
The convergence of artificial intelligence (AI) and optics is ushering in a new era of enhanced digital security, offering innovative solutions to combat increasingly sophisticated cyber threats. By integrating AI algorithms with advanced optical technologies, researchers and developers are creating powerful defense mechanisms that operate at the physical layer, providing a robust and often undetectable [..]
Read More
A new study presents a novel method for precisely measuring temperature changes in the retina during laser therapy using phase-sensitive optical coherence tomography (pOCT) in vivo. The researchers demonstrate that Phase-Sensitive OCT can accurately detect temperature rises with a precision of less than 1 °C, crucial for calibrating laser power for patient-specific, non-damaging treatments. Notably, [..]
Read More
A groundbreaking advancement in DNA sequencing technology, nanopore sequencing, is dramatically accelerating the analysis of brain tumor DNA. Researchers have demonstrated the ability to comprehensively profile brain tumor DNA using nanopore sequencing in an unprecedented 30 minutes. This rapid turnaround time represents a significant leap forward compared to traditional sequencing methods, which can take hours [..]
Read More
Dual-chirped comb LiDAR represents a significant advancement in distance measurement technology, offering unprecedented accuracy and range for a variety of applications. This innovative approach leverages the unique properties of frequency combs, specifically dual-chirped frequency combs, to achieve high-resolution measurements over extended distances. Unlike traditional LiDAR systems, which rely on pulsed lasers, dual-comb LiDAR utilizes two [..]
