing a robust and often undetectable [..]
Read More
Dual-chirped comb LiDAR represents a significant advancement in distance measurement technology, offering unprecedented accuracy and range for a variety of applications. This innovative approach leverages the unique properties of frequency combs, specifically dual-chirped frequency combs, to achieve high-resolution measurements over extended distances. Unlike traditional LiDAR systems, which rely on pulsed lasers, dual-comb LiDAR utilizes two [..]
Read More
A novel metasurface optical element promises to significantly advance our understanding of atmospheric aerosols. This innovative technology offers a compact, lightweight, and highly efficient alternative to traditional optical components, enabling more precise and detailed measurements of these tiny airborne particles. Atmospheric aerosols play a crucial role in Earth’s climate system, influencing cloud formation, precipitation patterns, [..]
Read More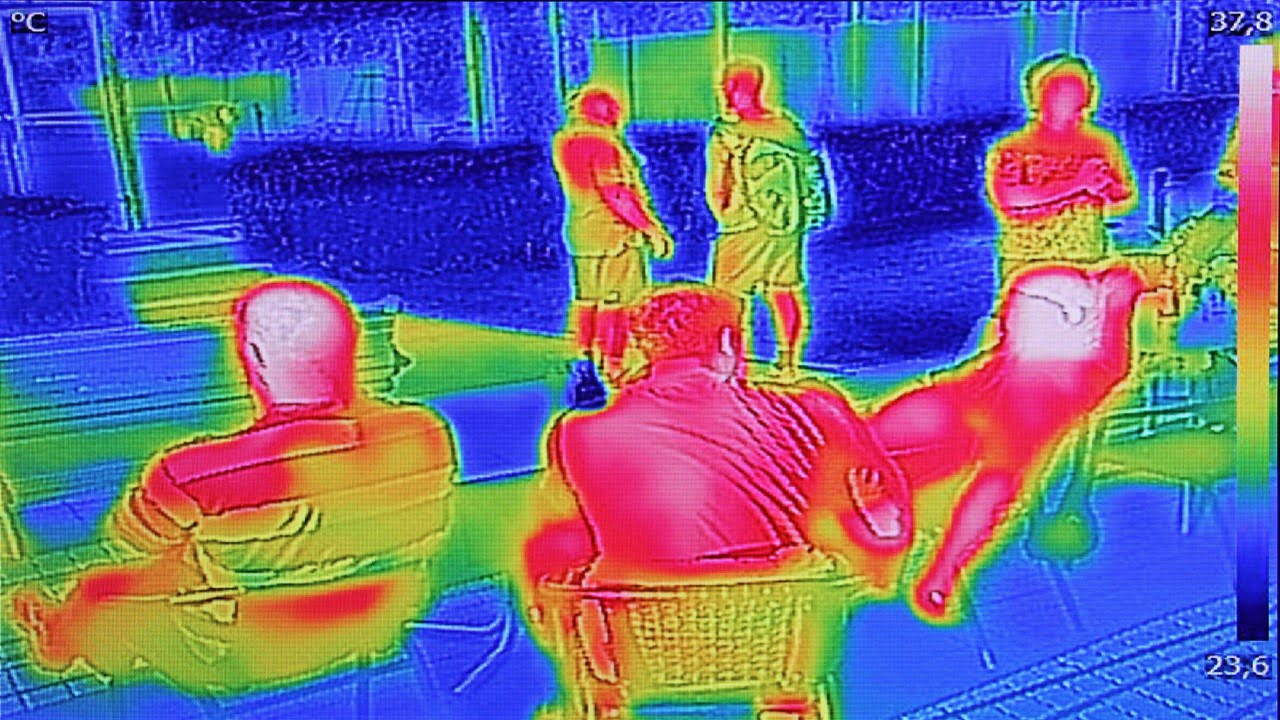
A significant advancement in thermal imaging technology has been developed, offering a non-contact and highly accurate method for tracking vital signs. Researchers have engineered a phasor thermography system that, through sophisticated image processing, can reliably extract physiological data such as body temperature, respiration rate, and heart rate from thermal images. This innovation holds immense potential [..]
Read More
Data centers, the backbone of our digital infrastructure, face increasing pressure to reduce energy consumption. Linear Pluggable Optics (LPO) has emerged as a promising solution to address this challenge, offering a more efficient way to move data within server racks. Unlike its predecessor, Co-Packaged Optics (CPO), which integrates optical components directly into the electrical package, [..]
