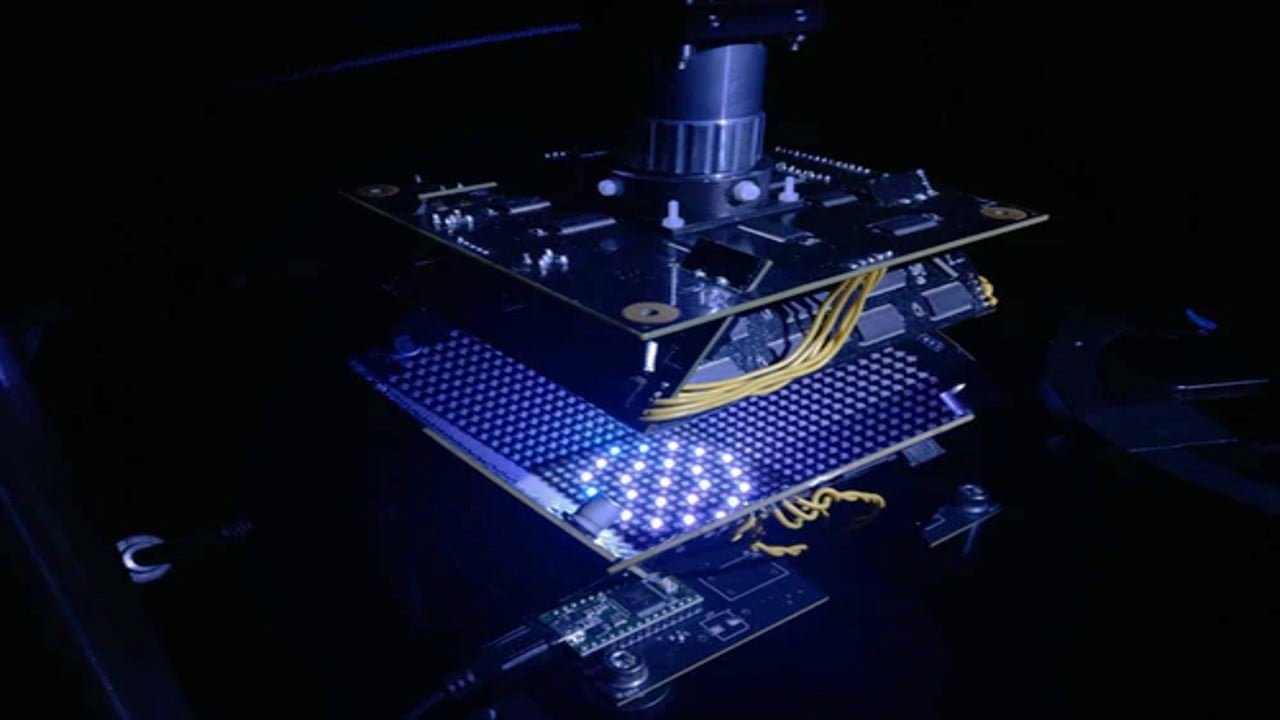
Engineers have created a microscope that adapts its lighting angles, colors, and patterns while teaching itself the best settings for a given diagnostic task. The microscope developed a lighting pattern and classification system simultaneously in the engineering team’s study, allowing it to quickly identify red blood cells infected by the malaria parasite more accurately than [..]
