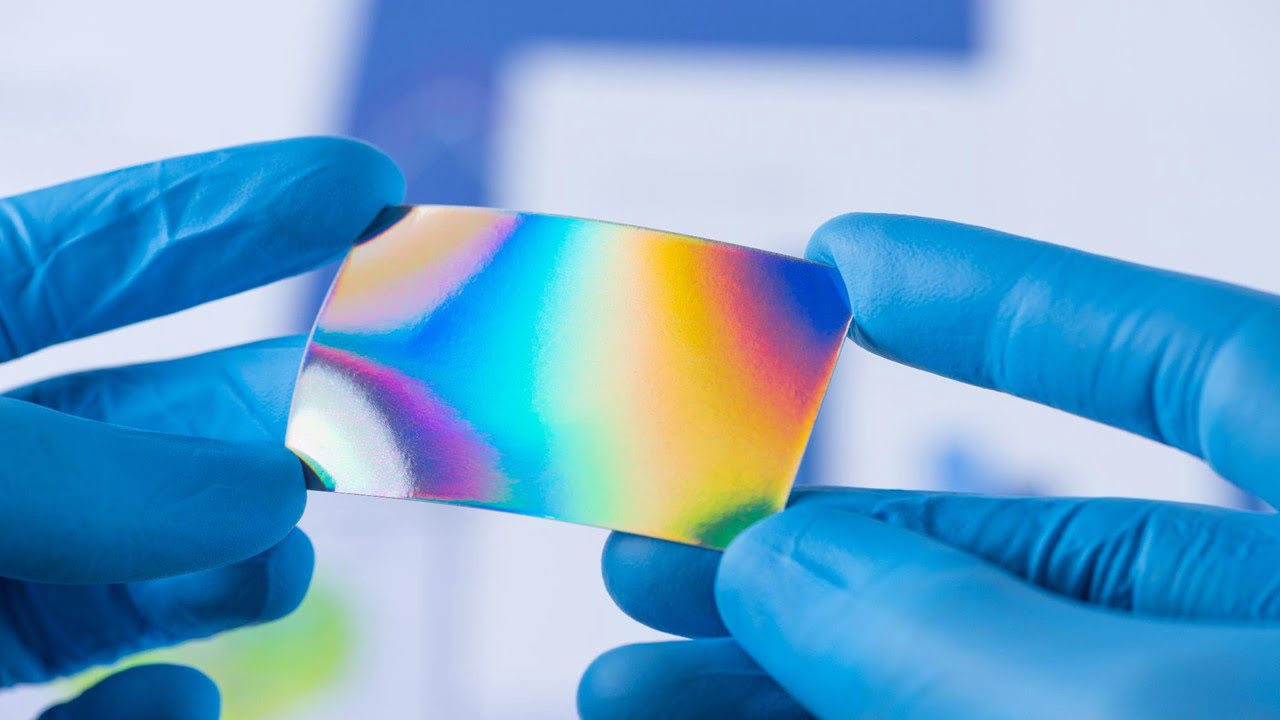

Block copolymers, which are self-assembling materials known to form various predictable, regular patterns, can now be made to form much more complicated patterns, according to a team of researchers. It could lead to the development of new materials design fields. The polymers can self-assemble in designs that differ from conventional symmetrical arrays thanks to a [..]
Read More
Without using possibly harmful X-rays, researchers have found microscopic twists in the internal structure of plant and animal cells. The method rotates terahertz imaging in real-time and is said to be its first successful application. It may lead to novel cosmology, encrypted communications, and medical imaging uses. Although terahertz imaging can enter the body for [..]
Read More
According to a recent study titled “The Current Reality of Facial Recognition,” although AI technology has progressed, there is still a long way to go. The article’s opening line reads, “With closed-circuit television (CCTV) cameras installed everywhere, from shops to buses to private homes, the UK is one of the most watched nations in the [..]
Read More
Researchers have developed a noninvasive, cost-effective method using IR imaging technology to locate hard-to-find breast cancer tumors. The system consists of an IR camera on a track mounted underneath a cushioned table. It is angled and can be adjusted as the clinician moves it to take images. The team is also using advanced computer simulation [..]
