
Researchers have made a groundbreaking advancement in laser technology by developing a method to “print” lasers using an inkjet printer. This innovative inkjet-printed laser approach could revolutionize display technology, offering brighter and more vibrant colors than current OLED and liquid crystal displays. The process involves inkjet printing tiny droplets of a special organic liquid that [..]
Read More
Scientists constantly strive for clearer images of the microscopic world within us, pushing the boundaries of what is visible to the naked eye. A recent breakthrough in Raman microscopy offers a new way to capture these intricate details with unprecedented clarity. Raman microscopy is a powerful tool for biological imaging. It provides valuable chemical information [..]
Read More
Plastic pollution in our oceans is a critical environmental challenge, impacting marine life and human livelihoods. Traditional methods for detecting and analyzing these plastics are often slow, costly, and labor-intensive. But now, a team of researchers has developed a groundbreaking solution: a hyperspectral Raman imaging lidar system that can remotely identify different types of plastics. [..]
Read More
Traditional methods for trace gas detection, like laser spectroscopy, often fall short when it comes to real-time, in situ applications. However, a new technology, microscale fiber photoacoustic spectroscopy (FPAS), is poised to change the game. Researchers have developed an all-in-one FPAS system that miniaturizes the key components. Imagine a device where the photoacoustic cell and [..]
Read More
Metasurfaces, engineered surfaces with nanoscale structures, are revolutionizing the field of optoelectronics. These surfaces manipulate light in ways not possible with traditional optics, offering exciting possibilities for miniaturized and highly efficient optical devices. Recent advancements in metasurface technology have led to the development of various innovative applications, including: Compact and efficient optical components: Metasurfaces can [..]
Read More
Sea sponges, masters of underwater architecture, build intricate and robust glass skeletons. Now, scientists have harnessed the power of these marine creatures to create bio-inspired microlenses. Researchers have engineered bacteria to produce silica, mimicking the sea sponge’s bioglass. Microlenses, typically challenging and costly to manufacture, are tiny lenses about the size of a single cell [..]
Read More
Researchers have developed a groundbreaking solar-powered synaptic device that enhances the efficiency of edge AI for optical sensing applications. This innovation addresses the growing need for real-time processing of time-series data in edge AI devices, which are crucial for predicting natural disasters and medical emergencies. The device mimics the behavior of human synapses, using physical [..]
Read More
The search for dark matter has led to innovative detection strategies, especially for lower-mass candidates that interact weakly. A collaboration has proposed a novel quantum detector leveraging superfluid helium and optomechanics. This approach offers a promising path to dark matter detection in the keV mass range. Due to the extremely weak signals produced, traditional detection [..]
Read More
A team of researchers has developed a groundbreaking technique for infrared “color” detection and imaging that could revolutionize fields like thermal imaging, medical diagnostics, and space exploration. This innovative approach to LWIR detection offers a cost-effective way to overcome the limitations of current infrared technology. Traditional infrared detectors struggle to differentiate between wavelengths of infrared [..]
Read More
Newborn screening is a crucial public health program identifying infants at risk for serious conditions. Traditionally, this screening has involved a heel prick blood test to check for specific disorders. However, recent advances in genomics have opened up the possibility of using genome sequencing to screen for a much wider range of conditions. The BeginNGS [..]
Read More
A team of researchers has developed a new type of metasurface that can trap light more efficiently than previous designs. This breakthrough could lead to the development of more sensitive and compact biosensors. The new light-trapping metasurface has a thin silicon layer with a patterned surface. The pattern is designed to trap light in a [..]
Read More
A collaborative effort is underway to push the boundaries of vision restoration through whole-eye transplantation. This ambitious project involves a diverse team of scientists and clinicians working together to overcome significant technical challenges and bring this groundbreaking technology to fruition. Key Research Areas: Neural Interface Technology: Developing advanced electrode interfaces to precisely connect the optic [..]
Read More
Drug discovery is undergoing a paradigm shift, moving away from simplistic, single-endpoint assays toward more complex phenotypic analyses. One such powerful technique, cell painting, employs imaging to visualize cellular structures and quantify changes in cellular state. However, analyzing these complex, large-scale datasets has historically been a major bottleneck. Researchers have developed SPACe (Swift Phenotypic Analysis [..]