Read More
A novel metasurface optical element promises to significantly advance our understanding of atmospheric aerosols. This innovative technology offers a compact, lightweight, and highly efficient alternative to traditional optical components, enabling more precise and detailed measurements of these tiny airborne particles. Atmospheric aerosols play a crucial role in Earth’s climate system, influencing cloud formation, precipitation patterns, [..]
Read More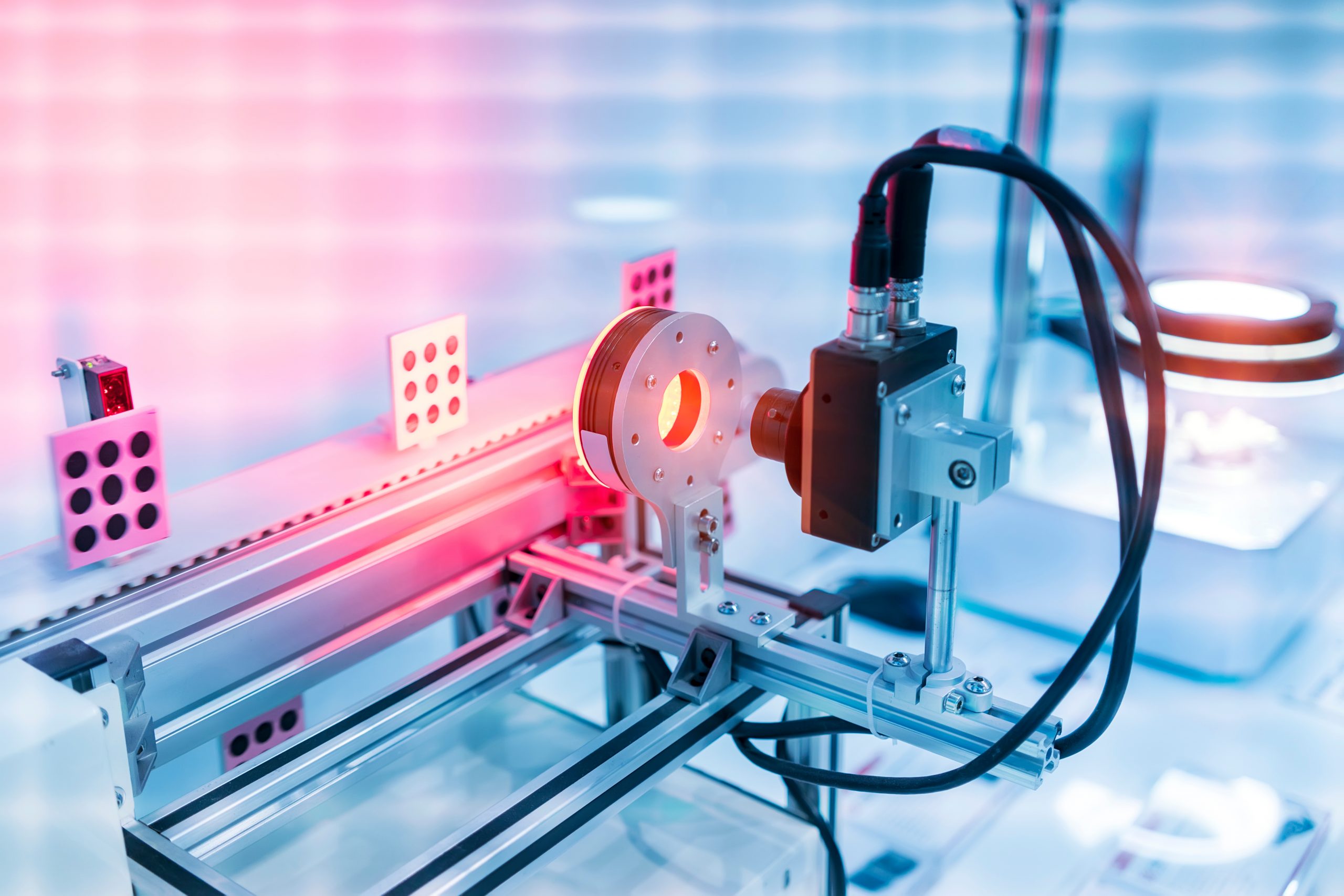
In-line machine vision systems are revolutionizing the field of metrology, offering a powerful approach to automate and enhance precision measurement in manufacturing processes. By integrating vision technology directly into production lines, these systems enable real-time quality control, leading to significant improvements in efficiency, accuracy, and overall product quality. This integration eliminates the need for manual [..]
Read More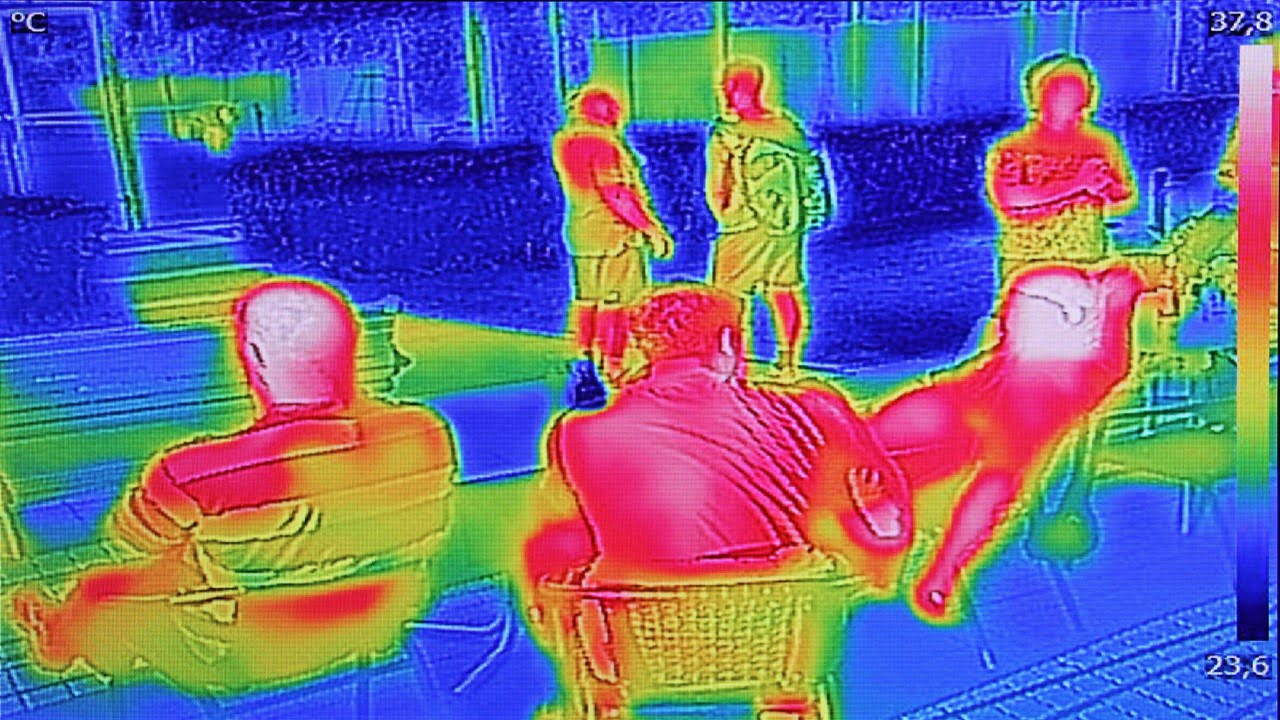
A significant advancement in thermal imaging technology has been developed, offering a non-contact and highly accurate method for tracking vital signs. Researchers have engineered a phasor thermography system that, through sophisticated image processing, can reliably extract physiological data such as body temperature, respiration rate, and heart rate from thermal images. This innovation holds immense potential [..]
