
Metamaterials are artificial composites that can interact with electromagnetic waves, including visible light. Our brains generate electromagnetic waves as they process information. The brain waves can trigger changes in metamaterials. Not exactly like telekinesis and telepathy in science fiction, but the research can have applications in real-life scenarios. In a study, researchers used a brainwave [..]
Read More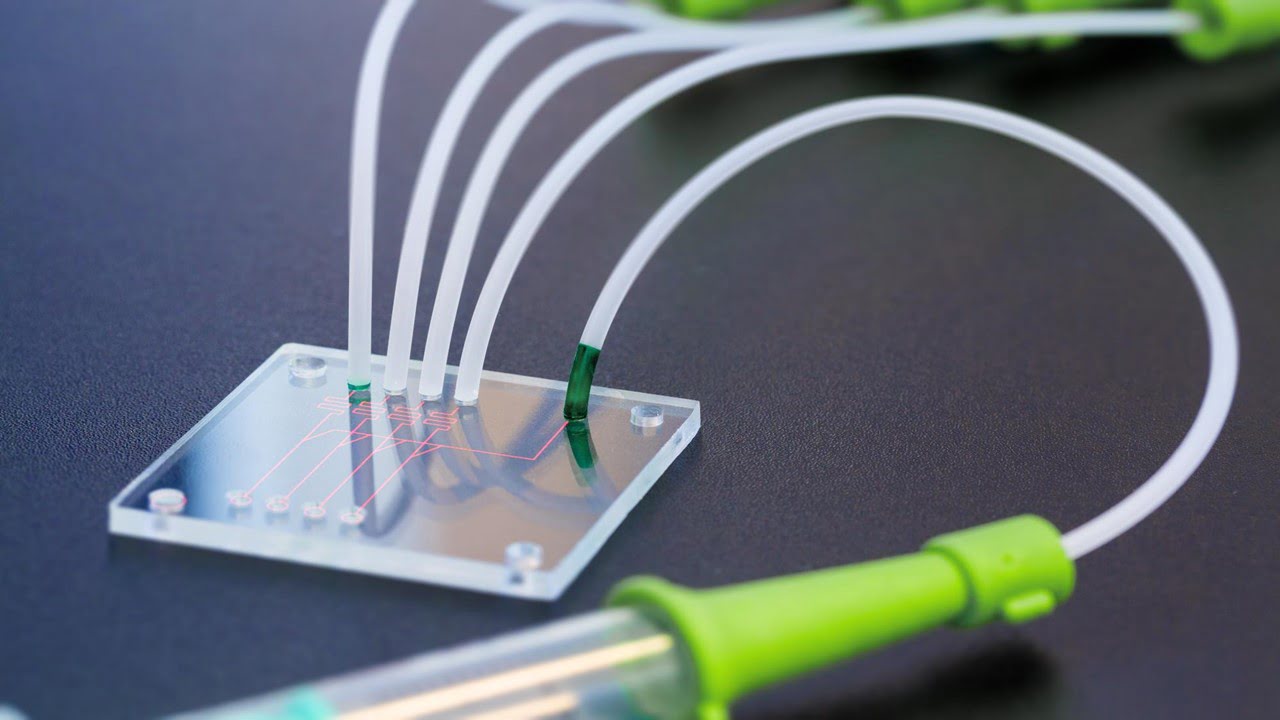
Researchers have developed a nonlinear optical crystal-based compact terahertz (THz)-microfluidic chip with several I-design meta-atoms for attomole (amol)-level sensing of trace amounts of solution samples. The I-design meta-atoms consist of metallic strips with micrometer-sized gaps sandwiched by other metallic strips, periodically arrayed in a row of 1 × 5 units. A point THz source (locally [..]
Read More
Lithium Niobate (LN) does not exist in the natural world and is a purely artificial inorganic material. It is composed of lithium, niobium, and oxygen. People usually refer to LN as a distorted perovskite type of crystal. LN has many unique features, such as a wide operational wavelength window, electro-optic (Pockels) effect, nonlinear optical polarizability, [..]
Read More
Researchers have built erbium-doped waveguide amplifier (EDWA) based on silicon nitride (Si3N4) photonic integrated circuits of a length up to a half-meter on a millimeter-scale footprint. The device generates a record output power of more than 145 mW. It provides a small-signal net gain above 30 dB, translating to over 1000-fold amplification in the telecommunication [..]
Read More
Researchers have developed a nanofluidic scattering microscopy technique to study biomolecules in their natural state. When developing medicines and vaccines, it is crucial to study individual proteins’ behavior and interaction with each other. The new microscopy method can help find the most promising candidates at an early stage. The technique also has the potential for [..]