Read More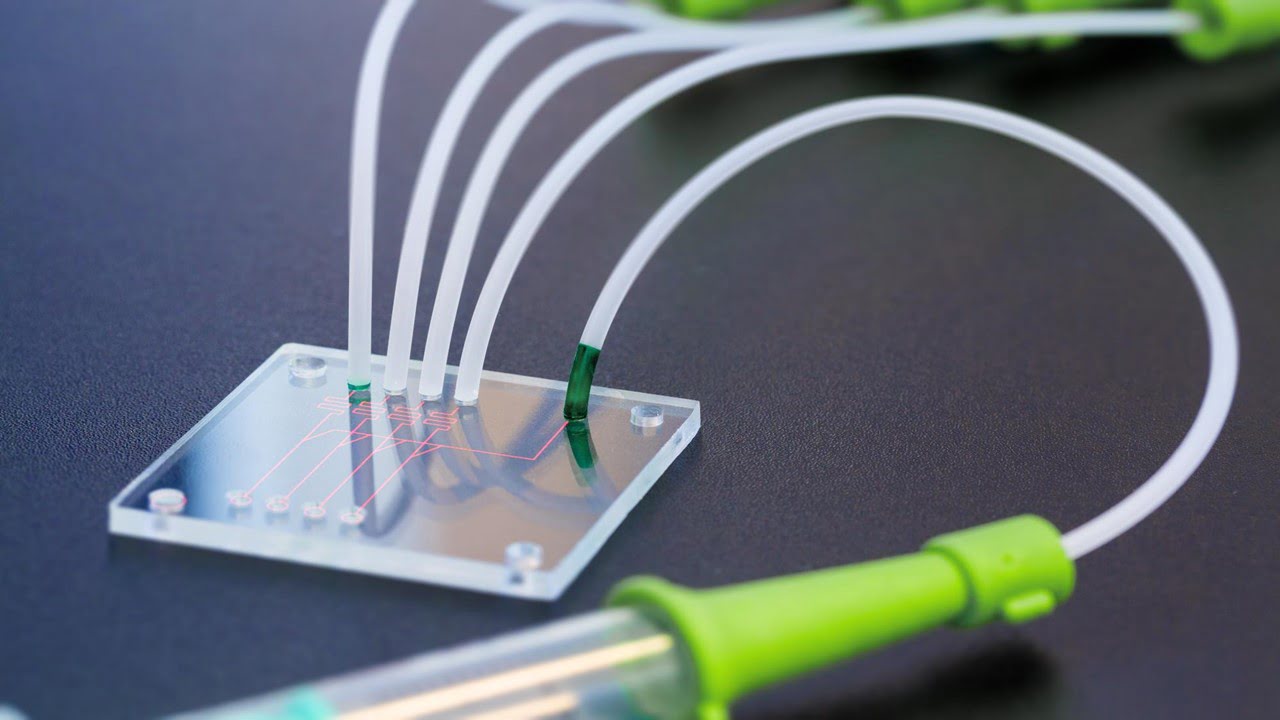
Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) is a growing global health crisis, threatening the effectiveness of antibiotics and other antimicrobial agents. To combat this issue, researchers are constantly seeking innovative methods to understand and counter the evolution of drug resistance. A recent study introduces a groundbreaking microfluidic system that dramatically speeds up the study of AMR. By concentrating [..]
Read More
Silicon photonics, a cornerstone of modern optical communications, has served us well for decades. Yet, as we push the boundaries of technology, its limitations are becoming increasingly apparent. A recent study highlighted the urgent need to explore alternative materials and configurations for optical modulators. The Silicon Ceiling While silicon photonics has enabled significant advancements, it [..]
Read More
Lightning, a breathtaking display of nature’s power, remains a complex phenomenon scientists are still unraveling. As our planet warms, the frequency and intensity of lightning strikes increase, making it crucial to understand and predict these events. Researchers have turned to innovative technologies to gain deeper insights into lightning’s behavior. A recent breakthrough involves an event-based [..]
