Researchers have built an intelligent quantum sensor – the size of about 1/1000 of the cross-section of a human hair – that can simultaneously detect the intensity, polarization, and wavelength of light, tapping into the quantum properties of electrons. The breakthrough could help advance the fields of astronomy, healthcare, and remote sensing. Twisting certain materials [..]
Read More
Researchers have found a way to identify lung cancer at the cellular level in real-time during a biopsy, promising to detect the disease earlier and with more confidence. The researchers call the new technology NIR-nCLE. It combines the cancer-targeted near-infrared (NIR) tracer with a needle-based confocal laser endomicroscopy (nCLE) system, modified to detect the NIR [..]
Read MoreTemperature monitoring with a high spatial and temporal resolution is vital in various disciplines, including industrial manufacturing, environmental protection, and healthcare monitoring. Because of their benefits of remote detection, minimum intrusion, tolerance to electromagnetic interference, and high resolution, optical-based sensors offer attractive alternatives for temperature monitoring in biological diagnostics. The luminous intensity, wavelength, peak width, [..]
Read More
Researchers have studied unusual regimes of operation of a laser with a gain medium with a large Raman scattering cross-section, which is often inherent in new types of gain media such as colloidal and epitaxial quantum dots and perovskite materials. A strong electron-phonon coupling characterizes these media. Using the Fröhlich Hamiltonian to describe the electron-phonon [..]
Read More
While solar cells are a great alternative to fossil fuels, the environmental impact of the processes involved in manufacturing solar cells has been a concern. Solar panel fabrication often involves toxic materials such as cadmium and industrial waste. In a new study, researchers have developed an eco-friendly method that eliminates toxic cadmium in the production [..]
Read More
Researchers have demonstrated, for the first time, light-induced thermomagnetic recording in a magnetic thin-film on silicon waveguides. The new writing technique is poised to enable miniature high-performance magneto-optical memories that don’t require bulky optics or mechanical rotation. The devices are nonvolatile — meaning that data is saved even when no power is supplied to the [..]
Read More
Researchers are developing a low-cost handheld device that could cut the rate of unnecessary skin biopsies in half and give dermatologists and other frontline physicians easy access to laboratory-grade cancer diagnostics. The team’s device uses millimeter-wave imaging — the same technology used in airport security scanners — to scan a patient’s skin. Healthy tissue reflects [..]
Read More
Consumers are looking for AR/VR glasses that are compact and easy to wear, delivering high-quality imagery with socially acceptable optics that don’t look like “bug eyes.” Researchers have developed a novel technology to deliver those attributes with maximum effect. The researchers imprinted freeform optics with a nanophotonic optical element called a metasurface. The metasurface is [..]
Read More
Because of their capacity to measure heart rates (HRs) without contact with human skin, photoplethysmography imaging (PPGI) sensors have been the focus of considerable attention. A PPGI sensor uses a camera capable of face detection and records images of facial skin, as the skin can represent changes in arterial blood volume between the systolic and [..]
Read More
Exciton polaritons are hybrid particles that combine light and molecules of organic material, making them ideal vessels for energy transfer in organic semiconductors. Thanks to their photonic origins, they are both compatible with modern electronics and move speedily. However, they are difficult to control, and much of their behavior is a mystery. Researchers have found [..]