Read More
Imaging techniques are essential in cancer diagnosis and treatment, but their use remains limited in prostate cancer surgeries. Systematic prostate biopsies locate cancerous tissue and guide treatment. While magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) can yield greater insight into tumor characteristics, the extent to which it improves treatment outcomes needs a national scale. The new research demonstrates [..]
Read More
Researchers have developed an enhanced version of optical coherence tomography (OCT scan) that can image biomedical samples at higher contrast and resolution over a wider 3D field of view than was previously possible. The new 3D microscope could be useful for biomedical research and enable more accurate medical diagnostic imaging. The researchers describe the new [..]
Read More
A progressive loss of central vision characterizes age-related macular degeneration (AMD). It is the commonest cause of blindness in the elderly. Intermediate AMD is a risk factor for progression to advanced stages categorized as geographic atrophy (GA) and neovascular AMD. However, rates of progression to advanced stages vary between individuals. Recent advances in imaging and [..]
Read More
Researchers have built an intelligent quantum sensor – the size of about 1/1000 of the cross-section of a human hair – that can simultaneously detect the intensity, polarization, and wavelength of light, tapping into the quantum properties of electrons. The breakthrough could help advance the fields of astronomy, healthcare, and remote sensing. Twisting certain materials [..]
Read More
Researchers have found a way to identify lung cancer at the cellular level in real-time during a biopsy, promising to detect the disease earlier and with more confidence. The researchers call the new technology NIR-nCLE. It combines the cancer-targeted near-infrared (NIR) tracer with a needle-based confocal laser endomicroscopy (nCLE) system, modified to detect the NIR [..]
Read More
Researchers have studied unusual regimes of operation of a laser with a gain medium with a large Raman scattering cross-section, which is often inherent in new types of gain media such as colloidal and epitaxial quantum dots and perovskite materials. A strong electron-phonon coupling characterizes these media. Using the Fröhlich Hamiltonian to describe the electron-phonon [..]
Read More
While solar cells are a great alternative to fossil fuels, the environmental impact of the processes involved in manufacturing solar cells has been a concern. Solar panel fabrication often involves toxic materials such as cadmium and industrial waste. In a new study, researchers have developed an eco-friendly method that eliminates toxic cadmium in the production [..]
Read More
Researchers are developing a low-cost handheld device that could cut the rate of unnecessary skin biopsies in half and give dermatologists and other frontline physicians easy access to laboratory-grade cancer diagnostics. The team’s device uses millimeter-wave imaging — the same technology used in airport security scanners — to scan a patient’s skin. Healthy tissue reflects [..]
Read More
Because of their capacity to measure heart rates (HRs) without contact with human skin, photoplethysmography imaging (PPGI) sensors have been the focus of considerable attention. A PPGI sensor uses a camera capable of face detection and records images of facial skin, as the skin can represent changes in arterial blood volume between the systolic and [..]
Read More
Conjunctival goblet cells (CGCs) are specialized epithelial cells secreting mucins to form the mucus layer of the tear film. The mucus layer spreads the tear film on the ocular surface for protection. The dysfunction and death of CGCs cause tear film instability and are associated with various ocular surface diseases, including dry eye disease (DED). [..]
Read More
Researchers have developed new polymer materials that are ideal for making the optical links necessary to connect chip-based photonic components with board-level circuits or optical fibers. The polymers can be helpful to easily create interconnects between photonic chips and optically printed circuit boards, the light-based equivalent of electronic printed circuit boards. These new materials and [..]
Read More
Researchers have developed a temperature sensing method using naturally occurring atom-like defects in diamonds. The defects, known as Nitrogen-Vacancy (NV) defects, are naturally occurring flaws in diamonds (two adjacent carbon atoms replaced by a nitrogen atom and a hole). They are easy to obtain and have unusual quantum and nonlinear optical properties. Among them is [..]
Read More
A new MRI innovation that makes cancerous tissue glow in medical images could help doctors more accurately detect and track cancer progression over time. The MRI innovation creates images in which cancerous tissue appears to light up compared to healthy tissue, making it easier to see. This new technology has promising potential to improve cancer [..]
Read More
In-sensor computing allows image sensors with internal computing capabilities to reduce communication latency and power consumption for machine vision in distributed systems and robotics. Because of its tunable electrical and optical properties and amenability for heterogeneous integration, two-dimensional semiconductors have several advantages in creating intelligent vision sensors. Researchers have developed a multipurpose infrared image sensor [..]
Read More
Dual-detection impulsive vibrational spectroscopy (DIVS) is a Raman spectroscopy technique. It permits monitoring two types of vibrational signals simultaneously. It offers ultrafast, real-time spectral detection over the low-frequency, or terahertz area of the Raman spectrum and the fingerprint region at a rate of 24,000 spectra per second. The fingerprint and terahertz spectral areas provide complementary [..]
Read More