Read More
Microlenses have previously been created using microscopic glass blowing, but this typically entails gas expansion from a single reservoir. Researchers have now created a technique for fabricating axicons that use gas expansion from various reservoirs to create the conical shape of the optical component. Unlike conventional methods like etching transfer from a 3-D mask that [..]
Read More
A team of researchers has combined the expansion microscopy method, a nanoscale microscopy technique, and virtual reality (VR) to allow enlarging, exploring, and analyzing of cell structures beyond conventional light microscopy’s capabilities. The advancement aims to improve researchers’ knowledge of autoimmune and infectious diseases and their capacity to create disease diagnostics and preventative and therapeutic [..]
Read More
Though conceptually simple, the goal of the developing field of photopharmacology is to use light as an external stimulus to activate drug molecules with a high degree of control over the time and location where this occurs. This task necessitates an interdisciplinary effort involving chemical synthesis and light delivery technology. A molecule whose therapeutic action [..]
Read More
Researchers have developed a new laser method that can detect electric charges and chemicals of interest with unprecedented sensitivity. The new approach could one day offer a way to scan large areas for radioactive material or hazardous chemicals for safety and security applications. The new laser method, called mid-infrared picosecond laser-driven electron avalanche, detects extremely [..]
Read More
The past decade has seen significant progress in the development of novel mid-infrared (mid-IR) coherent light sources spanning a broad spectral bandwidth, and new spectrometric techniques to make the most of them. Researchers now harness such light sources — based on mode-locked lasers and nonlinear frequency conversion, on frequency comb generators, on supercontinua, and on [..]
Read MoreA growing number of applications, including smartphone cameras, depend on microlens arrays to boost performance, for example by compensating for the “dead space” around detector pixels. However, although micro-optics are commercially available, they can be prohibitively expensive to fabricate and hard to add to existing devices. Even with traditional microlens fabrication methods (see single point [..]
Read MoreAmoebas are unusual creatures that form when a dispersed population of cells spontaneously comes together and reorganizes itself into a multicellular macroscopic organism. To do this, a few leader cells emit chemical pulses that cause the other individual cells to move in the direction opposite to that of the traveling pulses, leading to the formation [..]
Read More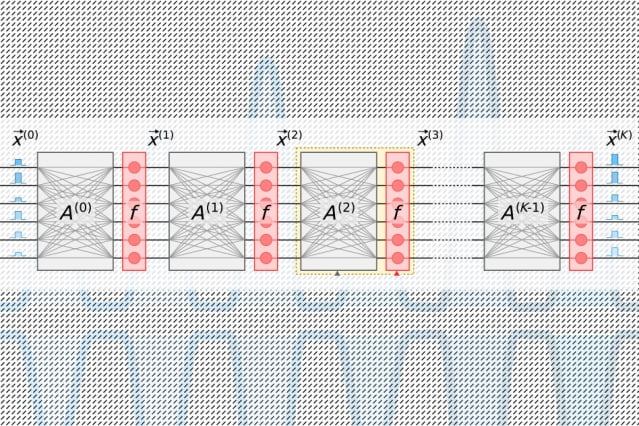
Researchers have developed a novel photonic chip that uses light instead of electricity — and consumes relatively little power in the process. The chip design could be used to process massive neural networks millions of times more efficiently than today’s classical computers do. Neural networks are machine-learning models that are widely used for such tasks [..]
Read More
Researchers have developed a new way of operating miniature quantum cascade lasers (QCLs) to rapidly measure the absorption spectra of different organic molecules in the air simultaneously. The technique offers a sensitive method for detecting low concentrations of volatile organic compounds (VOCs), improving the ability to track how these compounds affect human health, industrial processes, [..]
