Laser-plasma accelerators (LPAs) hold promise for generating compact, cost-effective proton beams, but challenges like target replacement and beam divergence have hindered their progress. Now, researchers have made a surprising breakthrough using a simple stream of water. Instead of solid targets, the team used a thin water sheet, replenished after each laser pulse. This solved the [..]
Read More
New research presents a novel method for estimating body composition using 3D imaging and deep learning. Traditional methods like DXA scans, while accurate, involve radiation exposure. This research explores a non-invasive optical approach as a potential alternative. The study utilizes a dataset of 4286 3D body scans, some paired with DXA scan data for ground [..]
Read More
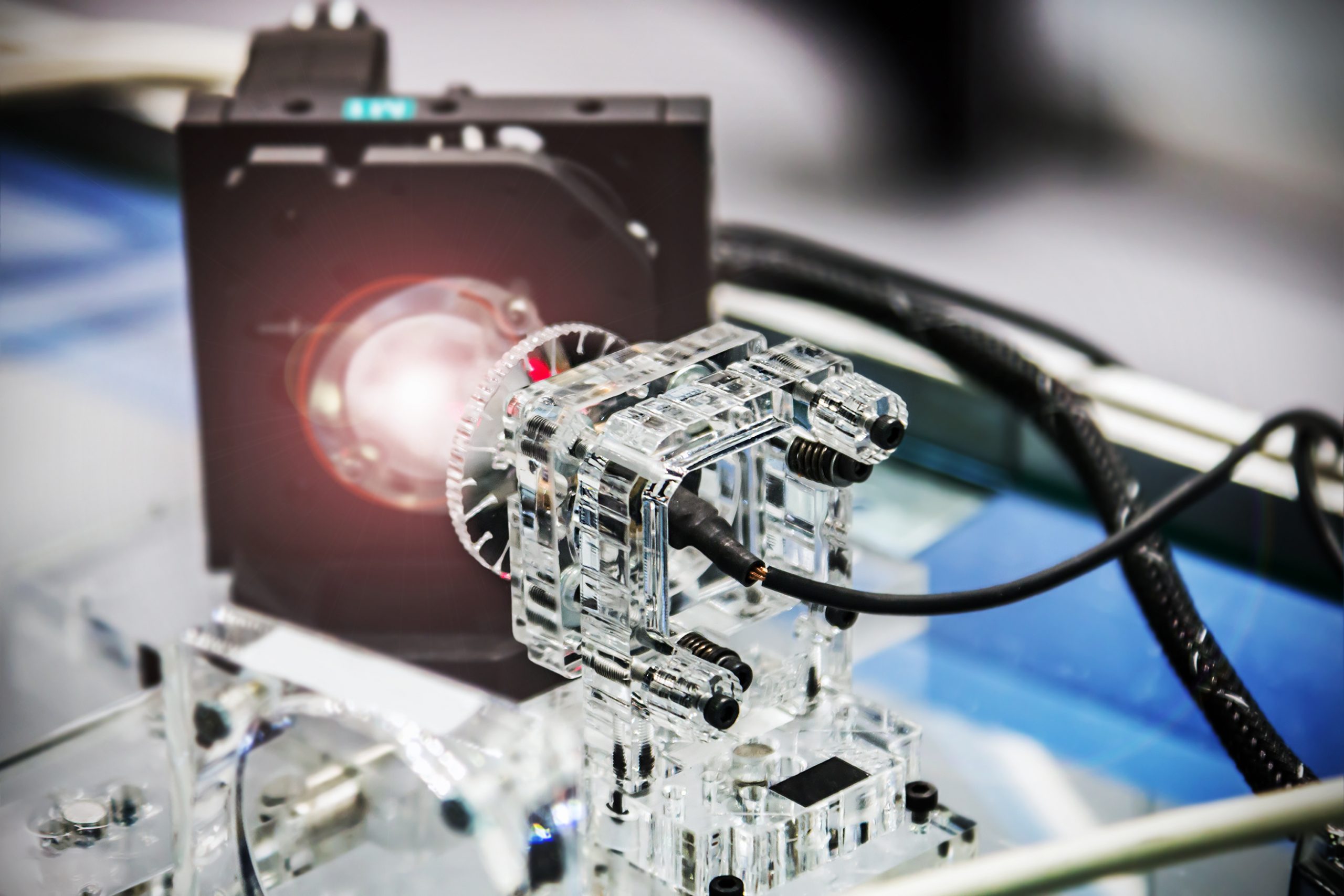
In a breakthrough for integrated photonics, researchers have demonstrated a high-power tunable laser on silicon photonics that reaches close to 2 Watts of output power. This is a significant milestone, as it is the first time that a high-power tunable laser has been demonstrated on silicon photonics. The new laser is based on silicon photonics, [..]
