
The human body is a complex system; monitoring its health vitals is crucial for early disease detection and prevention. However, traditional monitoring methods can be cumbersome and uncomfortable for patients. This is where biointegrated, flexible, stretchable optoelectronics come in. Biointegrated flexible, stretchable optoelectronics are a new class of devices that can be seamlessly integrated into [..]
Read More
Have you ever wondered where the periodic table ends? Scientists are pushing the boundaries by studying superheavy elements beyond uranium (element 92), which can only be created in labs. A recent study sheds light on the structure of these exotic elements. The key lies in nuclear radii. Using laser spectroscopy, researchers measured the size of [..]
Read More
A groundbreaking study has introduced a novel computational holography-based method that promises to revolutionize the field of imaging through scattering media. This innovative technique addresses the long-standing challenge of obtaining high-resolution images through highly scattering materials, such as biological tissues or turbid water. When light passes through a scattering medium, it undergoes multiple scattering events, [..]
Read More
Researchers have introduced a revolutionary imaging technology, DEEPscope, that promises to reshape our understanding of the brain. This innovative microscope overcomes the limitations of traditional multiphoton microscopy, enabling deep and wide-field visualization of neural activity at unprecedented resolution.Multiphoton microscopy, a gold standard for deep-tissue imaging, faces significant hurdles. As imaging depth increases, the field of [..]
Read More
Traditional computers rely on electrons to transmit information, which can limit their processing speed. However, a new frontier in computing is emerging – photonics – which utilizes light for data transmission. A recent breakthrough in 3D integrated photonics has paved the way for a new generation of photonic processors that can tackle complex problems significantly [..]
Read More
Lead exposure is a serious public health concern, particularly for children. Traditional methods for detecting lead exposure can be time-consuming and expensive. This research highlights two promising advancements in lead exposure detection that utilize innovative applications of optics and photonics. The first technique leverages portable X-ray fluorescence (XRF) analyzers. XRF spectroscopy is a non-destructive analytical [..]
Read More
A groundbreaking discovery has the potential to revolutionize non-invasive medical diagnostics. Researchers have harnessed the power of orbital angular momentum (OAM) light to improve imaging and data transmission through biological tissues. OAM light is a special light beam with a unique spatial structure, often described as a “twisted” light beam. Unlike traditional light beams, it [..]
Read More
Chalcogenide glasses, composed of elements like sulfur, selenium, or tellurium, are emerging as a promising material for infrared (IR) optics. These glasses offer unique properties, including transparency in the IR spectrum and the ability to be tailored for specific applications. Recent research has unveiled an extraordinary property of chalcogenide glasses: self-healing chalcogenide glasses. These glasses [..]
Read More
Contactless hand biometrics, a technology that captures 3D images of hands for identification purposes, has gained significant attention in recent years. While it offers the potential for more secure and convenient authentication, its application in forensic investigations is still in its early stages. A recent study has highlighted the limitations of contactless hand biometrics in [..]
Read More
A new technique has been developed to improve illumination uniformity in direct-drive inertial confinement fusion. This technique is more efficient than previous methods and can be applied to other pellet geometries and at other facilities. Inertial confinement fusion is a fusion power that uses lasers to compress and heat a target fuel pellet, causing it [..]
Read More
A groundbreaking study introduces a revolutionary technique for noninvasive, high-resolution imaging through highly scattering media. Researchers developed this method, which leverages computational holography to overcome the limitations of traditional optical imaging. The key innovation lies in using computational optimization to emulate wavefront shaping experiments. By optimizing multiple “virtual SLMs” simultaneously, the researchers could reconstruct high-quality [..]
Read More
A recent study has shed new light on the early stages of substance use. Researchers used a specialized type of MRI, called neuromelanin-sensitive MRI, to examine the brains of young adults who had a history of extensive alcohol and drug use. Neuromelanin is a pigment in certain brain areas, including the midbrain, where dopamine is [..]
