
Have you ever wondered why some people are tall, and others are short? Scientists have been chipping away at this question for decades, and a new study has shed new light on the genetics that influence human height. This study employed a powerful whole-genome sequencing technique to pinpoint rare genetic variations associated with height. Whole-genome [..]
Read More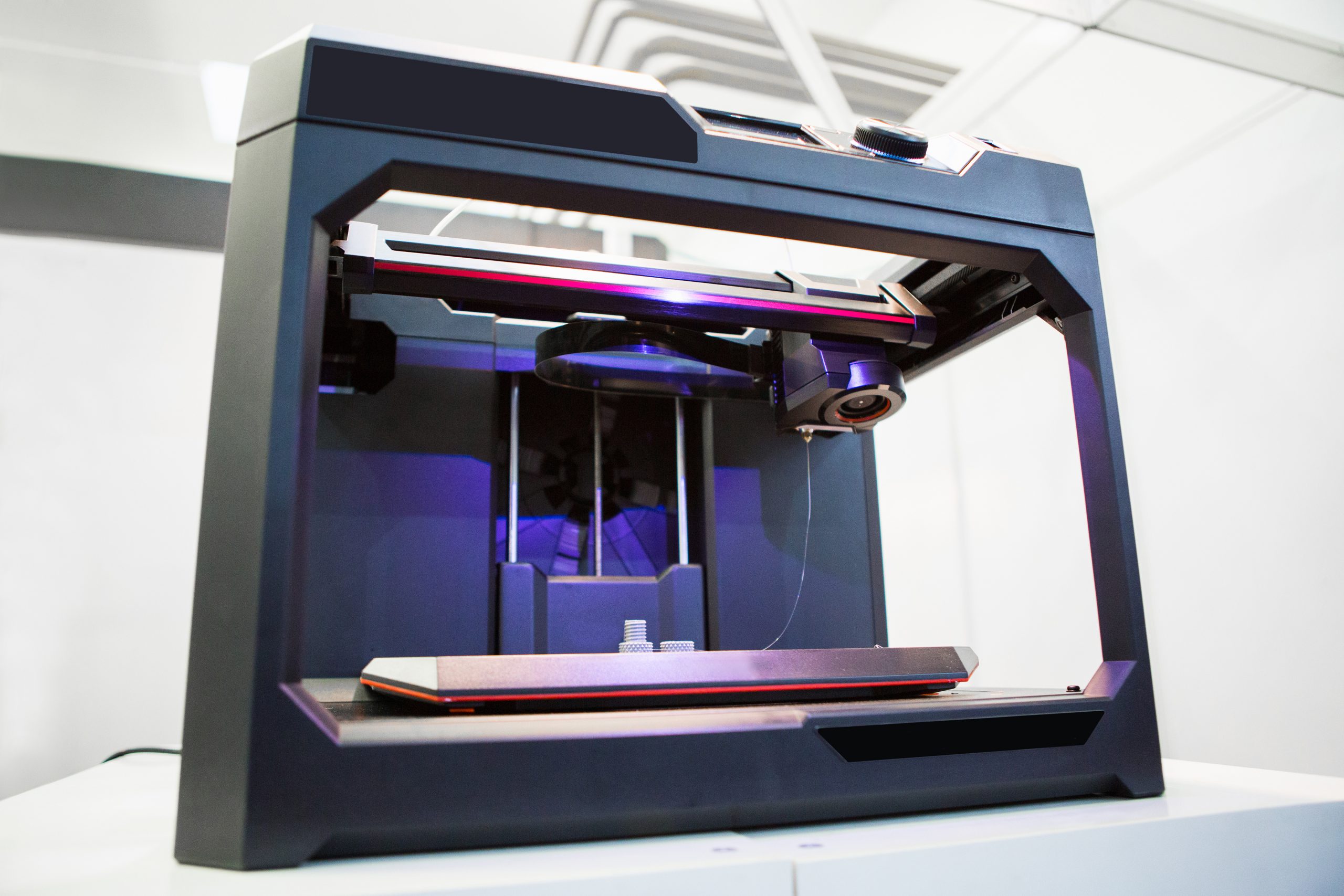
In a groundbreaking collaboration, researchers developed a novel fluorescent 3D printing process incorporating fluorescent ring-shaped molecules. This innovation can potentially revolutionize the field of biomedical implants by creating intricate, glowing structures that are easier to track and monitor within the body. The team combined their expertise in engineering and chemistry to create a technique that [..]