Read More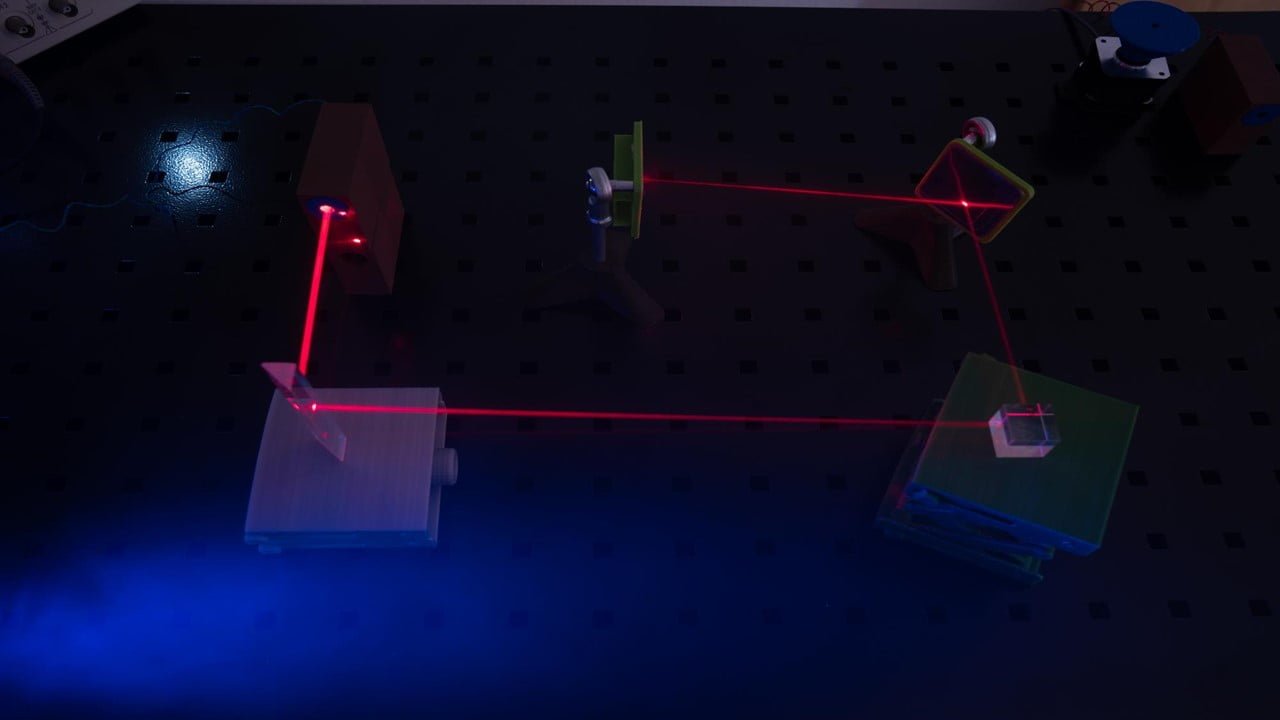
Researchers have developed a new laser ultrasound technique capable of performing on-demand characterization of melt tracks and detecting the formation of defects in a popular metal 3D printing process. The researchers propose a diagnostic using surface acoustic waves (SAW), generated by laser ultrasound, that can reveal tiny surface and sub-surface defects in laser powder bed [..]
Read More
Conjunctival goblet cells (CGCs) are specialized epithelial cells secreting mucins to form the mucus layer of the tear film. The mucus layer spreads the tear film on the ocular surface for protection. The dysfunction and death of CGCs cause tear film instability and are associated with various ocular surface diseases, including dry eye disease (DED). [..]
Read More
Scientists have created a novel electromagnet that could help gadgets ranging from tokamaks (doughnut-shaped fusion reactors) to medical instruments that capture detailed human body images. Tokamaks rely on a central electromagnet, a solenoid, to generate electrical currents and magnetic fields that confine the plasma (a hot, charged state of matter made up of free electrons [..]
Read More
Atrial fibrillation (AF) is diagnosed with an electrocardiogram, the gold standard in clinics. However, sufficient arrhythmia monitoring takes a long time, and many of the tests take place in only a few seconds, which can miss arrhythmia. Researchers have developed a combined method to detect the effects of AF on atrial tissue. The researchers characterized [..]
Read More
Researchers have developed new polymer materials that are ideal for making the optical links necessary to connect chip-based photonic components with board-level circuits or optical fibers. The polymers can be helpful to easily create interconnects between photonic chips and optically printed circuit boards, the light-based equivalent of electronic printed circuit boards. These new materials and [..]
Read More
Polarization holography is a newly researched field that has gained traction with the development of tensor theory. It primarily focuses on the interaction between polarization waves and photosensitive materials. The extraordinary capabilities in modulating light amplitude, phase, and polarization have resulted in several new applications, such as holographic storage technology, multichannel polarization multiplexing, vector beams, [..]
Read More
Researchers have developed a quick and cost-effective way to determine the age of malaria mosquitoes using mid-infrared spectroscopy. The new technology is vital for assessing the effectiveness of control interventions as only older mosquitoes can transmit the parasite. The scientists say that their approach could also help with other mosquito-borne and insect-borne diseases. The researchers [..]