Read More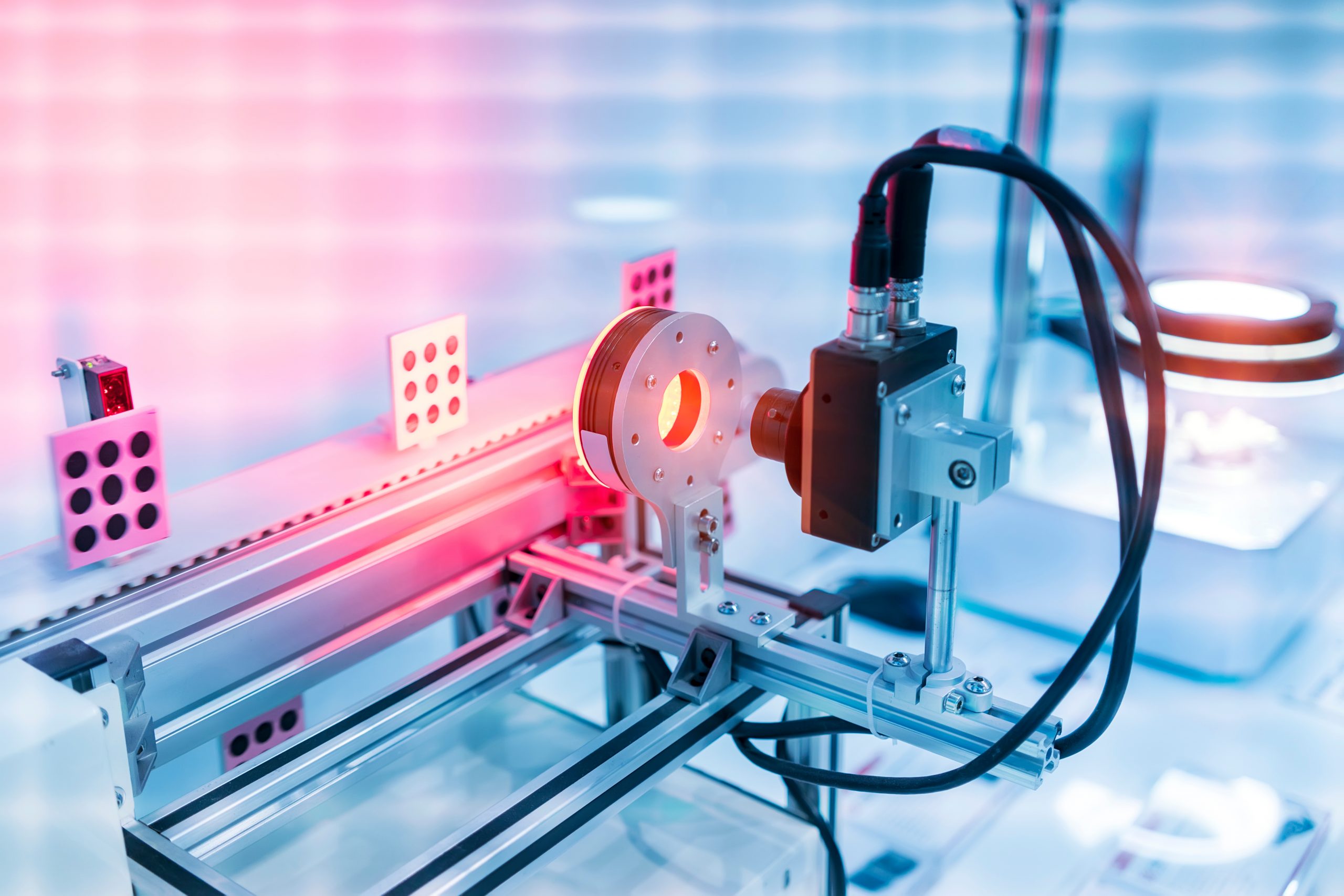
Machine vision is a critical technology in industrial automation, enabling businesses to analyze images, extract data, and make informed decisions. As the technology evolves, deep learning has emerged as a valuable tool for enhancing Its capabilities. However, machine vision and deep learning systems rely heavily on high-quality images for optimal performance. Proper lighting is paramount [..]
Read More
Researchers have developed a groundbreaking approach that combines infrared spectroscopy, machine learning, and computational chemistry to monitor C-C coupling reactions in real time. This innovative method offers a noninvasive and highly accurate way to track the formation of carbon-carbon bonds, a fundamental process in organic chemistry. The team trained a convolutional neural network (CNN) to [..]
Read More
Researchers have made significant strides in optoelectronic materials, paving the way for advancements in LEDs, X-ray scintillators, and direct X-ray detectors. Their work focuses on organic metal halide hybrids (OMHHs), a class of materials offering a unique combination of cost-effectiveness, environmental friendliness, and high performance. One of the key advantages of OMHHs is their ability [..]