Read More
A team of researchers has developed a promising new method for measuring stroke risk. This non-invasive device, which uses speckle contrast optical spectroscopy for early stroke detection, akin to a cardiac stress test, could revolutionize stroke care by enabling early detection and prevention. Strokes, a leading cause of neurological disability, occur when blood flow to [..]
Read More
New research describes a new, fast, all-optical 3D photoacoustic scanner for clinical vascular imaging. The scanner uses a novel photoacoustic tomography (PAT) technique to capture high-resolution 3D images of microvasculature within a few seconds or even milliseconds. This innovation paves the way for significantly faster imaging compared to conventional methods. The scanner’s core lies in [..]
Read More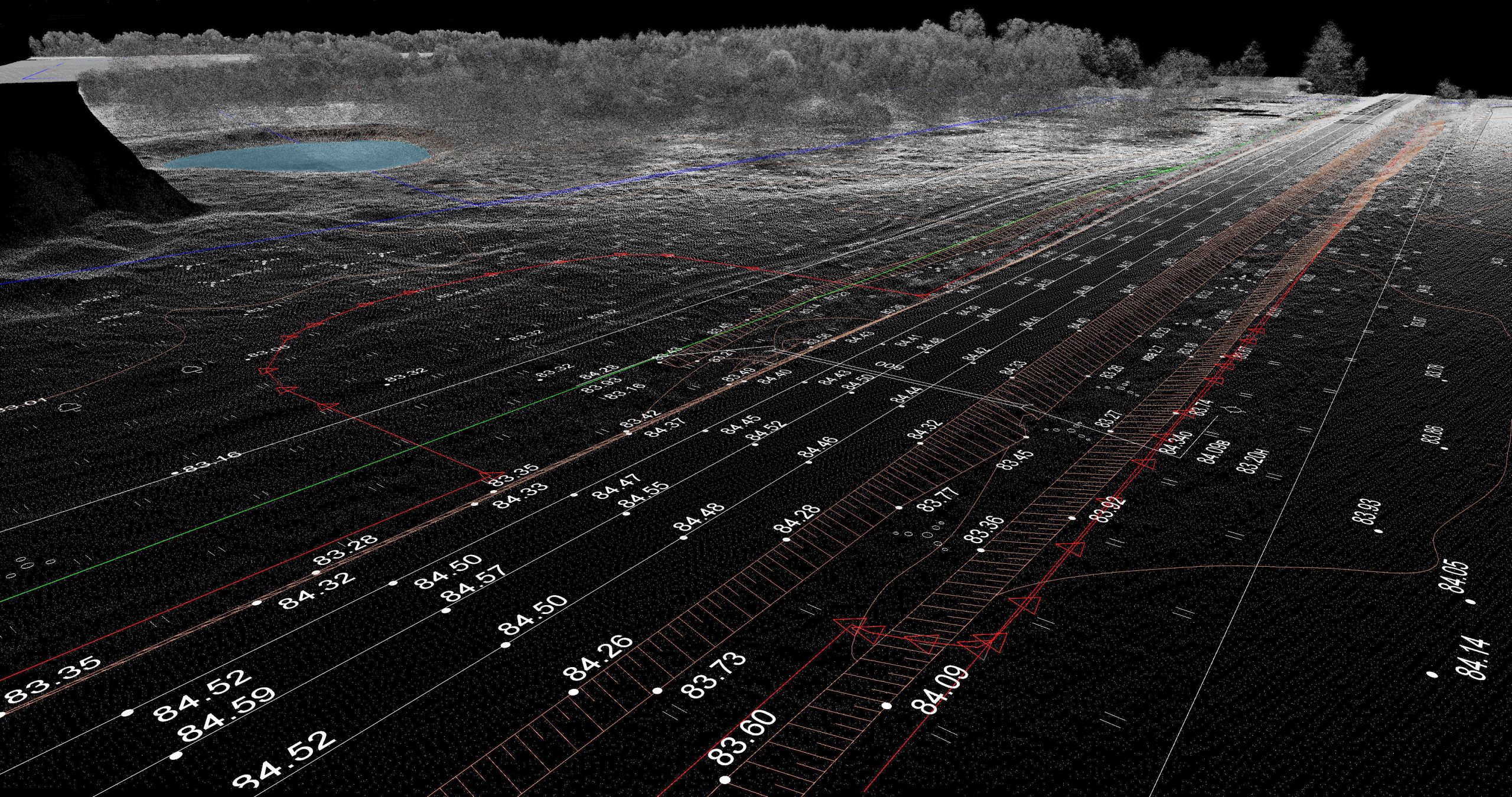
New research discusses a novel application of LiDAR technology to wildfire management. LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging) is a remote sensing method that uses light pulses to measure variable distances. By bouncing laser beams off objects and recording the time it takes for the signal to return, LiDAR systems can create highly detailed, three-dimensional (3D) [..]