Read More
Researchers have successfully generated strongly nonclassical light using a modular waveguide device, a waveguide-based light source. By combining a waveguide optical parametric amplifier (OPA) module created for quantum experiments and a specially designed photon detector, researchers produced light in a superposition of coherent states. The achievement represents a crucial step toward creating faster and more [..]
Read More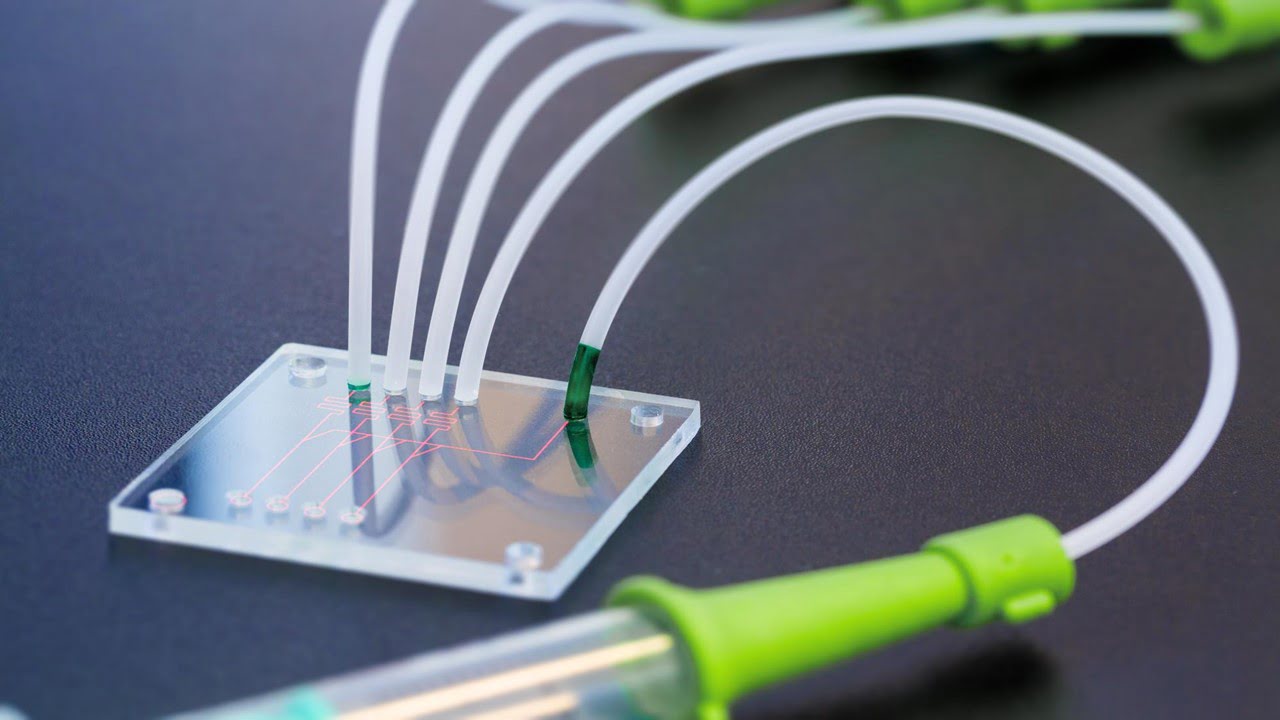
Researchers have developed a new platform for studying human hepatitis C immunity. The method marries microfluidic technology (which allows scientists to precisely manipulate fluid at a microscopic scale) with liver organoids (three-dimensional cell clusters that mimic the biology of real human livers). In the new hepatitis C immunity modeling system, liver organoids grown from adult [..]
Read More
Optoelectronic synapses combine non-volatile memory and photodetection functionalities in the same device. It paves the path for the realization of artificial retina systems which can capture, pre-process, and identify images on the same platform. Researchers have used a graphene/Ta2O5/graphene heterostructure to demonstrate optoelectronic synapses. The graphene interface exhibits synapse characteristics when visible electromagnetic radiation of [..]
Read More