Read More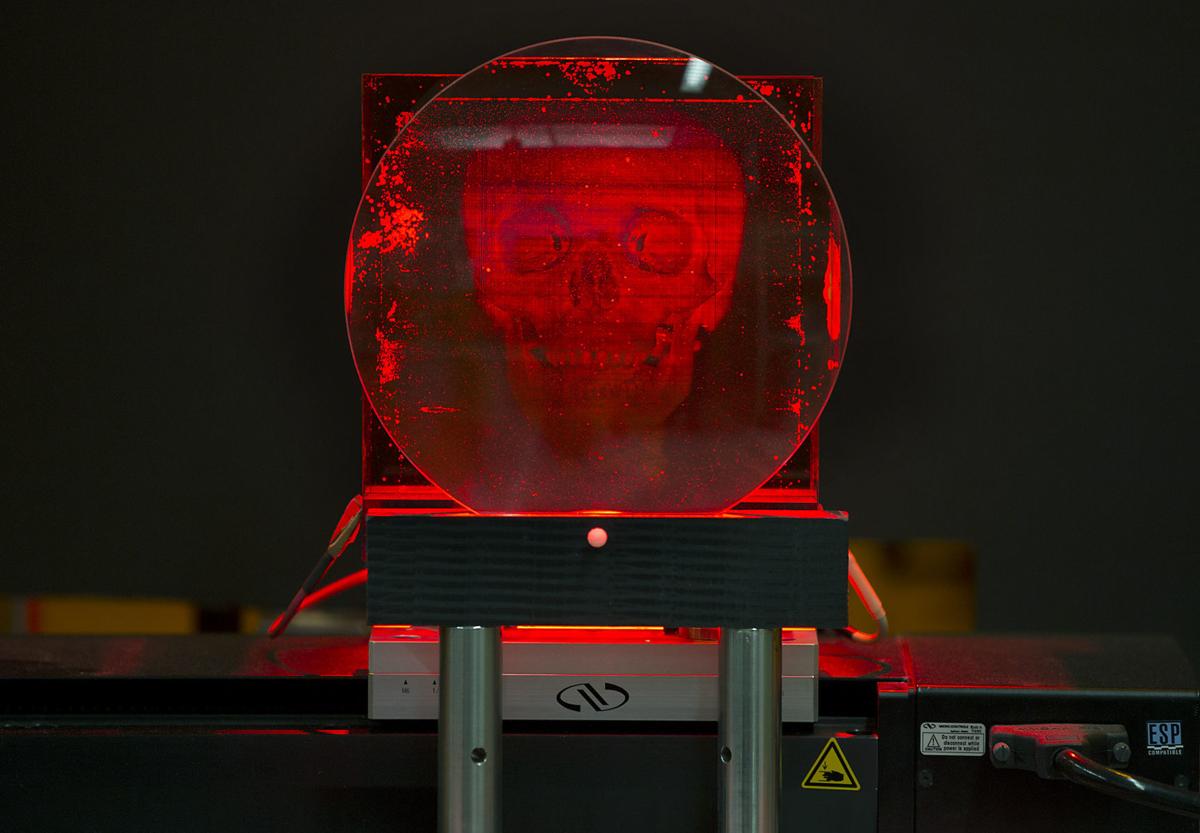
Scientists are working to perfect a new type of holographic display technology that can be incorporated into eyeglasses to superimpose video images on a user’s real-world view. The technology eventually could be incorporated into regular eyeglasses. Virtual reality systems are used with VR apps to create an immersive experience while blocking out the real world. [..]