Read More
A research team has unveiled a novel method for capturing high-resolution fluorescence microscopy images through complex scattering media. This innovative approach leverages the power of conventional widefield fluorescence microscopes to overcome the limitations imposed by light scattering. Light scattering, a common phenomenon in biological and other complex samples, often obscures the underlying structures of interest. [..]
Read More
Imagine lenses that can shift focus and intensity in the blink of an eye, conjuring three-dimensional imagery like a scene out of science fiction. Thanks to a new generation of holographic lenses, this isn’t the plot of a futuristic movie; it’s the potential future of virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR). Inspired by holographic [..]
Read More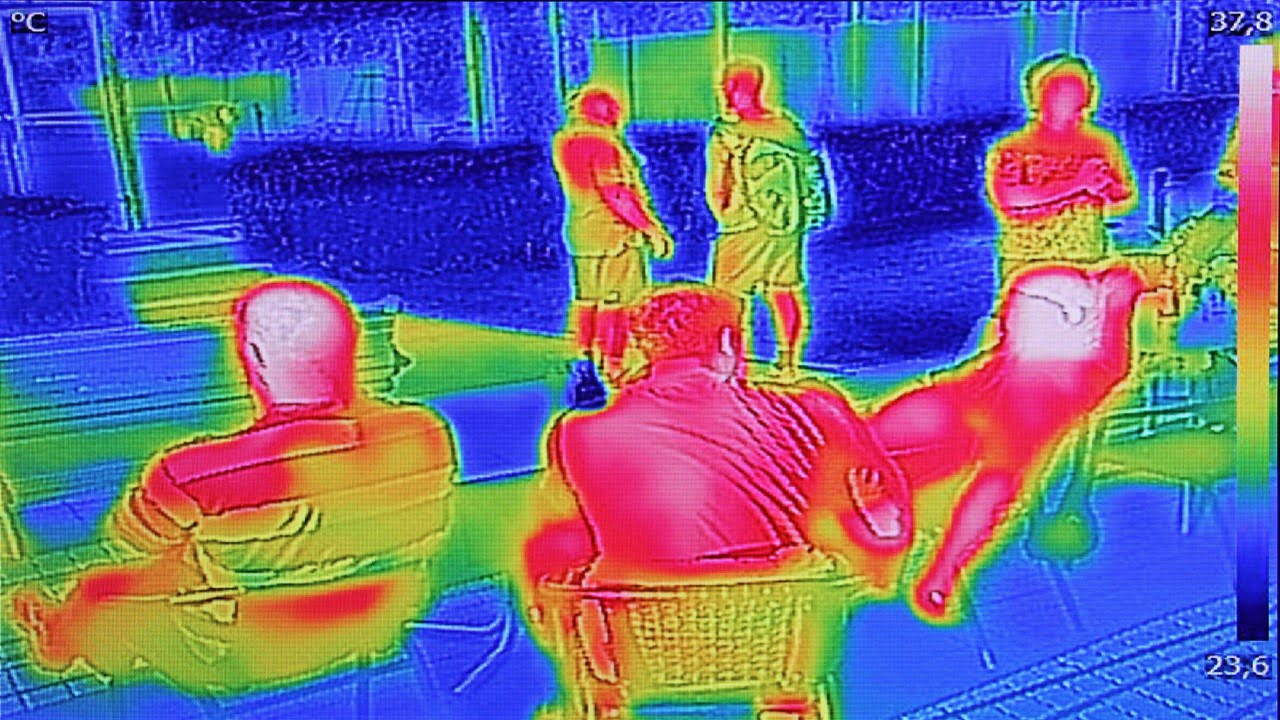
Thermal imaging technology monitors the temperature of fruits and vegetables before and after harvest. This helps reduce food waste and improve the quality of produce. In some environments, thermal imaging can replace old-school thermometers. The research discusses how thermal imaging technology works by detecting temperature variations. This allows farmers and produce handlers to identify fruits [..]
Read More
Researchers have developed a groundbreaking microfluidic platform, ReSCUE, that offers unprecedented control over the shape and behavior of tumoroids, 3D cell cultures that mimic real tumors. This innovation opens new avenues for cancer research, particularly in understanding the impact of tumor shape on cancer cell behavior and aggressiveness. While traditional cancer research often focuses on [..]
Read More