Read More
The pursuit of optical computing, a paradigm shift from traditional electronic computation, has spurred researchers to explore novel materials capable of manipulating light at the nanoscale. A significant breakthrough has emerged with the creation of nanoparticles exhibiting a unique bistable switching behavior, transitioning between dark and bright states upon exposure to light. This property is [..]
Read More
Data centers, the backbone of our digital infrastructure, face increasing pressure to reduce energy consumption. Linear Pluggable Optics (LPO) has emerged as a promising solution to address this challenge, offering a more efficient way to move data within server racks. Unlike its predecessor, Co-Packaged Optics (CPO), which integrates optical components directly into the electrical package, [..]
Read More
A revolutionary approach to manipulating light has emerged, promising to significantly enhance the efficiency and performance of various electronic devices, particularly those involving display technologies. Researchers have successfully demonstrated a method to “twist” light into spiral patterns, mimicking structures found in nature, and have shown its direct application in improving the performance of OLED displays [..]
Read More
A significant advancement has been achieved in the field of medical imaging, specifically targeting the intricate realm of intravascular analysis. Researchers have successfully engineered a miniaturized optical device that promises to revolutionize the way we visualize and understand the inner workings of blood vessels. This intravascular imaging development centers around the creation of a tiny [..]
Read More
Researchers have unveiled a novel augmented reality (AR) glasses design that significantly reduces weight and bulk by employing a “beaming displays” approach. This innovative system shifts the image generation burden from the glasses to an external projector. Traditional AR glasses struggle with weight and power limitations due to onboard batteries and electronic components. This new design addresses [..]
Read More
Direct-to-device (D2D) satellite communication is emerging as a transformative technology, poised to revolutionize how we connect to the internet and communicate globally. It aims to bridge the digital divide by enabling seamless connectivity in areas where traditional cellular networks are unavailable or unreliable. This technology allows everyday devices like smartphones to connect directly to satellites, [..]
Read More
Imagine a world where your light bulbs not only illuminate your home but also provide your internet connection. This is the promise of Li-Fi technology that uses light to transmit data. While Wi-Fi has become a ubiquitous part of our lives, Li-Fi offers a different approach to wireless communication. Li-Fi, short for Light Fidelity, utilizes [..]
Read More
In the ever-evolving landscape of biometric authentication, a groundbreaking development has emerged, pushing the boundaries of security and potential applications. Researchers have pioneered a novel method utilizing hyperspectral imaging and artificial intelligence (AI) to identify individuals based on the intricate network of blood vessels within their palms – palm vein biometrics. What sets this approach [..]
Read More
The longstanding barrier of light microscopy, the diffraction limit, has been challenged again. While super-resolution techniques like STED and PALM/STORM rely on molecular “ON/OFF” switching and revolutionized imaging, a recent breakthrough demonstrates resolution enhancement without this requirement. Researchers have unveiled a method utilizing a scanning beam with a central zero-intensity line (node). By analyzing the [..]
Read More
A breakthrough in volumetric 3D printing, HoloVAM, promises to revolutionize optics and photonics applications, particularly in bioprinting. Researchers have developed a holographic technique that significantly boosts efficiency and speed compared to traditional Tomographic Volumetric Additive Manufacturing (TVAM). Conventional TVAM, while capable of rapid, single-shot 3D printing by solidifying resin with light patterns, suffers from low [..]
Read More
Ecological disasters demand rapid and precise toxin analysis to safeguard public health. Surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS), a powerful label-free technique, offers sensitive detection of low-concentration toxins. However, the inherent variability of SERS spectra across different substrates has hindered its widespread application. Researchers have unveiled a machine-learning approach that significantly streamlines SERS analysis, enabling accurate toxin [..]
Read More
Researchers have developed a groundbreaking droplet microfluidic component library that is set to democratize microfluidic device fabrication. This innovation offers a rapid, cost-effective alternative to traditional PDMS-based methods, enabling device creation for under $12 and a full design-build-test cycle within a day. The library features biocompatible, high-throughput components capable of complex multistep workflows, including droplet [..]
Read More
Modern optoelectronic devices, from smartphone cameras to astronomical instruments, face a growing challenge: extracting more information from photons demands significant energy, limiting performance. Researchers are tackling this issue by developing novel, energy-efficient, light-sensing smart sensors inspired by the human eye. Current optical sensors typically transmit all raw data to a computer for processing, a power-hungry [..]
Read More