
Researchers looked at the nucleus of cells inside connective tissues that were deteriorating due to tendinosis. Disease-related disruptions in the environments in which cells exist resulted in the re-organization of the genome – the sum of an organism’s DNA sequences – inside the cell’s nucleus, changing the way cells function and rendering them unable to [..]
Read More
Scientists must study the processes inside an operating battery to understand battery failures. The observations guide the development of faster-charging and longer-lasting batteries. Current techniques to study battery materials are complicated and expensive. They are not quick enough to capture the rapid changes in electrode materials. To understand battery failures, the researchers studied micrometer-sized rod-like [..]
Read More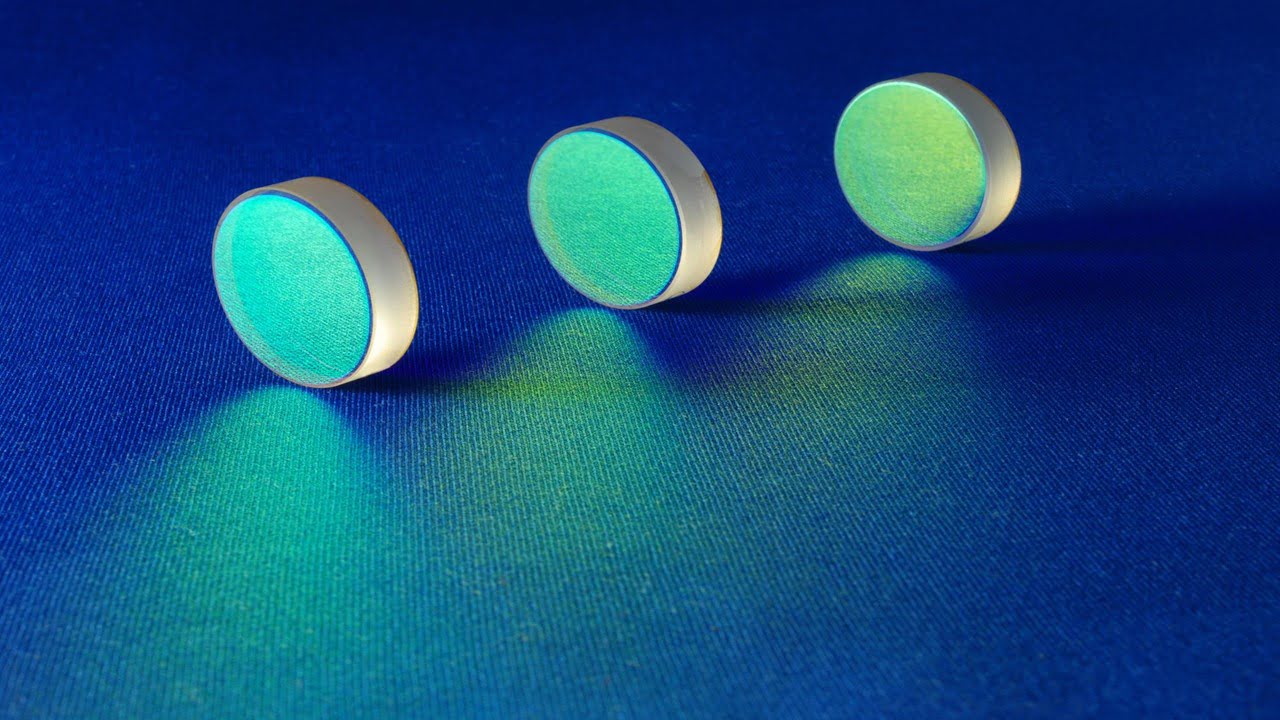
Researchers have made strides toward improving the performance of mixture-based quarter-wave plate laser beam splitter (PLBS) coatings. Because of their unique optical properties, plate beam splitters find uses in quantum communication, measurement, and laser systems. The quarter-wave plate laser beam splitter must have a specific spectral performance in high-power laser systems. It also requires a [..]