Read More
Unipolar quantum optoelectronics offers a game-changing approach for high-speed direct modulation and transmission in the 8–14 µm atmospheric window. The research explores its potential for free-space optical (FSO) communication in the mid-infrared (MIR) region. The system leverages unipolar quantum optoelectronic devices, including a distributed feedback quantum cascade laser (DFB-QCL) as the transmitter and a quantum [..]
Read More
A groundbreaking new method developed by researchers has revolutionized the field of chiral analysis. For the first time, nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy can directly elucidate the chiral structure of molecules—a crucial step in developing new drugs. Chirality, the spatial arrangement of atoms within a molecule, plays a vital role in its biological activity. Enantiomers, [..]
Read More
Researchers have made significant progress in developing a new class of transparent, high-porosity glasses. Due to their unique properties, these aluminum alkoxide network-forming glasses are particularly interesting for optics and photonics applications. The newly developed glasses exhibit well-defined transitions, indicating a clear transition from a viscous liquid to a rigid solid state. This property is [..]
Read More
Direction-of-arrival (DOA) estimation is fundamental in various applications, including radar, sonar, and wireless communication. Traditional methods for DOA estimation often rely on signal processing algorithms that can be computationally expensive and struggle with limitations like the diffraction limit. Researchers are exploring the potential of optical computing to overcome these limitations and achieve higher accuracy and [..]
Read More
Diamond, the epitome of hardness and durability, has long intrigued scientists for its potential in various applications. While its exceptional thermal conductivity and quantum properties are well-known, its suitability for high-power electronics has been hindered by fabrication challenges and limited understanding of its electrical behavior. Researchers have recently shed light on this diamond enigma by [..]
Read More
In a recent breakthrough, researchers have developed a new method to predict a patient’s response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy (NAC) for breast cancer. This method leverages the power of artificial intelligence (AI) and combines information from ultrasound images and pathology slides. NAC is a type of chemotherapy given before surgery to shrink tumors and improve surgical [..]
Read More
Researchers have successfully engineered a metasurface that can transform the chaotic, incoherent thermal emissions from thermal sources like incandescent bulbs into highly coherent, polarized, and directed beams. This groundbreaking achievement could revolutionize fields ranging from lighting and imaging to thermal management and control. Traditionally, metasurfaces have been limited to manipulating highly coherent laser light. However, [..]
Read More
Microfluidic biochips are tiny devices that manipulate fluids at the microliter scale. They have a wide range of applications in the medical field, including drug discovery, diagnostics, and personalized medicine. However, a new study has shown that these chips are vulnerable to cyber-physical attacks that can be launched by tampering with the manufacturing process. The [..]
Read More
Diabetic retinopathy (DR) is a complication of diabetes that can lead to vision loss. Early detection and treatment of DR are essential to prevent vision loss. Traditional fundus photography (FP) is a common screening method for DR. Still, it has limitations in detecting diabetic macular edema (DME), a type of fluid buildup in the macula, [..]
Read More
In silicon photonics, creating dependable sources of single photons and enabling strong interactions between them has been a substantial obstacle to quantum technologies. A recent study describes a novel technique for generating indistinguishable photons from a silicon waveguide incorporating a G center. G centers are intricate defects within silicon. They consist of two carbon atoms [..]
Read More
A new method for measuring urine C-reactive protein (CRP) levels has been developed using an optical sensor and machine learning algorithms. This method is believed to be more accurate and reliable than traditional methods, such as ELISA. CRP is a biomarker of inflammation, and a point-of-care test for CRP could be useful for various applications, [..]