Read More
Integrated photonics, a technology that miniaturizes and integrates optical components onto a chip, has made significant strides in recent years. Smaller, more versatile, and energy-efficient optical systems have been made possible by this technology, which has applications in various industries, including telecommunications, sensing, and medical diagnostics. Researchers have created a high-power tunable laser on a [..]
Read More
Scientists have developed a new, self-contained microfluidic test that uses particles to quickly and accurately measure iron and copper ion concentrations in water. This innovative approach addresses the limitations of current methods, which often require complex equipment and lengthy procedures. Iron and copper are essential minerals, but excessive amounts in drinking water can cause health [..]
Read More
Researchers have made a groundbreaking advancement in laser technology by developing a method to “print” lasers using an inkjet printer. This innovative inkjet-printed laser approach could revolutionize display technology, offering brighter and more vibrant colors than current OLED and liquid crystal displays. The process involves inkjet printing tiny droplets of a special organic liquid that [..]
Read More
Scientists constantly strive for clearer images of the microscopic world within us, pushing the boundaries of what is visible to the naked eye. A recent breakthrough in Raman microscopy offers a new way to capture these intricate details with unprecedented clarity. Raman microscopy is a powerful tool for biological imaging. It provides valuable chemical information [..]
Read More
Newborn screening is a crucial public health program identifying infants at risk for serious conditions. Traditionally, this screening has involved a heel prick blood test to check for specific disorders. However, recent advances in genomics have opened up the possibility of using genome sequencing to screen for a much wider range of conditions. The BeginNGS [..]
Read More
Have you ever wondered where the periodic table ends? Scientists are pushing the boundaries by studying superheavy elements beyond uranium (element 92), which can only be created in labs. A recent study sheds light on the structure of these exotic elements. The key lies in nuclear radii. Using laser spectroscopy, researchers measured the size of [..]
Read More
A groundbreaking study has introduced a novel computational holography-based method that promises to revolutionize the field of imaging through scattering media. This innovative technique addresses the long-standing challenge of obtaining high-resolution images through highly scattering materials, such as biological tissues or turbid water. When light passes through a scattering medium, it undergoes multiple scattering events, [..]
Read More
Researchers have introduced a revolutionary imaging technology, DEEPscope, that promises to reshape our understanding of the brain. This innovative microscope overcomes the limitations of traditional multiphoton microscopy, enabling deep and wide-field visualization of neural activity at unprecedented resolution.Multiphoton microscopy, a gold standard for deep-tissue imaging, faces significant hurdles. As imaging depth increases, the field of [..]
Read More
A groundbreaking discovery has the potential to revolutionize non-invasive medical diagnostics. Researchers have harnessed the power of orbital angular momentum (OAM) light to improve imaging and data transmission through biological tissues. OAM light is a special light beam with a unique spatial structure, often described as a “twisted” light beam. Unlike traditional light beams, it [..]
Read More
Chalcogenide glasses, composed of elements like sulfur, selenium, or tellurium, are emerging as a promising material for infrared (IR) optics. These glasses offer unique properties, including transparency in the IR spectrum and the ability to be tailored for specific applications. Recent research has unveiled an extraordinary property of chalcogenide glasses: self-healing chalcogenide glasses. These glasses [..]
Read More
A new technique has been developed to improve illumination uniformity in direct-drive inertial confinement fusion. This technique is more efficient than previous methods and can be applied to other pellet geometries and at other facilities. Inertial confinement fusion is a fusion power that uses lasers to compress and heat a target fuel pellet, causing it [..]
Read More
A groundbreaking study introduces a revolutionary technique for noninvasive, high-resolution imaging through highly scattering media. Researchers developed this method, which leverages computational holography to overcome the limitations of traditional optical imaging. The key innovation lies in using computational optimization to emulate wavefront shaping experiments. By optimizing multiple “virtual SLMs” simultaneously, the researchers could reconstruct high-quality [..]
Read More
Metasurfaces, a class of artificially engineered materials, have revolutionized the field of optics by offering unprecedented control over light at the nanoscale. However, until recently, metasurfaces faced limitations in achieving asymmetric optical responses, where the behavior of light differs depending on its direction of incidence. A team of researchers has successfully overcome this hurdle by [..]
Read More
Mid-infrared (Mid-IR) fiber lasers and amplifiers have gained significant attention due to their potential applications in various fields, including spectroscopy, sensing, and materials processing. However, the efficient coupling of pump light into these Mid-IR fibers remains a critical challenge. Traditional pump combiners often involve complex fabrication processes and can suffer from low coupling efficiencies. New [..]
Read More