Read More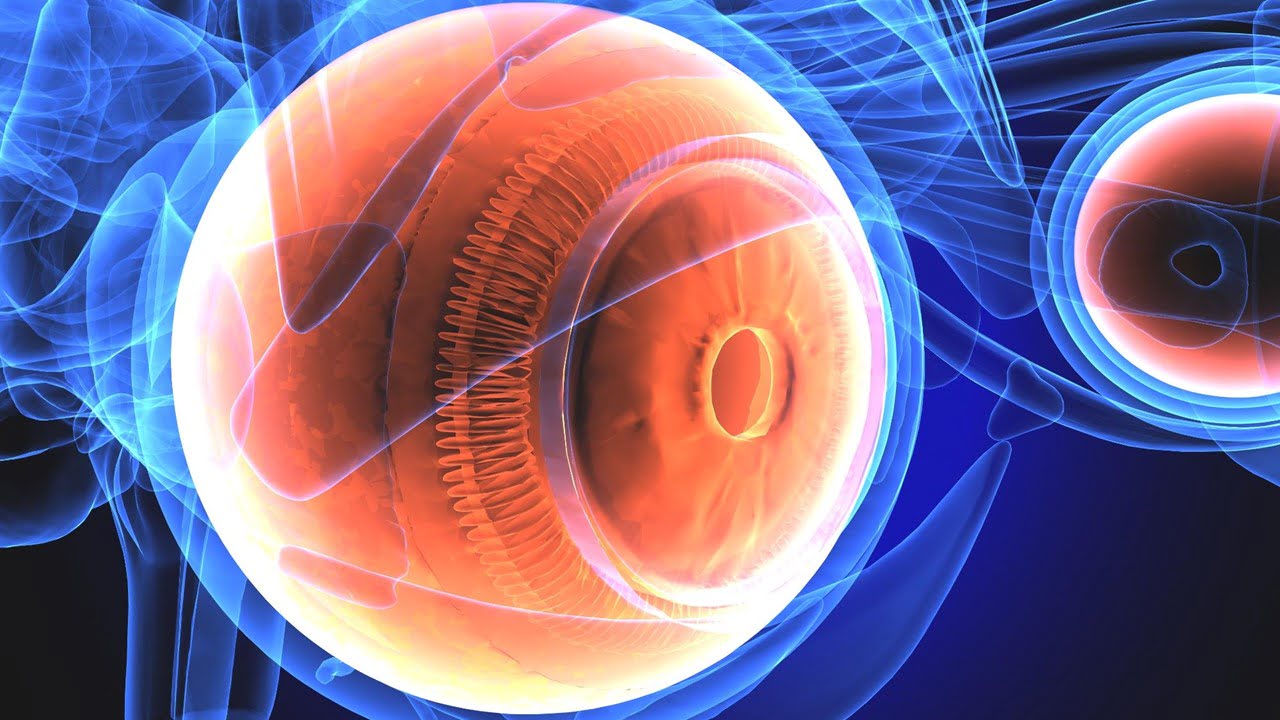
Fundus photography is essential in ophthalmology to screen, diagnose, and manage eye diseases. Wide-field fundus photography has demonstrated its utility in the clinical management of eye diseases such as diabetic retinopathy (DR), age-related macular degeneration (AMD), glaucoma, hypertensive retinopathy, retinal detachments, and vascular pathologies (vascular occlusions, vasculitis, etc.) with ocular metastasis. Choroidal and retinal imaging [..]
Read More
The surface temperature of a solar panel and the appearance of hotspots directly impact its efficiency. Researchers have developed a novel method for estimating the power efficiency of an on-field solar photovoltaics (PV) system based on data obtained from thermal imaging and weather instruments using an unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV). This method is designed explicitly [..]