Read More
Researchers have achieved a breakthrough in their understanding of retinal neovascularization. This condition, characterized by the abnormal growth of blood vessels in the retina, is a leading cause of vision loss in premature infants, diabetics, and the elderly. Traditionally, treatments for retinal neovascularization have been limited to laser therapy and anti-VEGF-A (vascular endothelial growth factor [..]
Read More
Researchers have unveiled a groundbreaking microscopy technique that promises to revolutionize our understanding and manipulation of nanomaterials. Their work introduces a method to visualize the intricate details of metamaterials, structures engineered at the nanoscale with extraordinary optical properties. Until now, exploring the nanoscale realm has been akin to studying an elephant with a magnifying glass. [..]
Read More
Imagine a world where telescopes in space and powerful lasers on Earth can function flawlessly for years without worrying about microscopic cracks or fractures diminishing their performance. This futuristic vision might inch closer to reality thanks to researchers’ recent discovery of self-healing glass. The crux of the challenge lies in the limitations of conventional materials [..]
Read More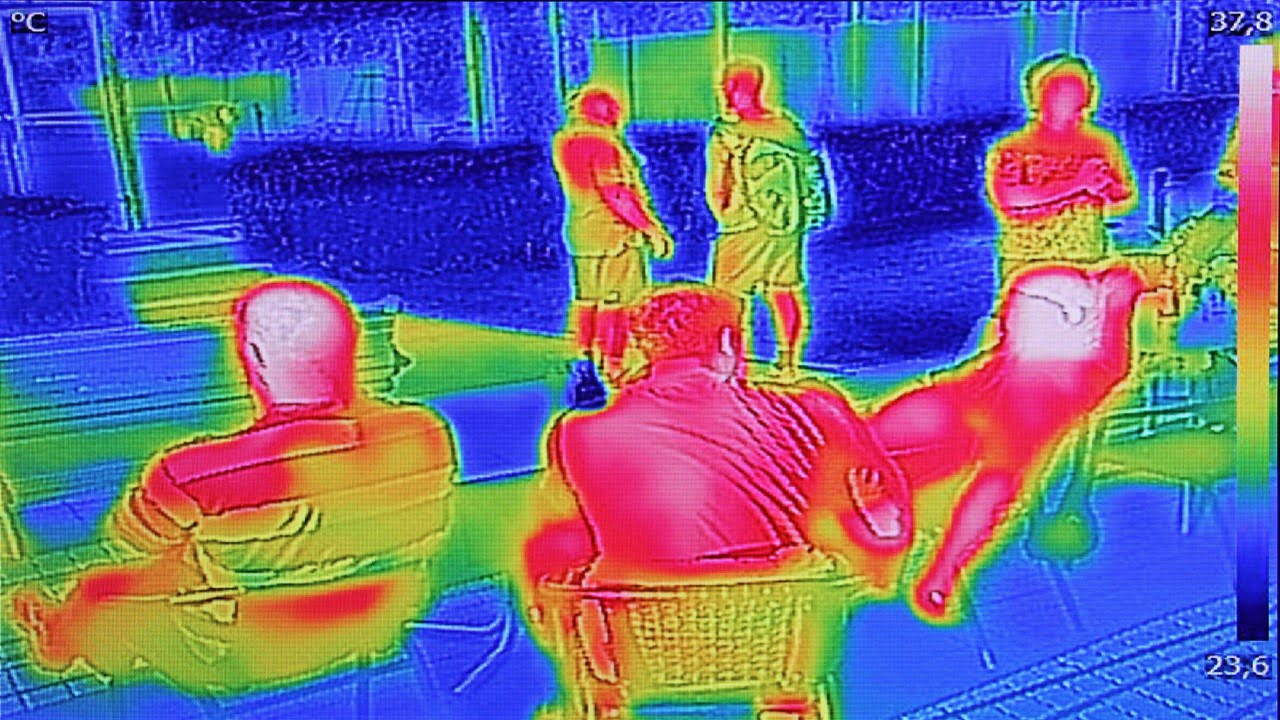
Jiming Bao, an electrical and computer engineering professor at the University of Houston, has invented a new method to improve thermal imaging and infrared thermography. These techniques measure and show temperature distributions without physically touching the photographed material. Thermal cameras and infrared thermometers are very sensitive tools used in various industries, including military and medical [..]
Read More