Read More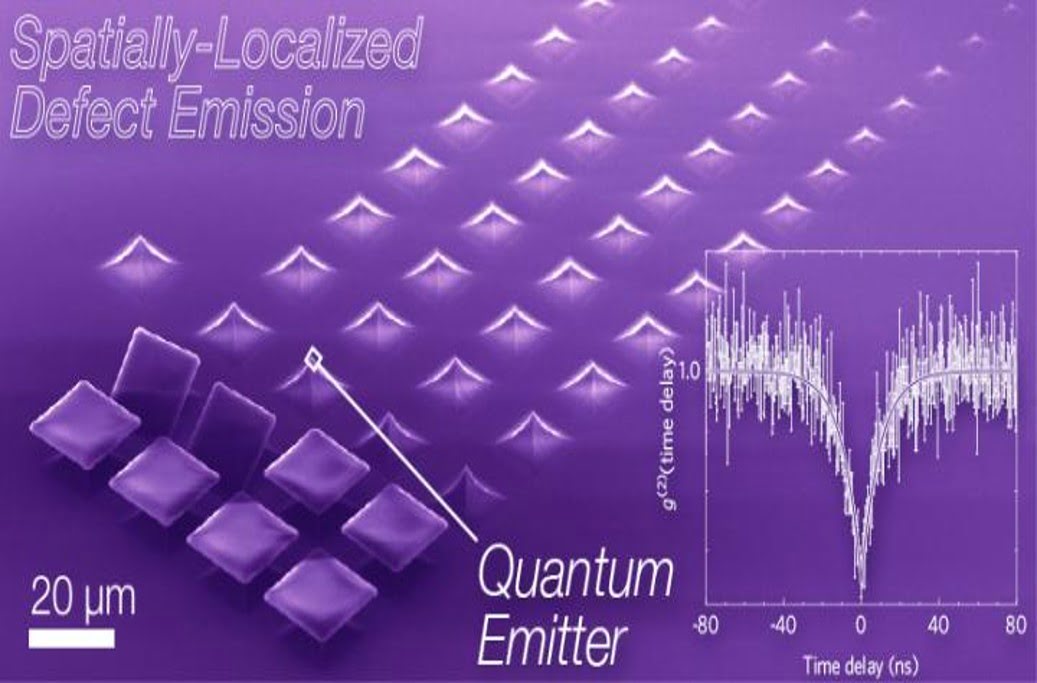
Efforts to create reliable light-based quantum computing and quantum key distribution for cybersecurity could benefit from a new study that demonstrates a new method for creating thin films to control single-photon emission. The approach exploits strain at highly spatially localized and spectrally well-separated defect emission sites, or tips, in the 750 to 800 nm regime [..]
Read More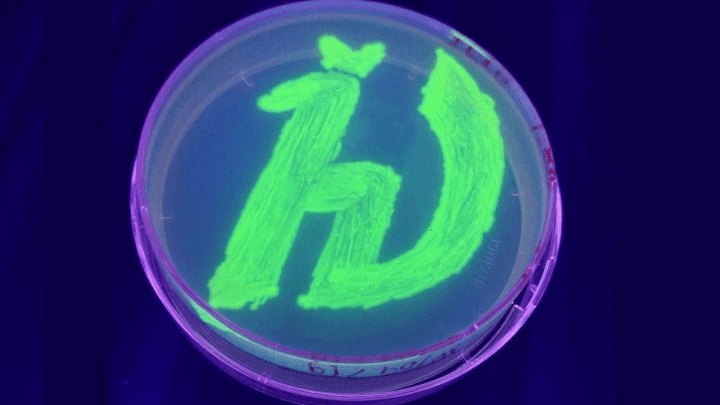
A team of biophysicists has created a new fluorescent protein that not only glows when irradiated with ultraviolet and blue light but is also exceedingly small and stable under high temperatures. The research team believes the protein holds promise for fluorescence microscopy, a technique being used in research on cancer, infectious diseases, and organ development. [..]
Read More
Early-stage research by a university team suggests that a new laser setup will double the energy of a proton beam – potentially offering a route to much wider access for high-precision cancer therapy. While proton beam treatment is already used on some patients, in particular children with deep-seated brain and spinal tumors that are difficult [..]