Read More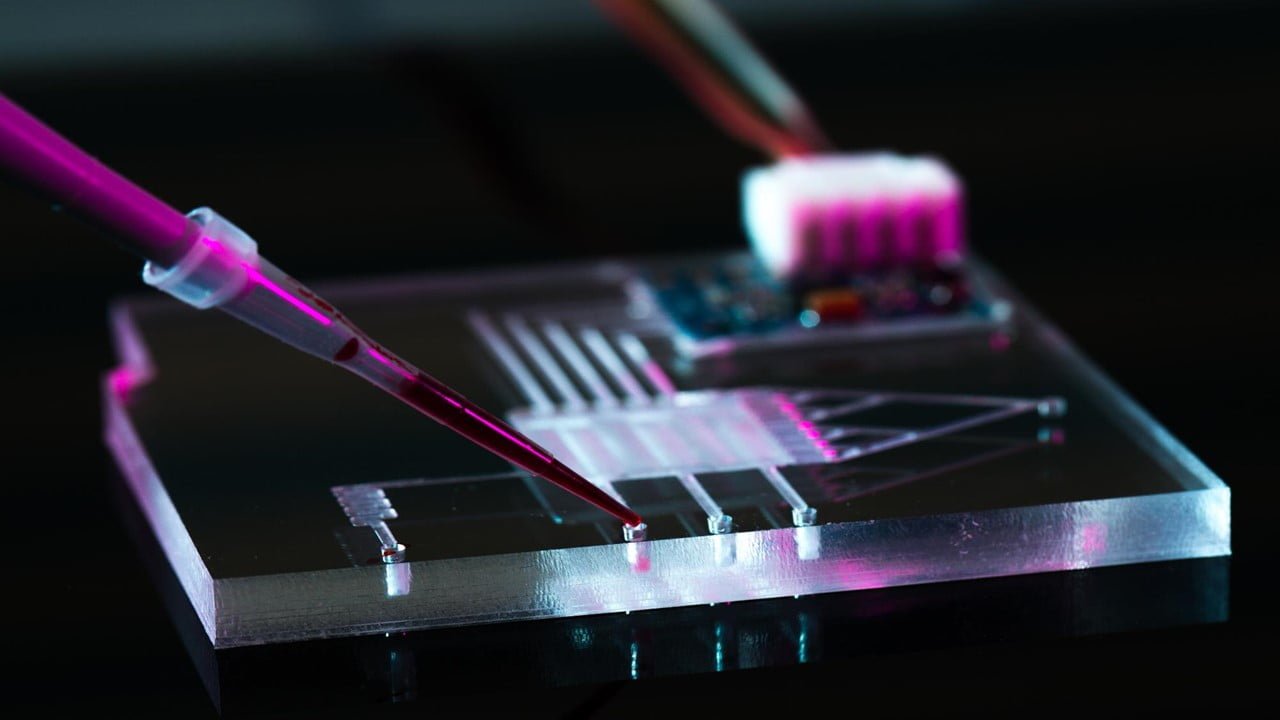
Light-induced charged slippery surfaces (LICS), which regenerate charge when illuminated, have the potential to pave the way for next-generation interfacial materials and microfluidics. A copolymer, tiny liquid metal particles, and lubricant-trapping microstructures make up the new material. It has the potential to be used in lab-on-a-chip devices, biological diagnostics, and chemical analysis. Slippery lubricant-infused porous [..]
Read More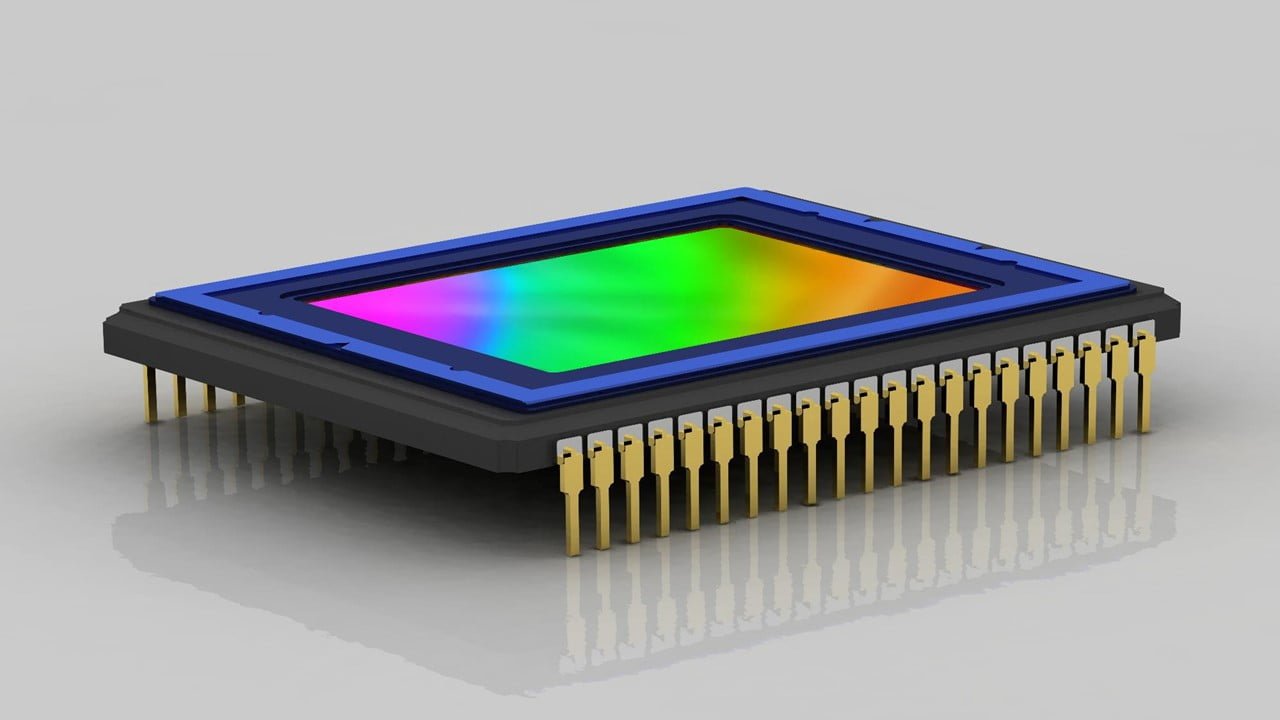
Researchers have developed a new ultrasensitive optical sensing instrument that could benefit science, medicine, and engineering. It is known as a Mach Zehnder-Fabry Perot (MZ-FP) hybrid fiber interferometer. It combines the benefits of the two types of interferometers currently available, making it compact and highly sensitive. Interferometers are precision measuring devices that work by creating [..]