Read More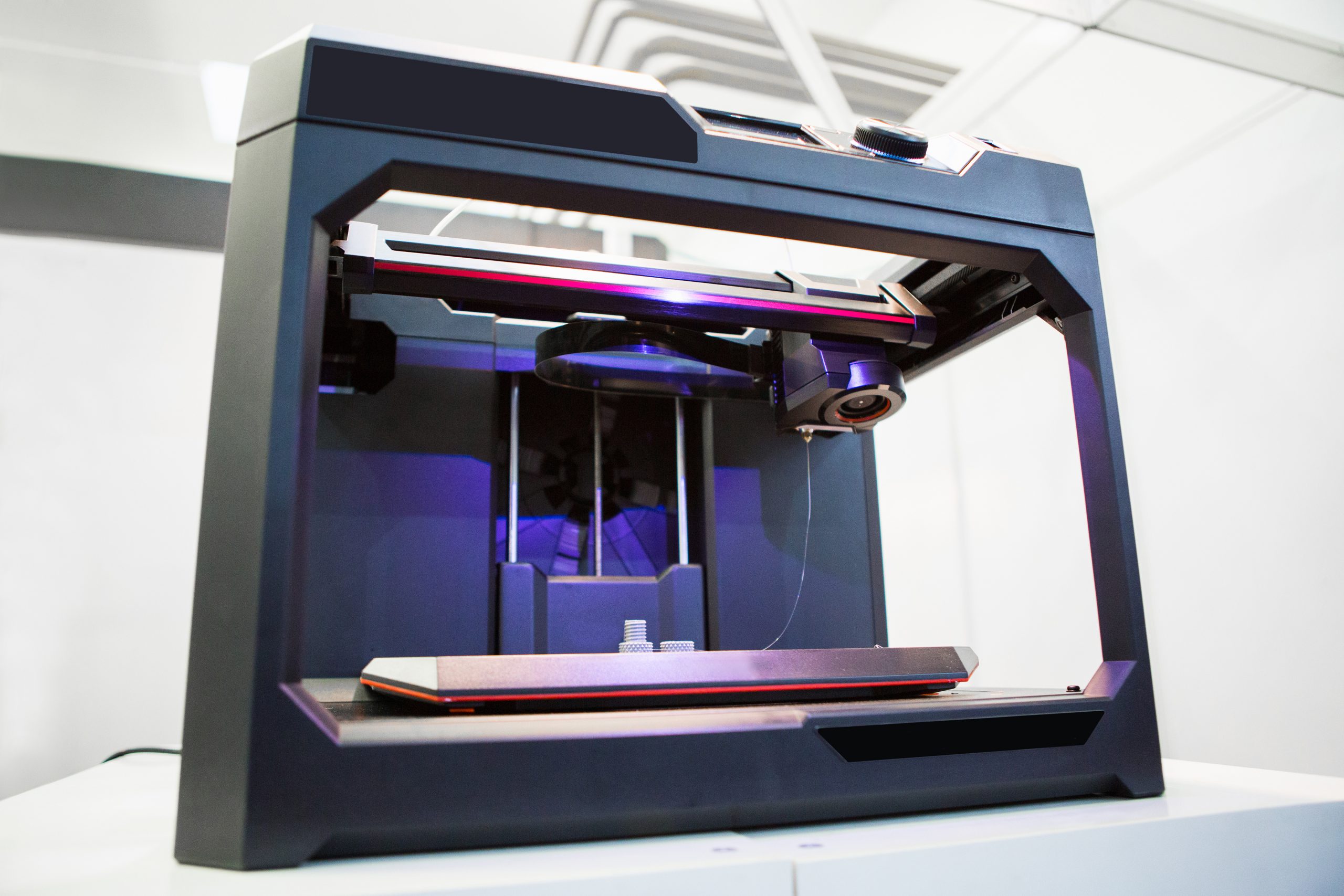
A significant advancement has been achieved in the field of medical imaging, specifically targeting the intricate realm of intravascular analysis. Researchers have successfully engineered a miniaturized optical device that promises to revolutionize the way we visualize and understand the inner workings of blood vessels. This intravascular imaging development centers around the creation of a tiny [..]
Read More
Direct-to-device (D2D) satellite communication is emerging as a transformative technology, poised to revolutionize how we connect to the internet and communicate globally. It aims to bridge the digital divide by enabling seamless connectivity in areas where traditional cellular networks are unavailable or unreliable. This technology allows everyday devices like smartphones to connect directly to satellites, [..]
Read More
In the ever-evolving landscape of biometric authentication, a groundbreaking development has emerged, pushing the boundaries of security and potential applications. Researchers have pioneered a novel method utilizing hyperspectral imaging and artificial intelligence (AI) to identify individuals based on the intricate network of blood vessels within their palms – palm vein biometrics. What sets this approach [..]
Read More
A breakthrough in volumetric 3D printing, HoloVAM, promises to revolutionize optics and photonics applications, particularly in bioprinting. Researchers have developed a holographic technique that significantly boosts efficiency and speed compared to traditional Tomographic Volumetric Additive Manufacturing (TVAM). Conventional TVAM, while capable of rapid, single-shot 3D printing by solidifying resin with light patterns, suffers from low [..]
Read More
Ecological disasters demand rapid and precise toxin analysis to safeguard public health. Surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS), a powerful label-free technique, offers sensitive detection of low-concentration toxins. However, the inherent variability of SERS spectra across different substrates has hindered its widespread application. Researchers have unveiled a machine-learning approach that significantly streamlines SERS analysis, enabling accurate toxin [..]
Read More