Read More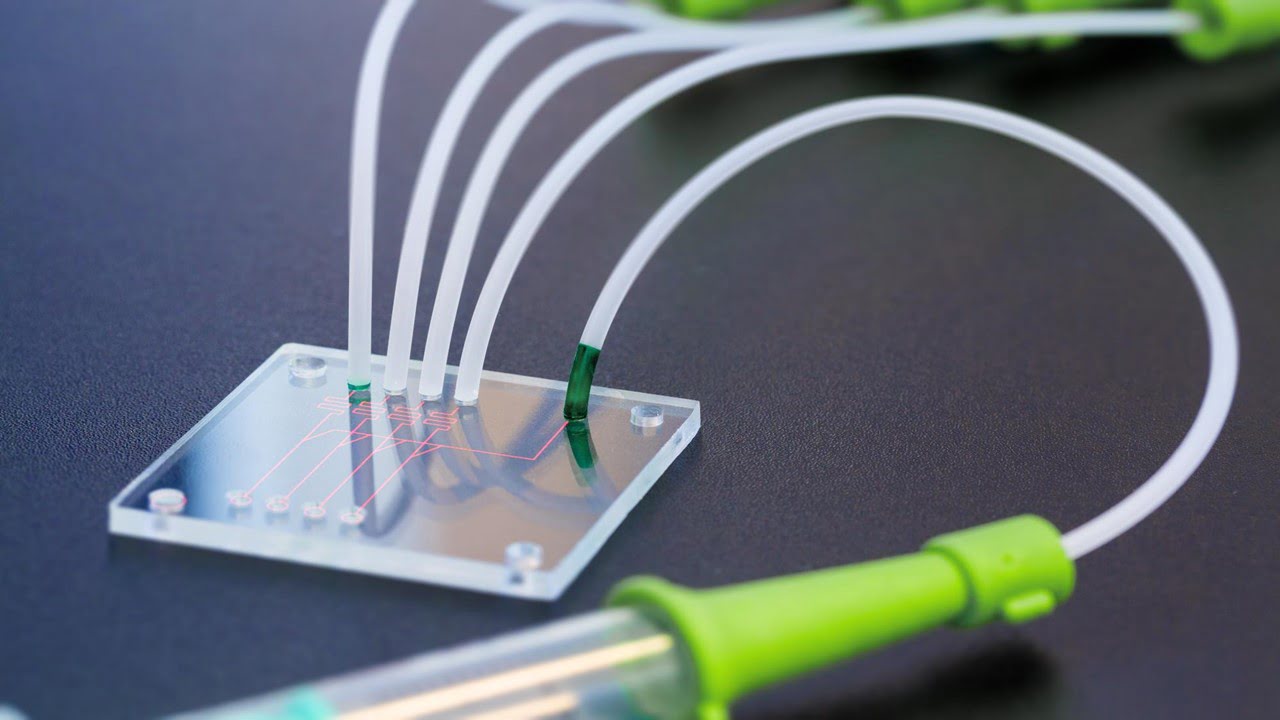
Biomimetics, the ability to imitate nature, gives scientists a blueprint for creating intricate micro- and nanoscale structures that mimic the beneficial properties of the plant or animal being mimicked. Researchers were able to make lens arrays from “liquid marbles” that have the same wide field of view, nearly infinite depth of field, peripheral vision without [..]
Read More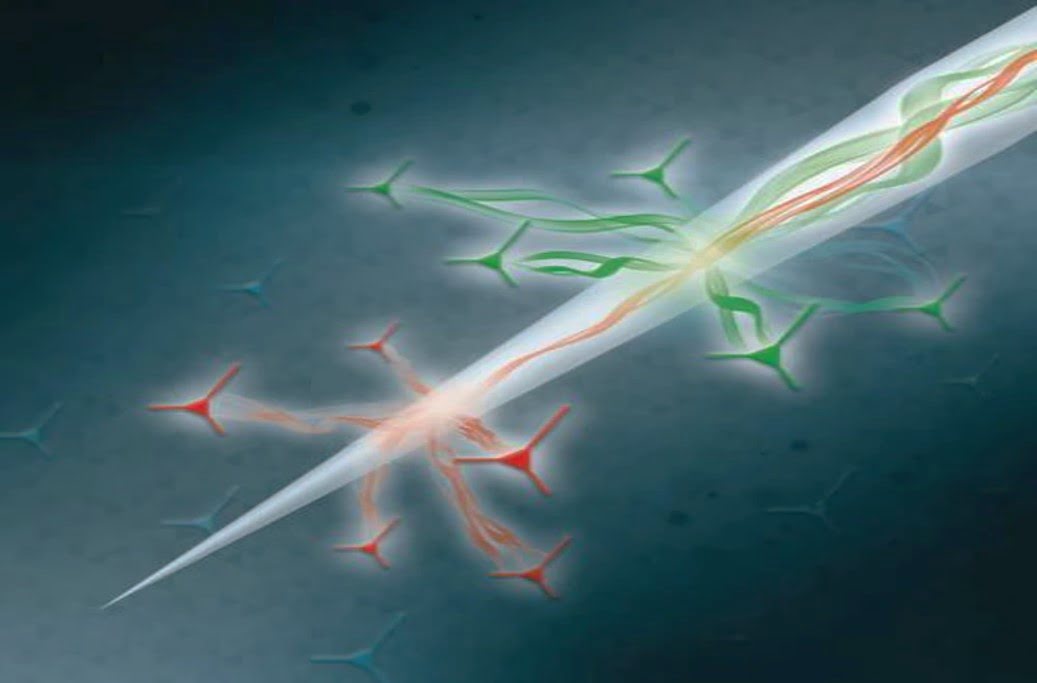
An international team of researchers used an optical probe to capture and pinpoint the brain’s neural activity epicenter. The method lays the groundwork for new ways to map connections across different brain regions, which could lead to the development of devices to image different brain areas and even treat conditions caused by malfunctions in the [..]