Read More
Bioactive glass, a specific mixture of sodium oxide, calcium oxide, silicon dioxide, and phosphorus pentoxide, is now used as an orthopedic treatment to restore damaged bone and repair bone defects. Bioactive glass is a material you put into your body, and it begins to dissolve, telling cells and bone to become more active and produce [..]
Read More
MRI, electroencephalography (EEG), and magnetoencephalography (MEG) have been the most widely used techniques to study brain activity for many years. A new study introduces a novel, AI-based dynamic brain imaging technology that can map rapidly changing electrical activity in the brain at high speed, high resolution, and low cost. The breakthrough follows more than 30 [..]
Read More
Researchers used the light-guiding properties of spider silk to create a sensor that can detect and measure tiny changes in the refractive index of a biological solution, such as glucose or other sugar solutions. The new light-based sensor could be useful for measuring blood sugar and other biochemical analytes in the future. Glucose sensors are [..]
Read More
Engineers have created a switch, one of the most fundamental components of computing, using optical rather than electronic components. The advancement could help in pursuing ultrafast all-optical signal processing and computing. Optics has the potential to revolutionize computing by allowing it to do more at faster speeds and with less power. However, one of the [..]
Read More
Currently, ultrasound imaging necessitates using large, specialized equipment only available in hospitals and doctor’s offices. On the other hand, a new design could make the technology as wearable and accessible as buying Band-Aids at the pharmacy. A new ultrasound sticker, the size of a stamp, adheres to the skin and can provide continuous ultrasound imaging [..]
Read MoreA new study looks at conjugating 2D perovskites with optically active transition metal dichalcogenides (TMDs). The study can improve optoelectronic device performance and extend the functionalities of the perovskites. Despite their structural differences, 2D perovskites and TMDs can form clean interfaces due to van der Waals interactions between the stacked layers. Using accurate first-principles calculations, [..]
Read More
Researchers have been experimenting with ways to reach people as VR technology improves, becomes cheaper, and more accessible – everything from treating PTSD to performing operas. Visual artists are the most recent to wonder how technology might push the boundaries of their field, looking for new ways to express themselves and share their work. However, [..]
Read More
Carbon-based materials have enormous potential for constructing a sustainable future; however, material scientists require tools to properly analyze their atomic structure, which determines their functional properties. One of the tools used for this is X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), but the results can be challenging to interpret. Now, researchers have created the XPS Prediction Server, a [..]
Read More
Respiratory motion can influence the efficacy and safety of radiation therapy in the thorax and abdomen. Free-breathing 4D-MRI is a promising alternative to 4D-CT for motion management in MRI-guided linac treatments, providing excellent soft-tissue contrast with no ionizing radiation. High-quality MR images free of motion artifacts can distinguish lesions from normal tissue. MRI techniques, however, [..]
Read More
Using carbon nanotubes, a new strain-sensing smart skin monitors and detects damage in large structures. The coating detects surface deformation by stress by utilizing the fluorescent properties of nanotubes. As part of the S4 non-contact optical monitoring system, the multilayered coating can be applied to large surfaces — bridges, buildings, ships, and airplanes, to name [..]
Read More
Mutations in RAS genes, which cause tumor growth in about a quarter of all cancer patients, are among the most infamous cancer drivers. Scientists have solved the molecular structure of SHOC2, a RAS-pathway protein, and two other proteins (that it binds to). The SHOC2-MRAS-PP1C (“SMP”) complex, a three-protein assembly, regulates the RAS signaling pathway and [..]
Read More
Researchers have developed a new, lighter convolutional neural network (CNN) model for facial expression recognition. The findings describe an Xception-based model that balances training speed, memory usage, and recognition accuracy. The original Xception model has 71 layers and can load a pre-trained version of the network trained on over a million images from the ImageNet [..]
Read More
Detecting gases is critical for pollution monitoring, public safety, and personal health care. The sensors must be small, lightweight, inexpensive, and simple in various environments and substrates, such as clothing or piping. A research team has created the first highly customizable microscale gas sensing devices by combining laser writing and responsive sensor technologies. The challenge [..]
Read More