Read More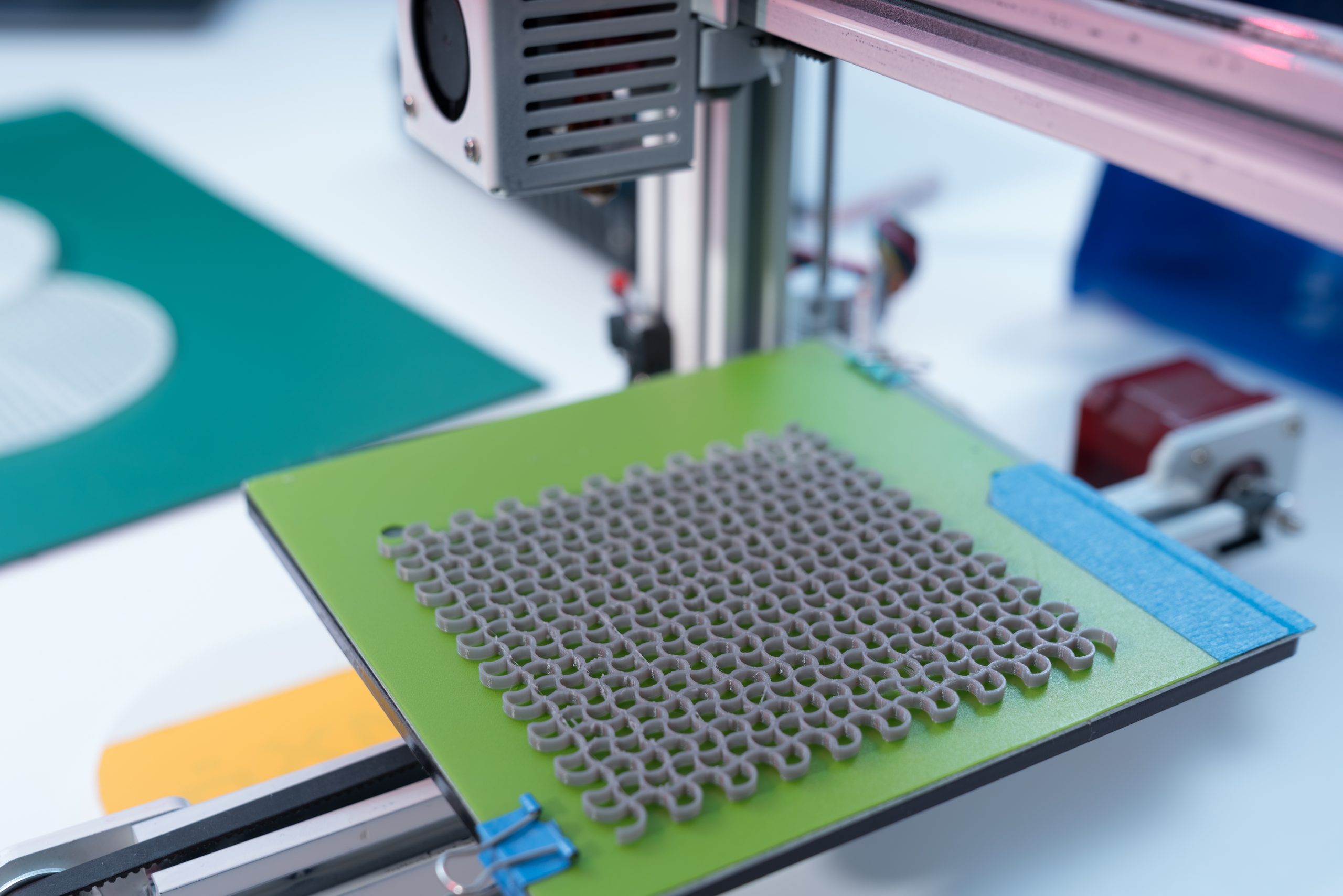
Metasurfaces, a class of artificially engineered materials, have revolutionized the field of optics by offering unprecedented control over light at the nanoscale. However, until recently, metasurfaces faced limitations in achieving asymmetric optical responses, where the behavior of light differs depending on its direction of incidence. A team of researchers has successfully overcome this hurdle by [..]
Read More
Optical tweezers are powerful tools that use light to trap and manipulate microscopic objects. They have a wide range of applications in biology and medicine, but current integrated optical tweezers have limitations. New research discusses a new approach that uses integrated optical phased arrays (OPAs) to overcome these limitations. The OPA system can trap and [..]
Read More
Event-based cameras, also known as neuromorphic sensors, have garnered significant attention in machine vision due to their energy efficiency and high temporal resolution. However, a critical limitation has hindered their widespread adoption: their inability to capture information on the edges of objects parallel to the camera’s motion. This issue can significantly impact the performance of [..]
Read More
Mid-infrared (Mid-IR) fiber lasers and amplifiers have gained significant attention due to their potential applications in various fields, including spectroscopy, sensing, and materials processing. However, the efficient coupling of pump light into these Mid-IR fibers remains a critical challenge. Traditional pump combiners often involve complex fabrication processes and can suffer from low coupling efficiencies. New [..]
Read More
Have you ever wondered why some people are tall, and others are short? Scientists have been chipping away at this question for decades, and a new study has shed new light on the genetics that influence human height. This study employed a powerful whole-genome sequencing technique to pinpoint rare genetic variations associated with height. Whole-genome [..]
Read More
Researchers have developed a wearable device that uses light to kill bacteria in chronic wounds. The ACEL mPDT device is powered by the wearer’s movements and designed to be safe and effective for treating wounds infected with MRSA. The device is made of a flexible material that conforms to the body. It contains a hydrogel [..]
Read More
In a groundbreaking collaboration, researchers developed a novel fluorescent 3D printing process incorporating fluorescent ring-shaped molecules. This innovation can potentially revolutionize the field of biomedical implants by creating intricate, glowing structures that are easier to track and monitor within the body. The team combined their expertise in engineering and chemistry to create a technique that [..]
Read More
A team of researchers has developed a promising new method for measuring stroke risk. This non-invasive device, which uses speckle contrast optical spectroscopy for early stroke detection, akin to a cardiac stress test, could revolutionize stroke care by enabling early detection and prevention. Strokes, a leading cause of neurological disability, occur when blood flow to [..]
Read More