Read More
Better biosensor technology, as described by the study team, “may help lead to safe stem cell therapies for treating Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s diseases and other neurological disorders,” they claim. The research, which uses a graphene and gold-based platform and sophisticated imaging equipment, tracks the growth of stem cells by spotting the genetic material (RNA) necessary [..]
Read More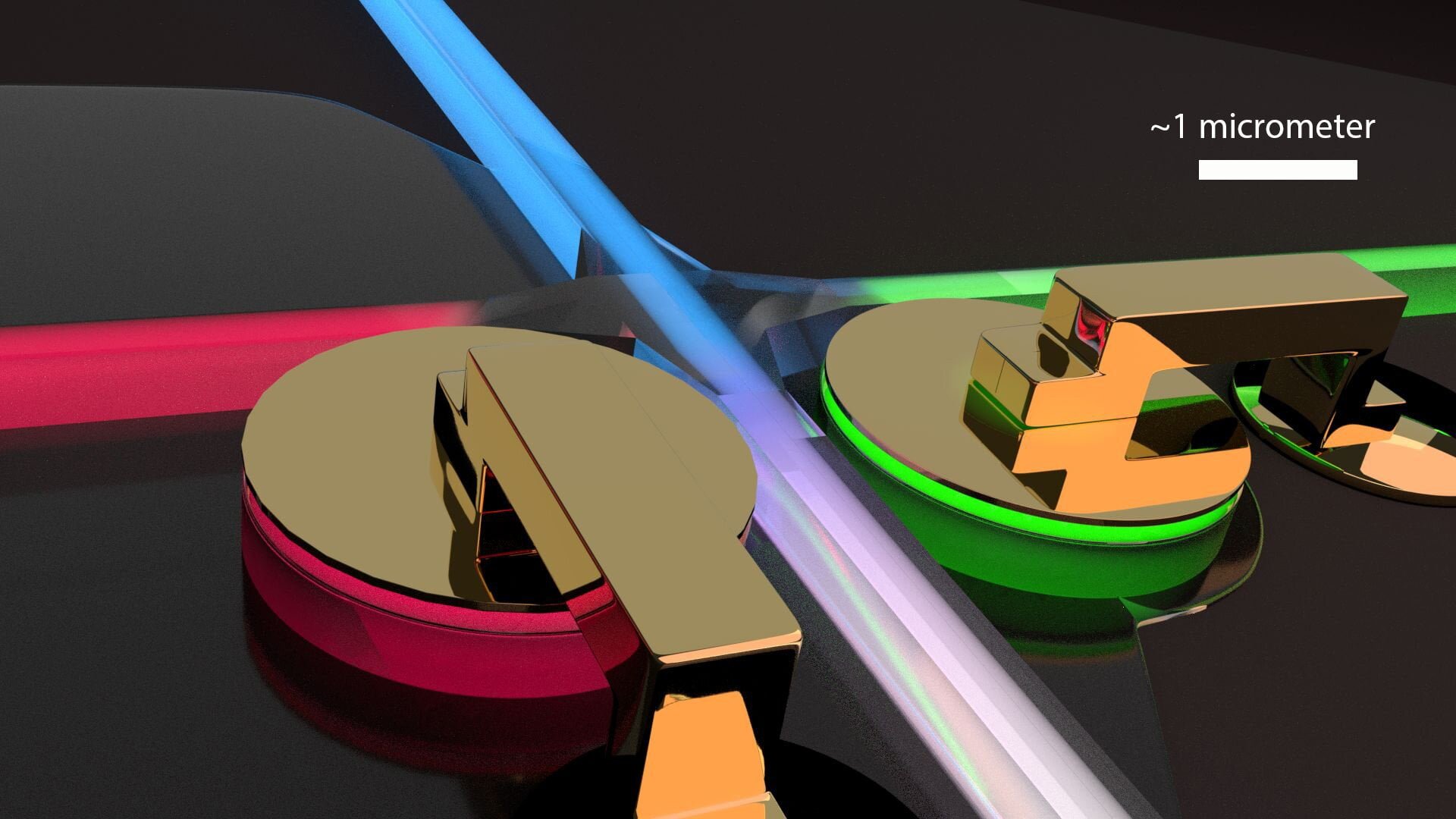
Researchers have created a tiny low-energy device – an optical switch that can move the light from one computer chip to another in 20 billionths of a second, faster than any other similar device. The compact switch is the first to redirect light with very low signal loss while operating at voltages low enough to [..]