Read More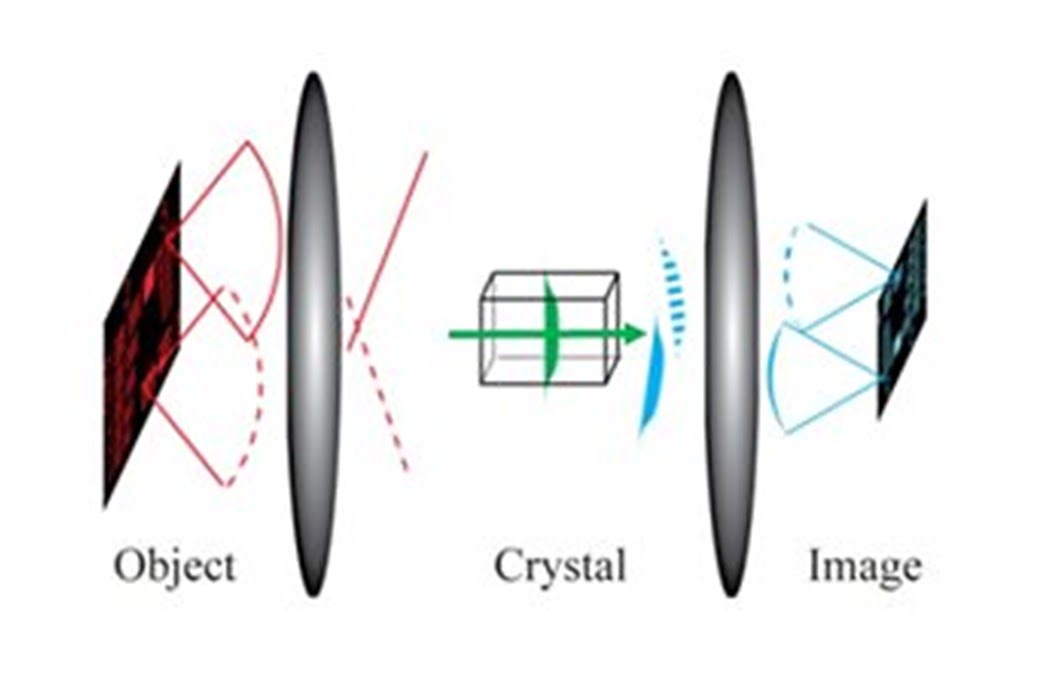
Researchers have developed a unique high-resolution imaging method that can capture mid-infrared spectral images of fast events or dynamic processes that take place on the order of milliseconds. This spectral range is used for many applications because it can reveal the detailed chemical composition of a sample. This novel approach could one day be used [..]
Read More
Researchers have developed a new mathematical technique that quickly determines the ideal makeup and arrangement of millions of individual, microscopic features on a metasurface, to generate a flat lens that manipulates light in a specified way. Previous work attacked the problem by limiting the possible patterns to combinations of predetermined shapes, such as circular holes [..]
Read More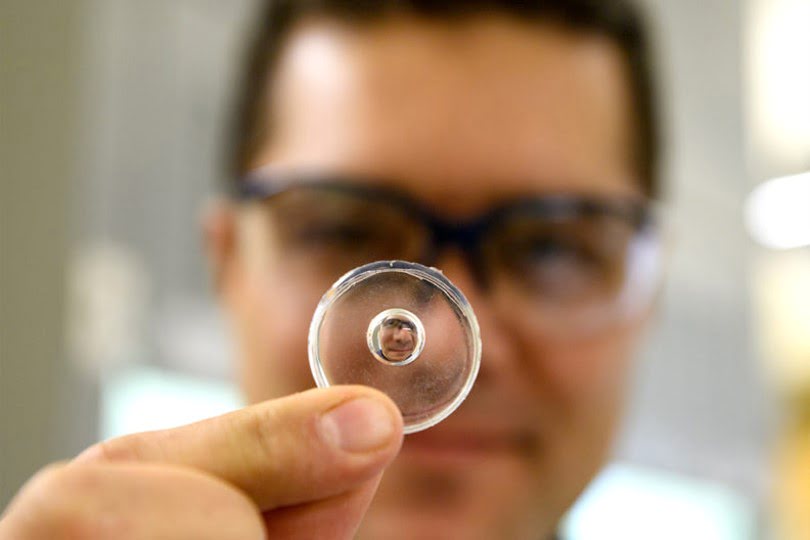
Researchers have developed a low-cost, easy way to make custom lenses that could help manufacturers avoid the expensive molds required for optical manufacturing. The researchers developed a liquid mold from droplets that they can manipulate with magnets to create lenses in a variety of shapes and sizes. High-quality lenses are increasingly used in everything from [..]
Read More