Read More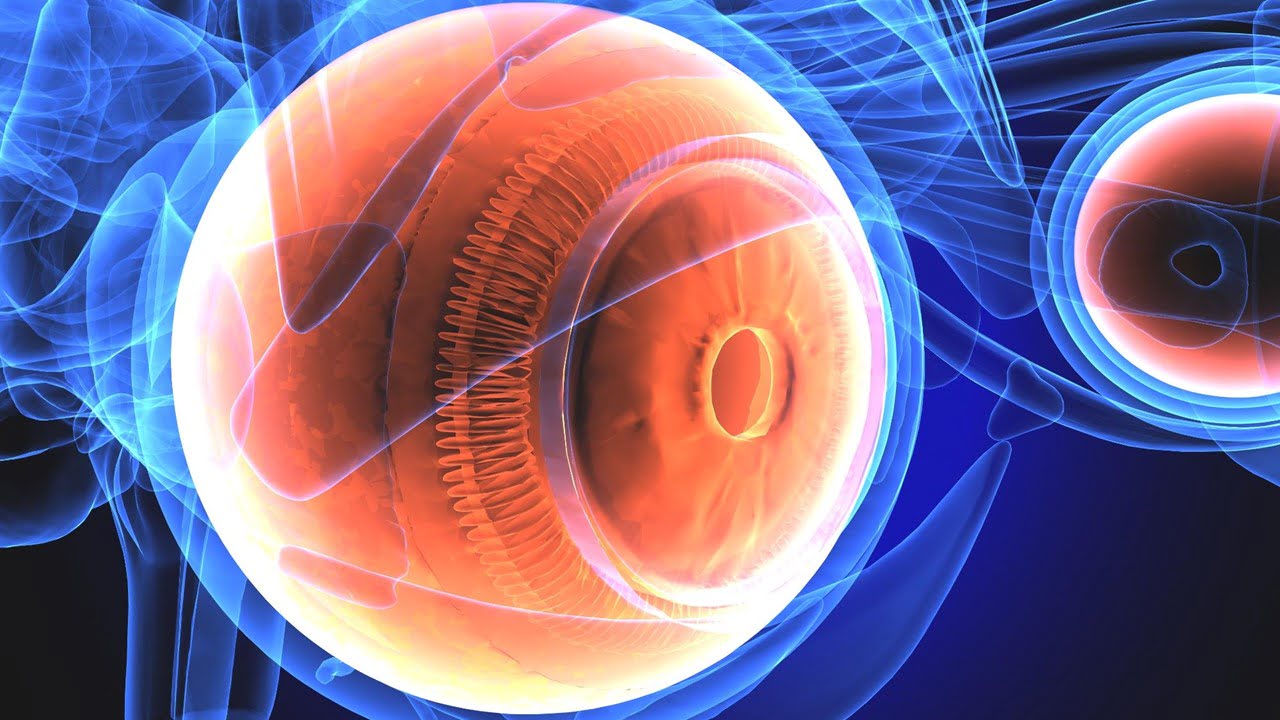
Researchers have devised a method to perform optical coherence tomography (OCT) in difficult-to-reach body parts like joints. The development might make new surgical and medical uses possible for this high-resolution biomedical imaging method. OCT is the best tool for detecting minute changes in tissue that could be signs of illness or damage because it can [..]
Read More
Scientists have created rewritable optical components for 2D light waves (surface light waves). A polariton is a particle that blurs the line between light and matter when certain materials confine a wave of light on a 2D plane. Polaritons allow light to be tightly confined to the nanoscale, potentially to a few atoms in thickness. [..]
Read More
We hear about climate change and its consequences almost daily, from wildfires in Greenland to melting ice in Antarctica to Europeans sweating in record-high summer temperatures. These stories, combined with dire warnings about rising sea levels and record levels of greenhouse gases, can elicit strong urges to “do something.” One of the first jobs is [..]
Read More
Researchers have developed a method to make reproducible nanoscale manufacturing possible. The team adapted a light-based technology employed widely in biology — known as optical traps or optical tweezers — to operate in a water-free liquid environment of carbon-rich organic solvents, enabling new potential applications. The optical tweezers act as a light-based “tractor beam” that [..]
Read More
Most leading security standards (for example, Advanced Encryption Standard, or AES, and Rivest-Shamir-Adleman, or RSA, which are used to secure online communications such as payments on shopping websites) used in secure communication methods do not make use of quantum technology. As a result, electronic transmission of PINs or passwords can be intercepted, posing a security [..]
Read More
Researchers have created a broadband laser-based sensor that can remotely detect the concentration level of key blood components like lactate, glucose, urea, ketones, or ethanol without drawing blood to make noninvasive blood analysis possible. Chronic disease patients, such as those with diabetes, won’t have to repeatedly prick their fingers to check their blood glucose levels [..]
Read More
Engineers have created a computer vision system that can detect minute changes in ground shadows to determine if a moving object is around the bend to increase the safety of autonomous systems. One day, autonomous vehicles may use the system to swiftly avoid collisions with other vehicles or pedestrians approaching from behind a building’s corner [..]
Read More
The microlens array has attracted significant attention with the increasing demand for optoelectronic miniaturization. It has become an important micro-optic device widely used in compact imaging, sensing, optical communication, and other applications. Microlens arrays are typically made up of multiple micron-sized lenses with optical surface smoothness and superior uniformity, which increases the need for machining [..]
Read More
These materials’ extraordinary optical, semiconducting, and mechanical qualities have increased interest in plastic electronics and photonics over the past few decades. For designing laser geometries of almost any form, plastic electronics based on conjugated polymers combine the advantages of cost-effective processability compatible with large-area deposition. With rigid inorganic semiconductor materials, this is not feasible. To [..]
Read More
By measuring the activity of a large number of individual neurons simultaneously, a new ultrasensitive optical nanoprobe that can monitor the bioelectric activity of neurons (and other cells that generate electrical impulses) could help researchers better understand how neural circuits function at previously unexplored scales. In the future, the device could aid in developing high-bandwidth [..]
Read More
An experiment that could result in more precise sensors and clocks will test Einstein’s twin paradox using quantum particles in a superposition state. According to the twin paradox, time can move at different rates for individuals depending on how close they are to a large mass or how quickly they are moving. For instance, a [..]
Read More
A novel method for adjusting and engineering the mirror symmetry of polarization in structured optical fields has been created by a research team. The team has named these polarization states kaleidoscope-structured vector optical fields (KS-VOFs) and claims that their adjustable symmetries and geometries provide an “additional degree of freedom” that may be useful in optical [..]
Read More
Physicists and materials scientists have created a small optical device with vertically stacked metasurfaces to produce microscopic text and full-color holograms for encrypted data storage and color displays. A study team implemented a 3-D integrated metasurface device to make the optical device smaller. The study team designed optical elements by modifying the wavefront of light [..]
Read More
For the precise diagnosis of people with chronic hepatitis B (CHB), a research team has created a test that combines highly sensitive coamplification at lower denaturation temperature polymerase chain reaction (COLD-PCR) with probe-based fluorescence melting curve analysis (FMCA). The straightforward, affordable test might be applied frequently in medical labs. The hepatitis B virus (HBV) can [..]
Read More
Researchers have demonstrated that they can picture the simultaneous electrical activity of many neurons in the brains of mice using a fluorescent probe that illuminates when brain cells are electrically active. Neuroscientists may be able to see the activity of brain circuits using this method, which can be carried out using a basic light microscope, [..]
Read More